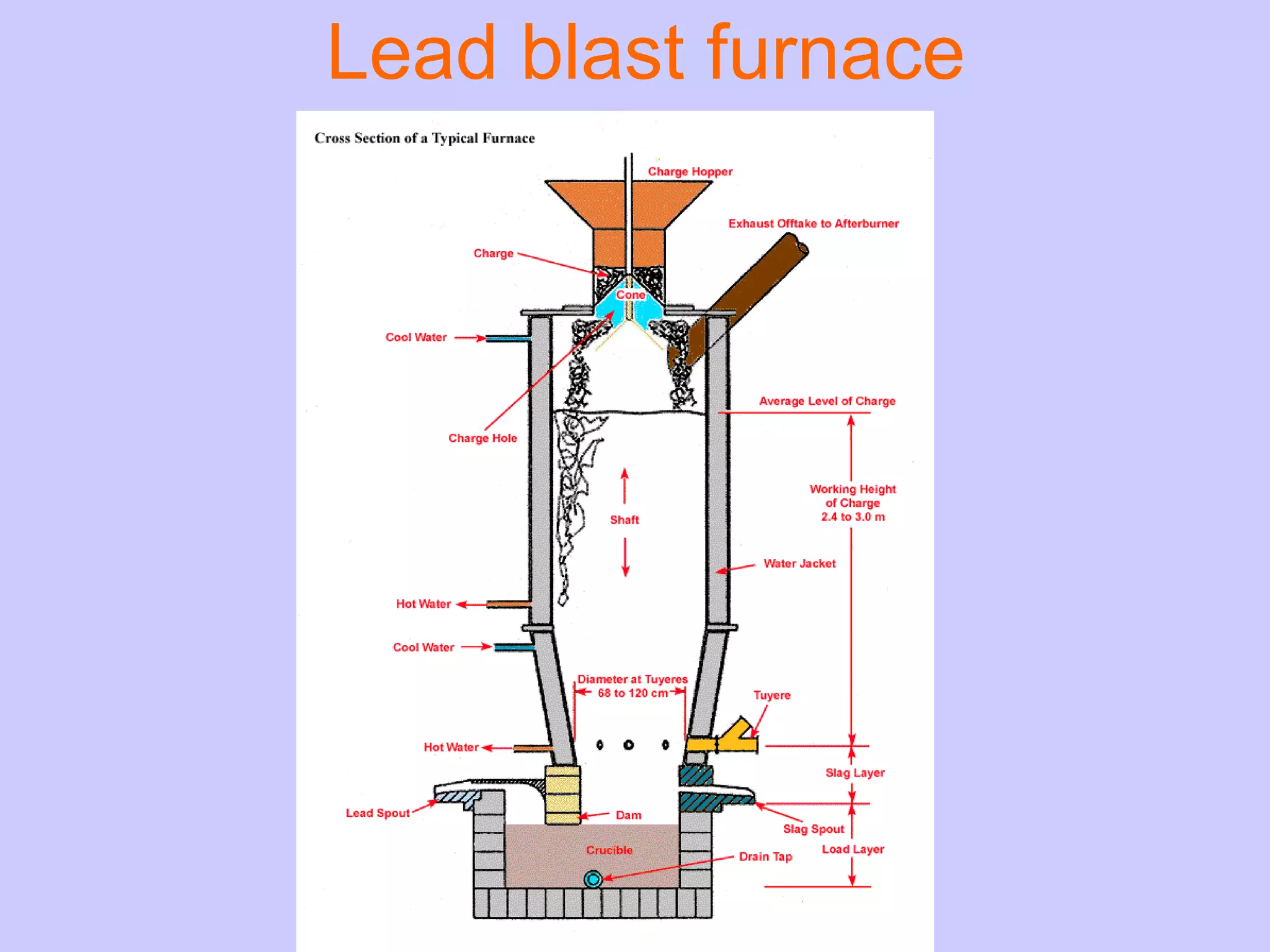
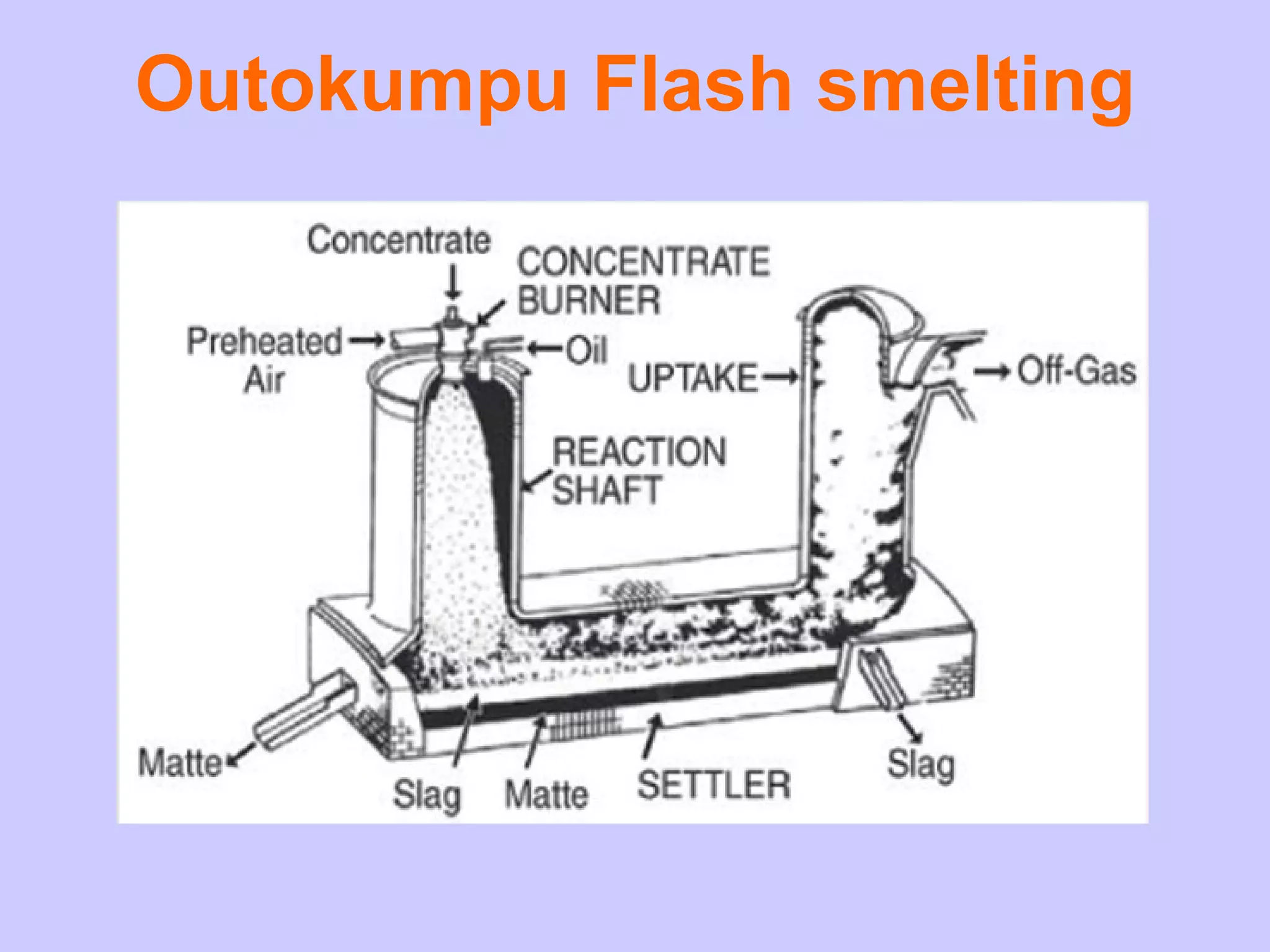
The document discusses various smelting processes used to extract metals from ores. Smelting involves melting the metal out of its ore using reducing substances. There are two main types of smelting: reduction smelting uses carbon to reduce the ore, while matte smelting does not use a reducing agent. Blast furnaces and reverberatory furnaces are commonly used smelting devices. Flash smelting is a high-temperature process that uses the energy in sulfur and iron to melt copper ore without external heating.