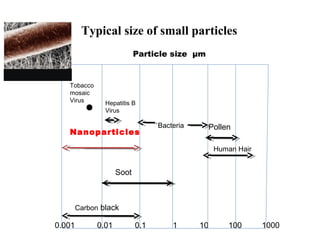
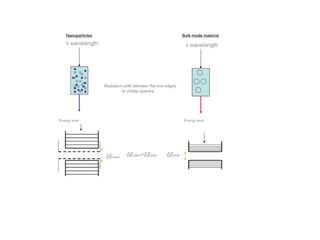
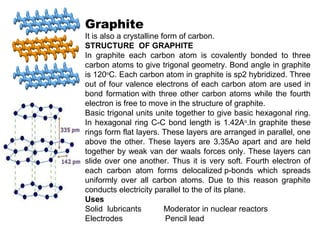
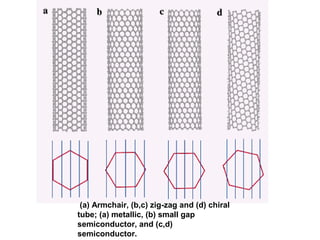
Nanomaterials are defined as materials with grain sizes in the nanometer range (1-100 nm), exhibiting unique properties due to increased relative surface area and quantum effects. Key examples include carbon nanotubes, fullerenes, and nanowires, each with significant applications in electronics, medicine, and materials science. The document emphasizes the potential of nanotechnology to innovate and improve various fields, albeit with a cautionary note on the need for responsible management of these technologies.