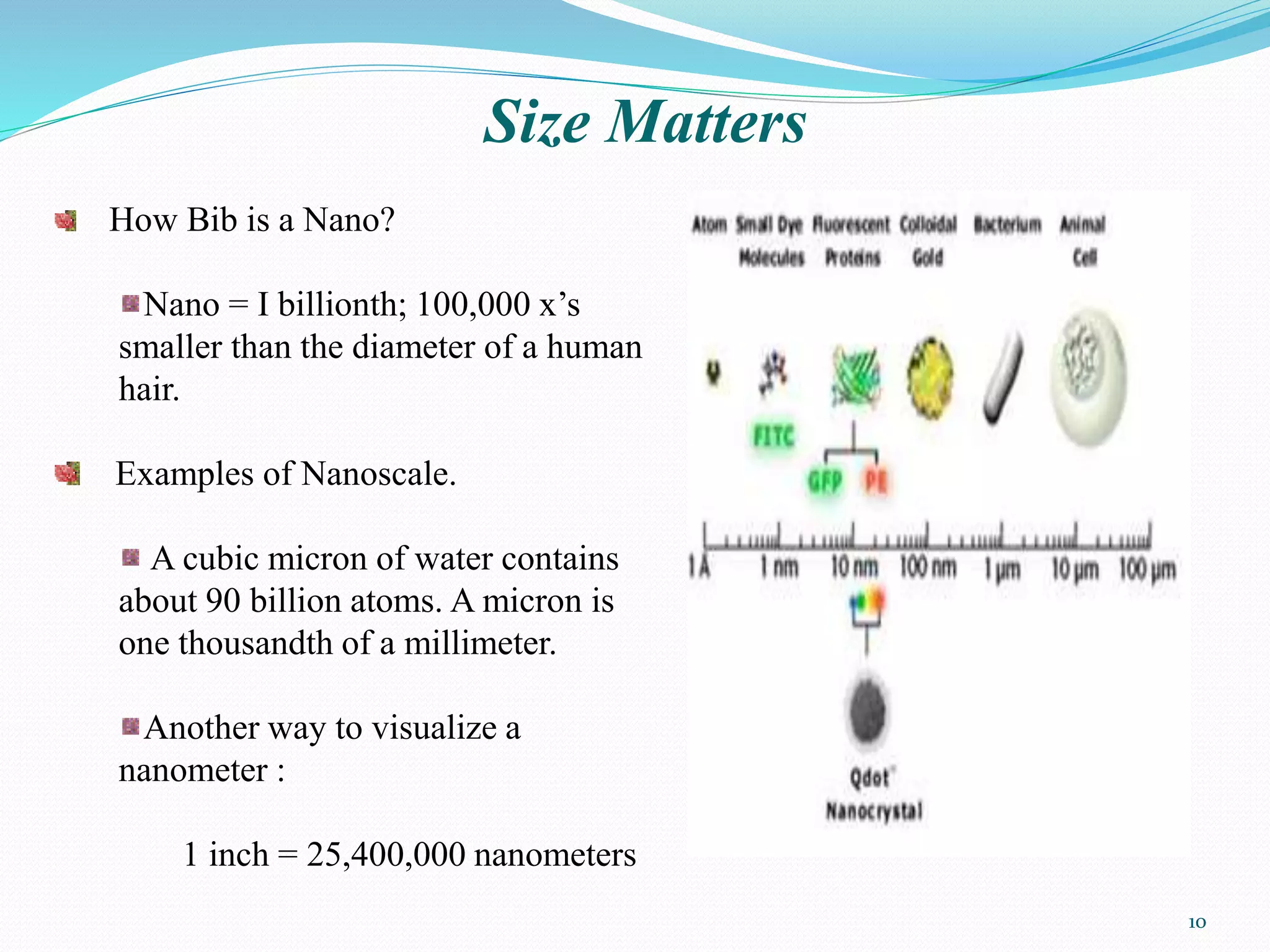
Nanotechnology refers to the manipulation of atoms and molecules to create new materials and devices, leading to advancements in various fields such as medicine and electronics. Its historical roots trace back to concepts discussed in 1959 and the emergence of key developments from 1974 onwards, including nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes and applications in cancer treatment. While nanotechnology offers significant economic and healthcare benefits, it also raises health, environmental, and social concerns that must be addressed.