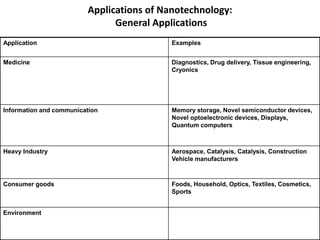
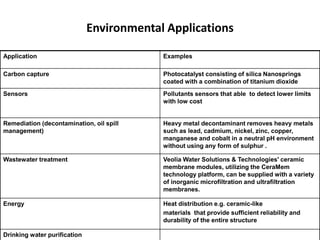
Nanotechnology involves manipulating materials at the nanoscale (1-100 nm) to create structures with novel properties. There are different classifications of nanostructures based on their dimensions, including zero-dimensional (0D), one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D), and three-dimensional (3D). Nanotechnology has applications in medicine such as drug delivery and tissue engineering, information/communication such as memory storage and displays, heavy industry such as catalysis, and consumer goods such as foods and cosmetics. Environmental applications include using nanoparticles for carbon capture, pollutant sensors, heavy metal remediation, and wastewater treatment.