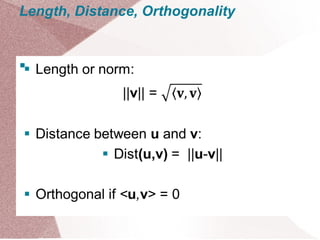
The document discusses orthogonal bases and the Gram-Schmidt process. It defines the Gram-Schmidt process as an algorithm for finding an orthogonal basis from a given basis by making each new vector orthogonal to the previous ones. It also discusses orthonormal bases, QR factorization, inner products, length and distance, and applying Gram-Schmidt to produce an orthogonal basis for the vector space of polynomials up to degree 2.