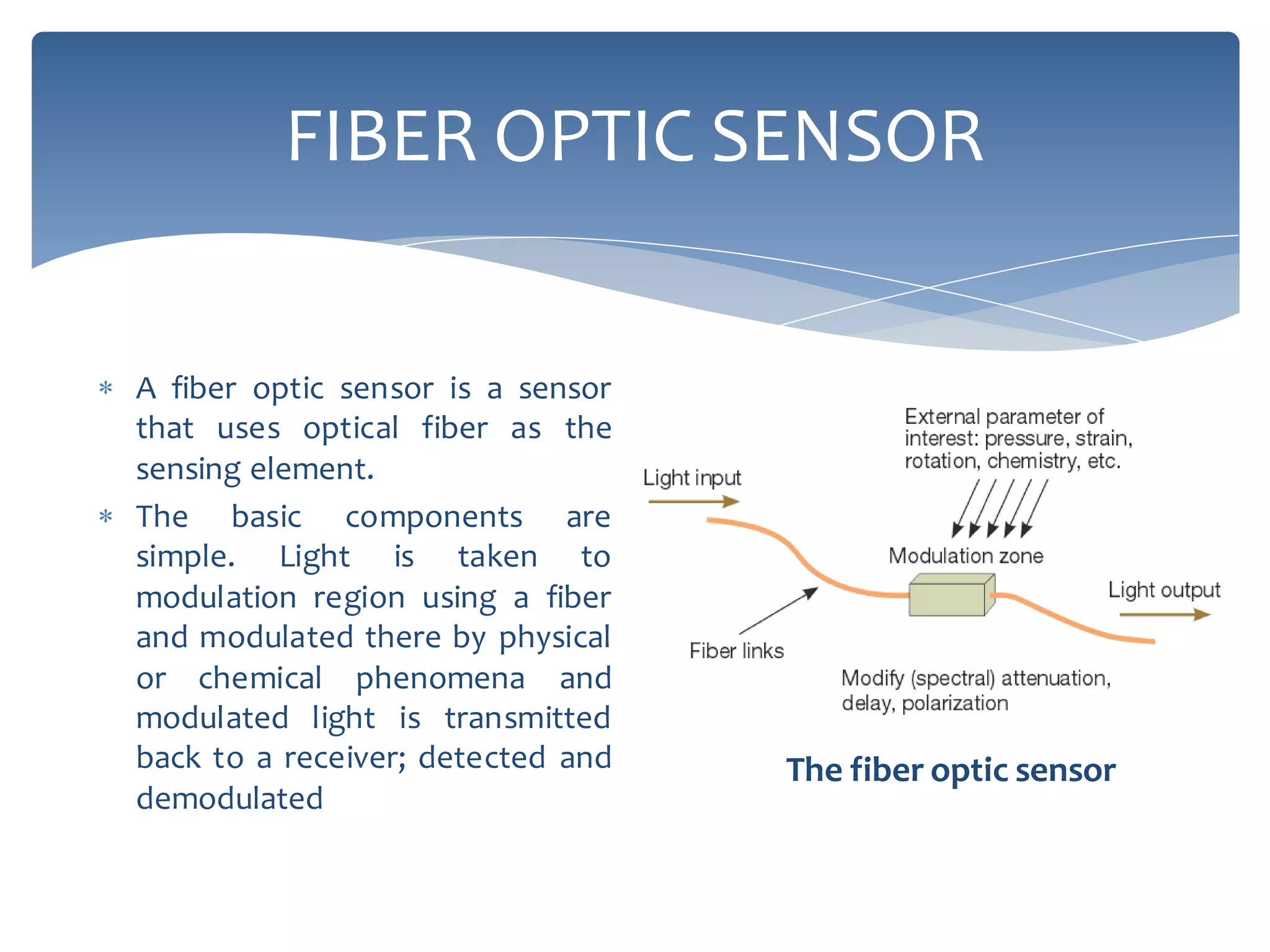
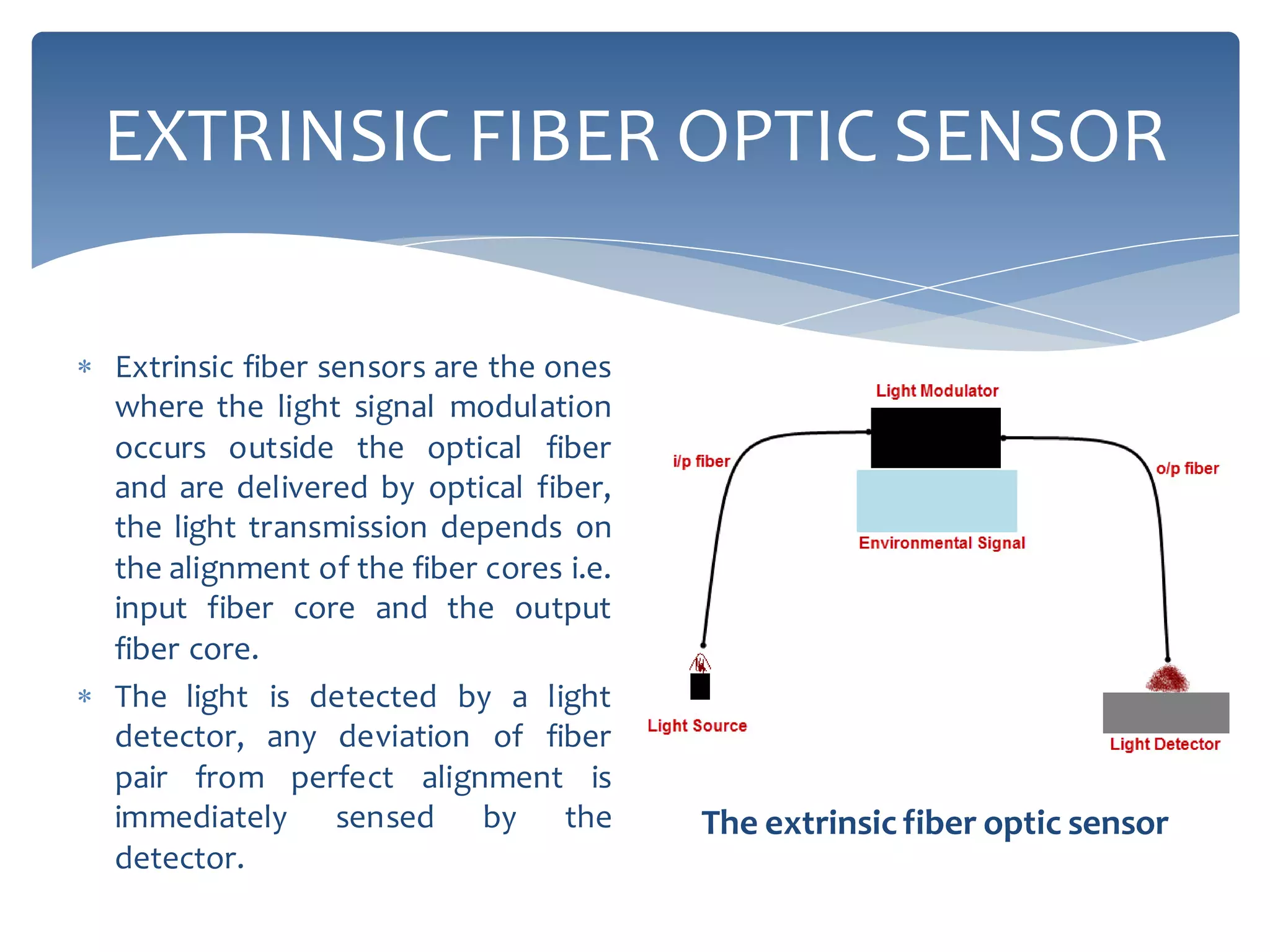
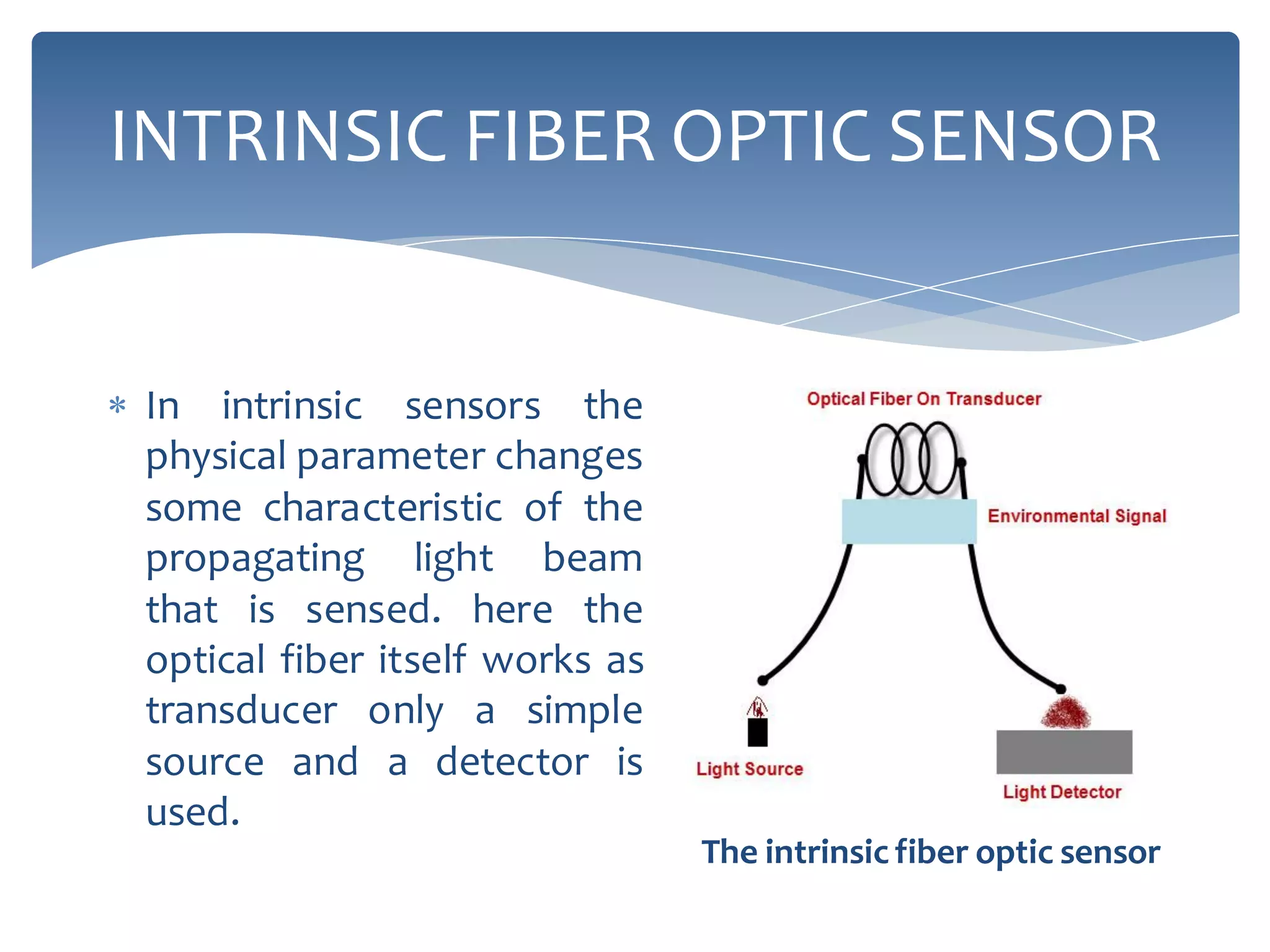
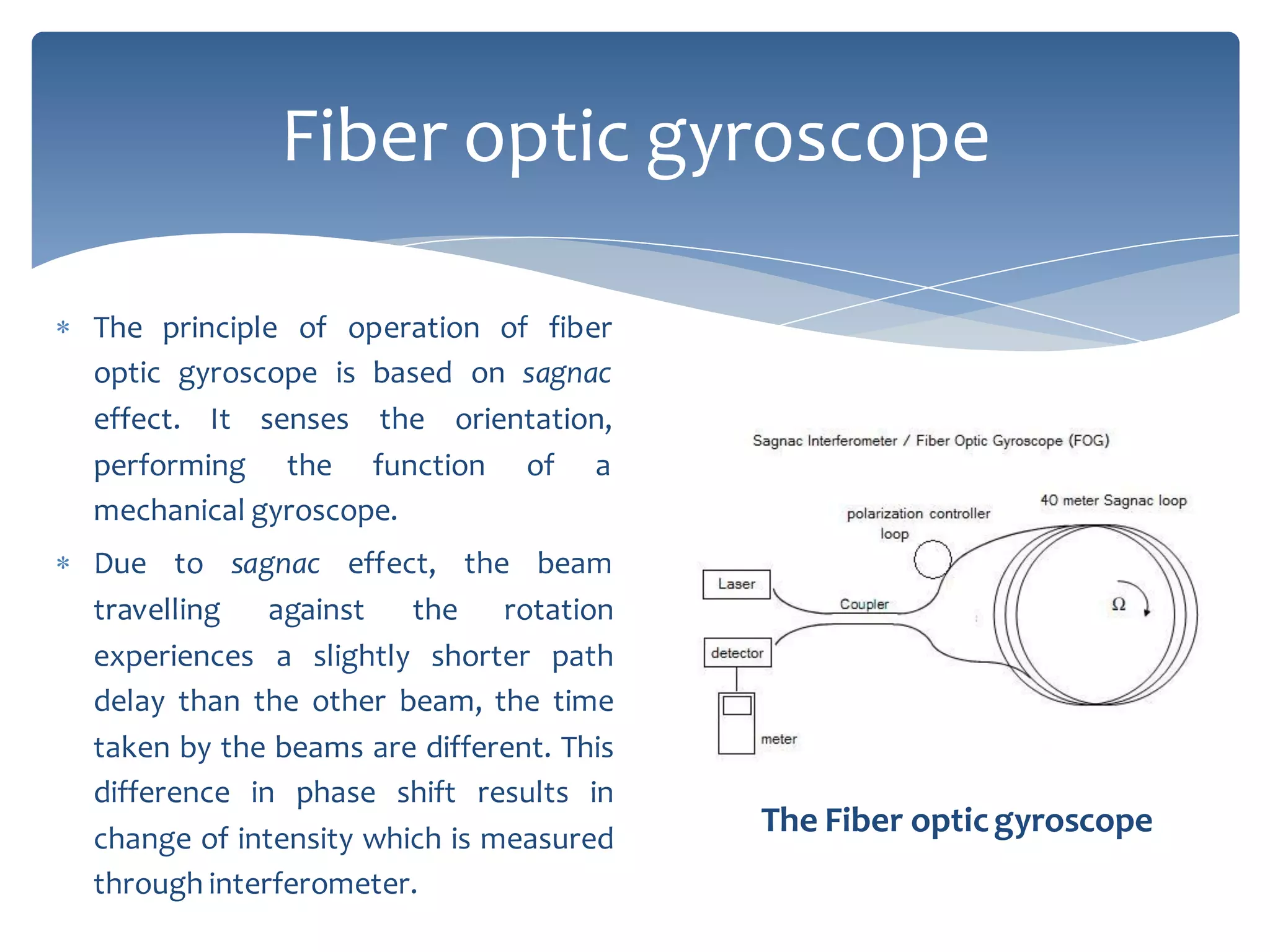
The presentation provides an overview of fiber optic sensor technology, detailing classifications, functions, and key types, notably the Mach-Zehnder interferometric sensor and the fiber optic gyroscope. Fiber optic sensors use optical fiber for sensing, with extrinsic sensors modulating signals outside the fiber, while intrinsic sensors rely on changes within the fiber's characteristics. The Mach-Zehnder sensor is known for extreme sensitivity, while the gyroscope operates on the Sagnac effect to measure orientation.