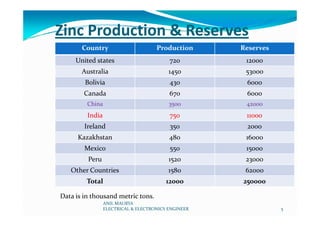
The document discusses the refining and purification process of zinc. It begins with an introduction to zinc including its chemical formula, atomic number, and color. It then discusses the history of zinc discovery and production. The main uses of zinc are then outlined, followed by global zinc production and reserve statistics. The key steps in the zinc refining and purification process are then described in detail, including roasting, leaching, purification, electrolysis, melting and casting. Gas cleaning and sulfuric acid production are also summarized. Finally, the main applications of zinc in automotive, construction, hot dip galvanizing, and zinc castings are briefly outlined.