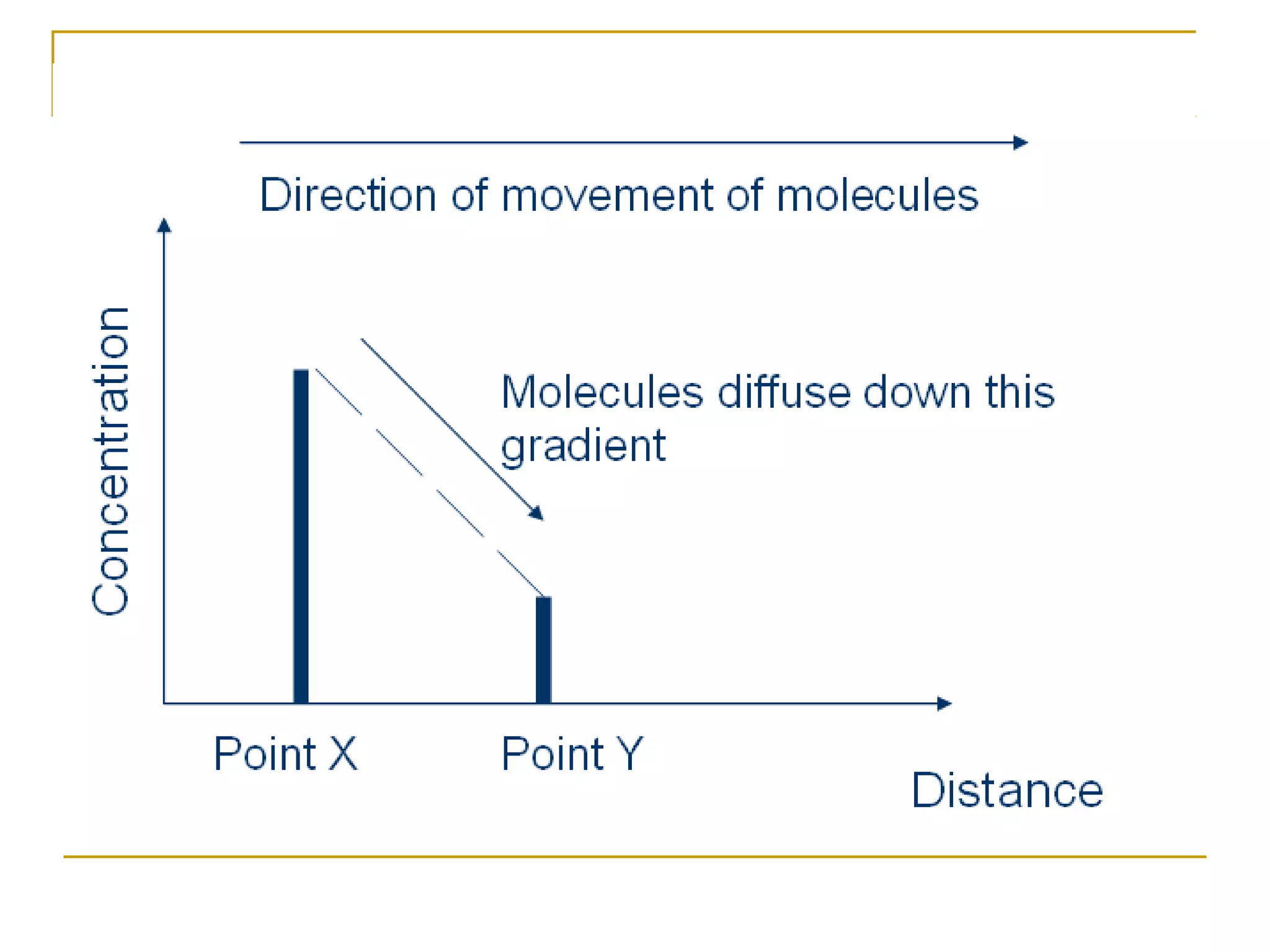
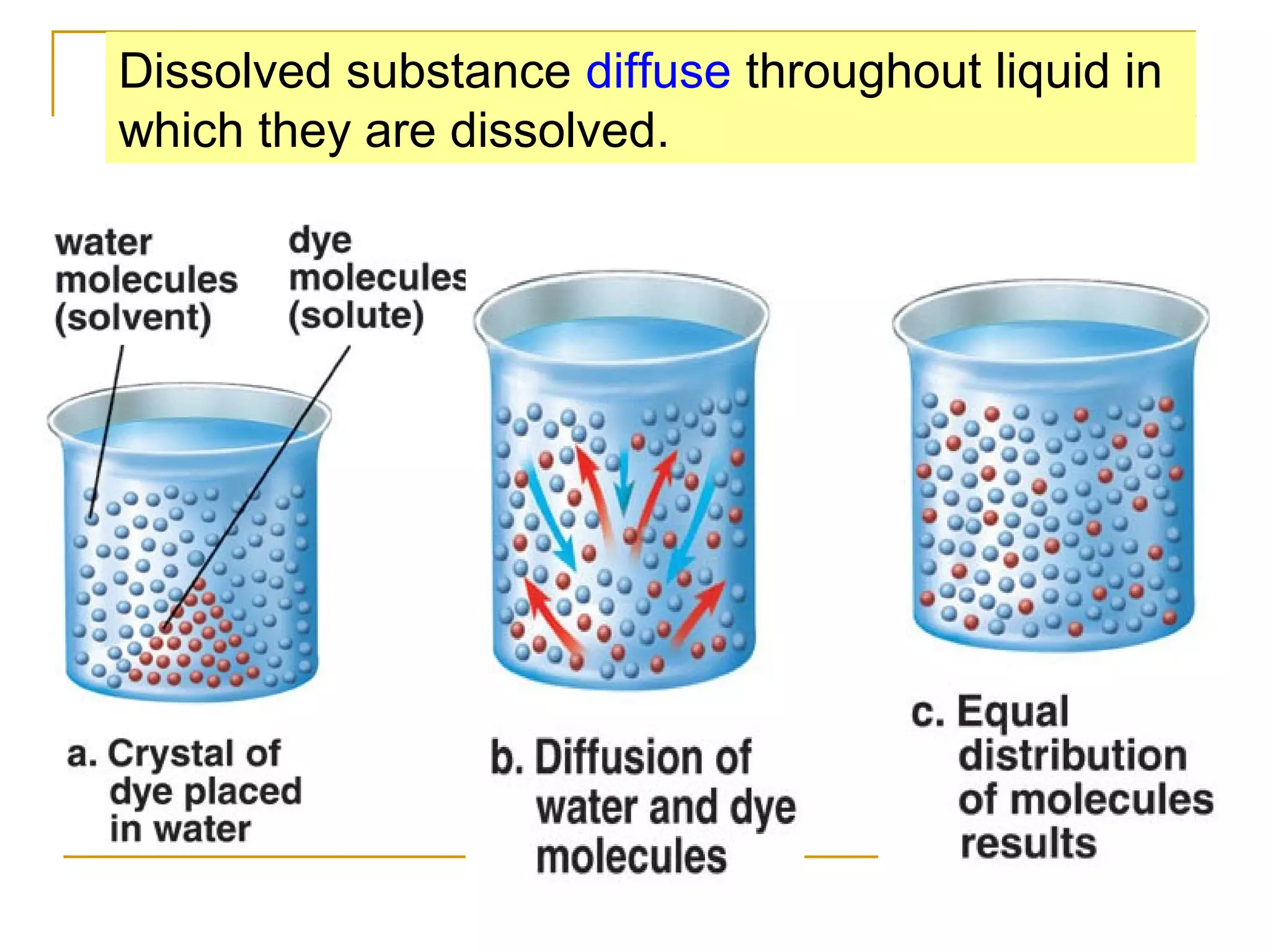
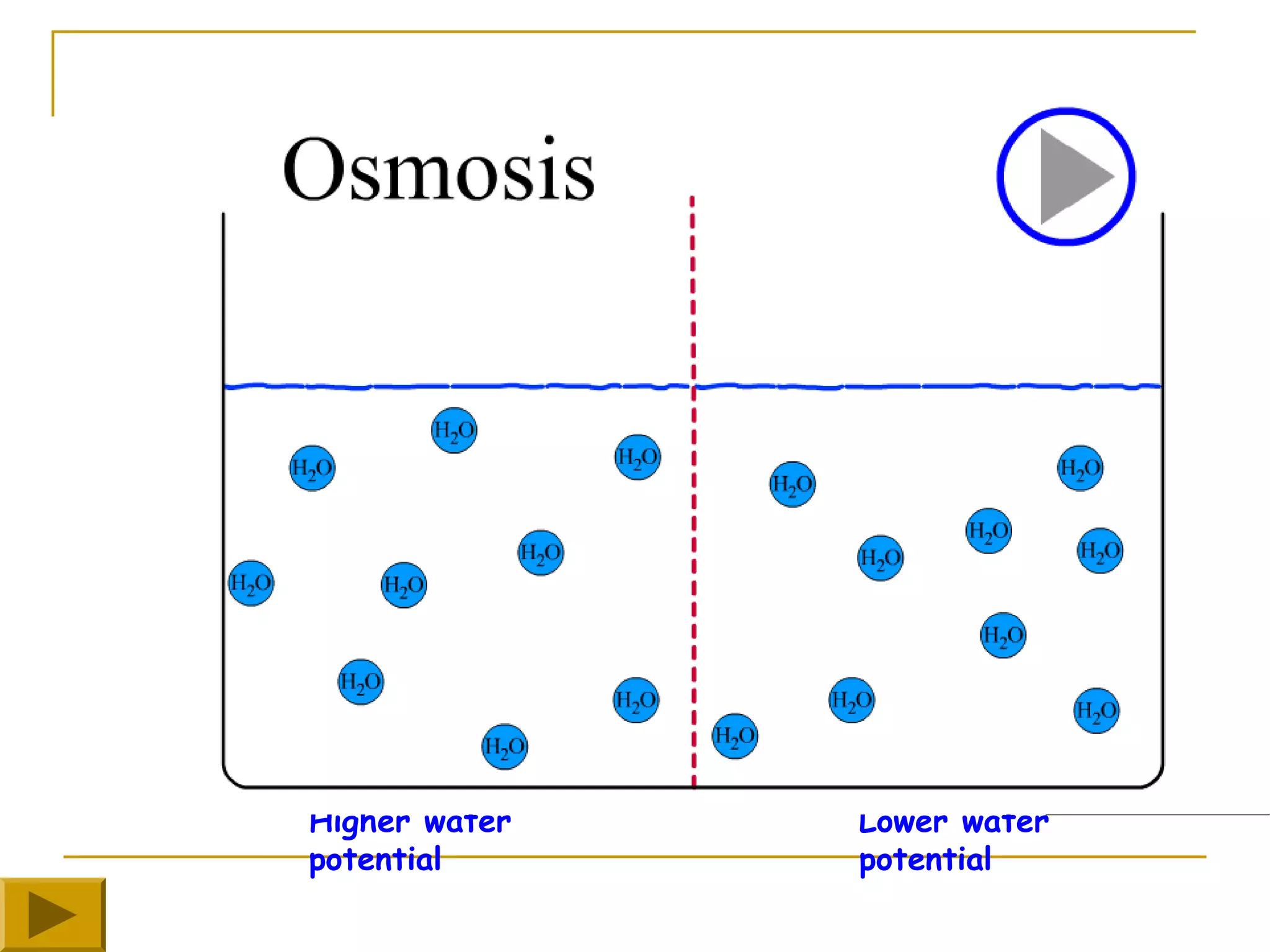
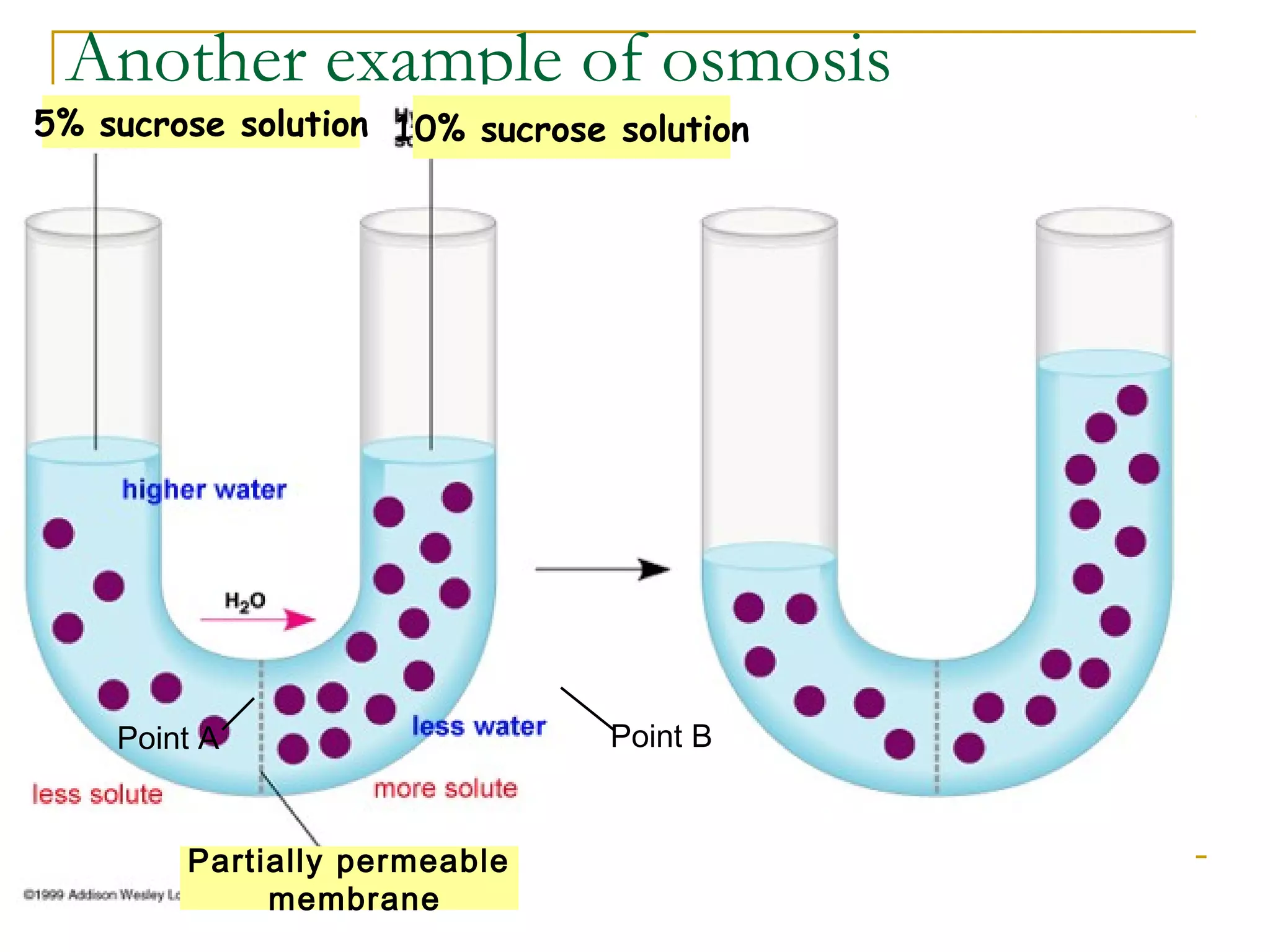
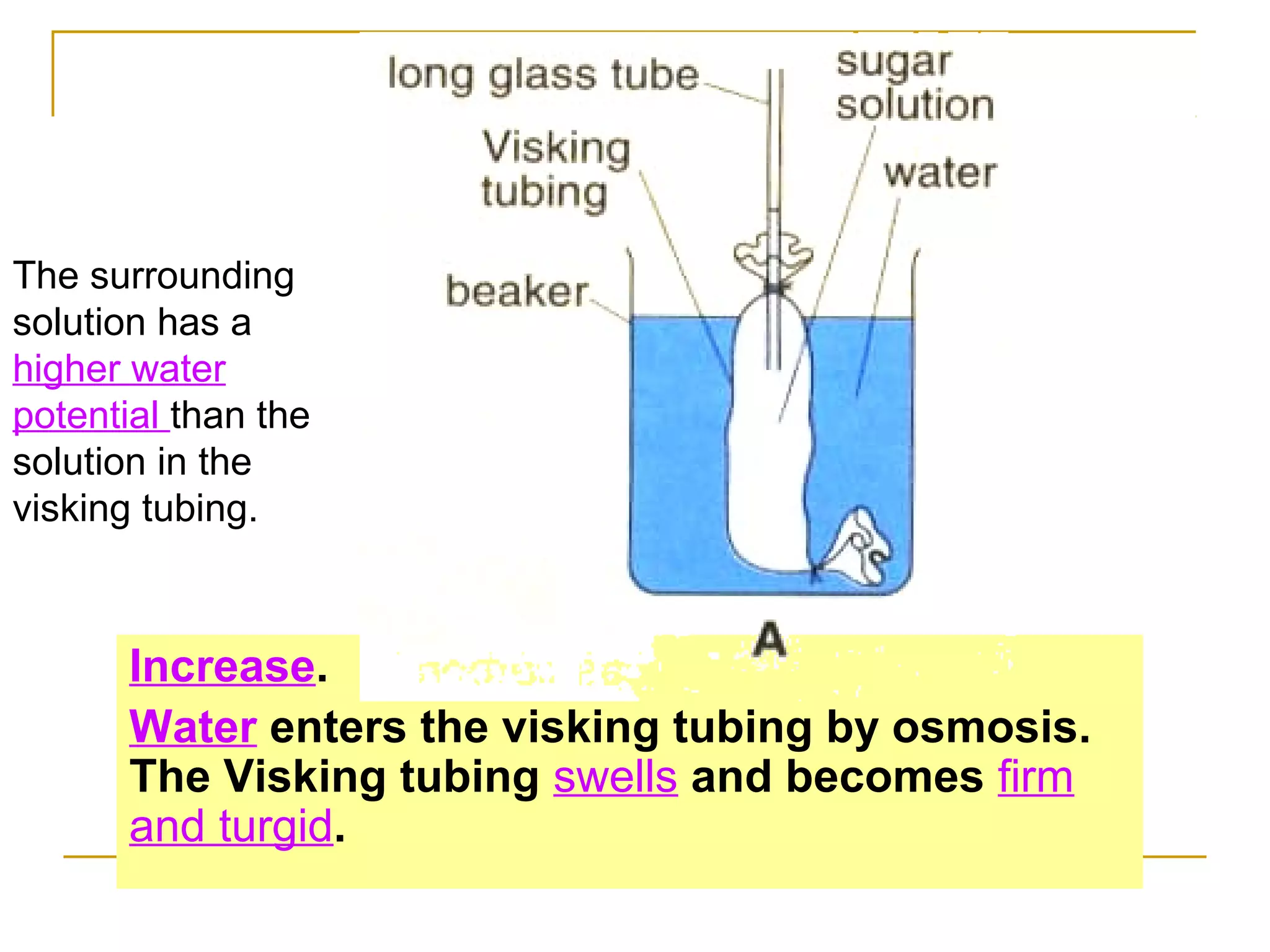
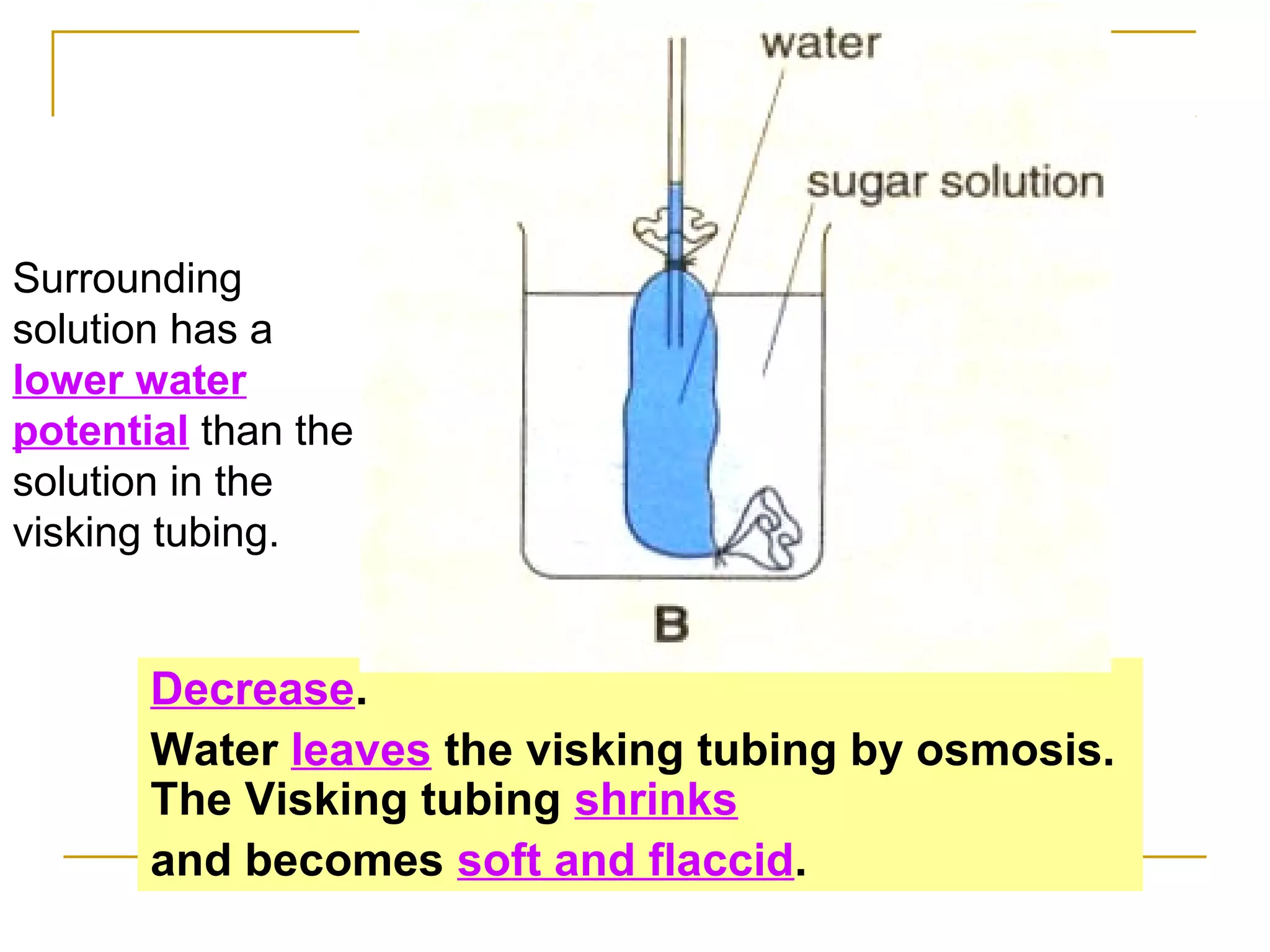
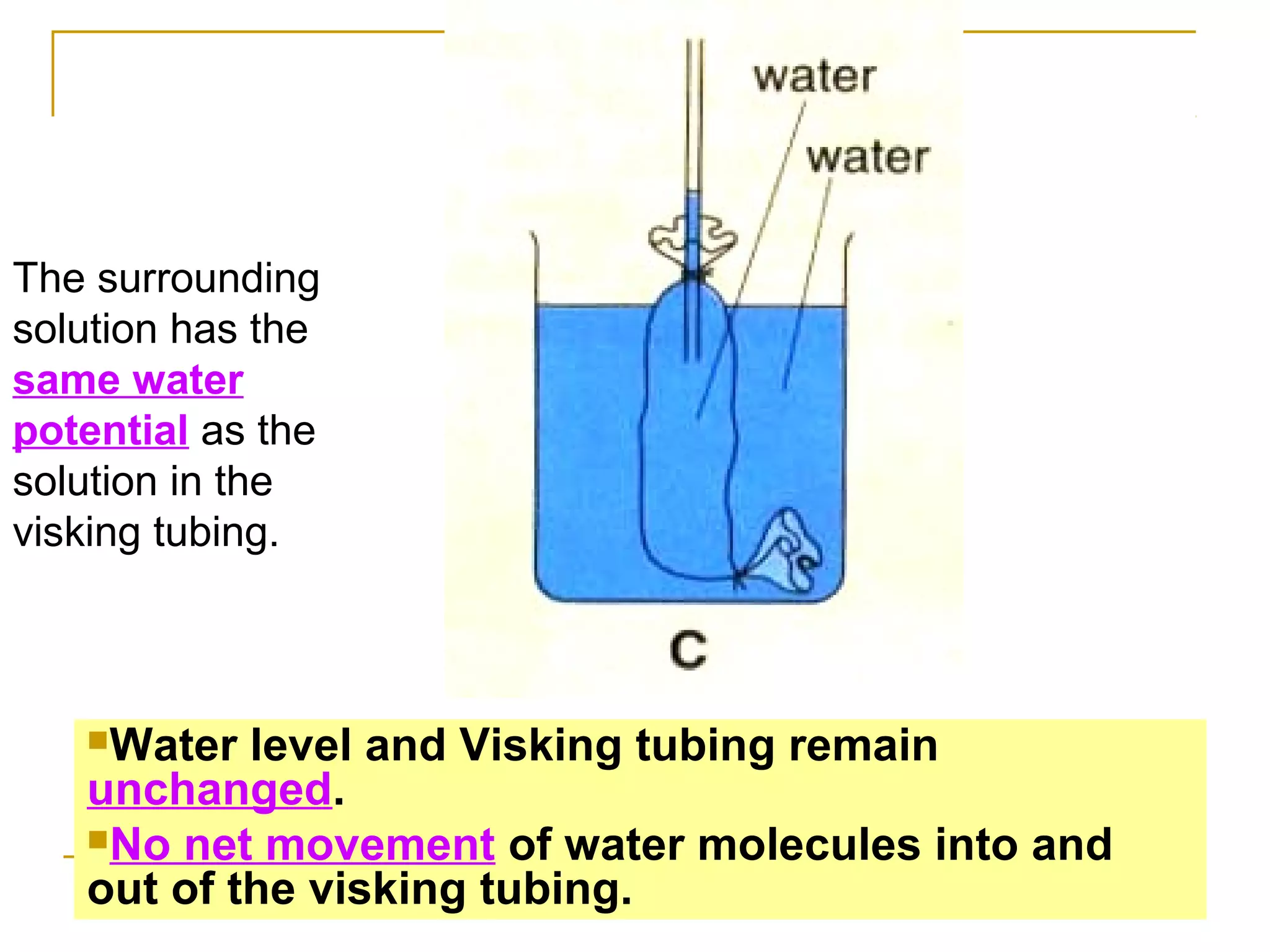
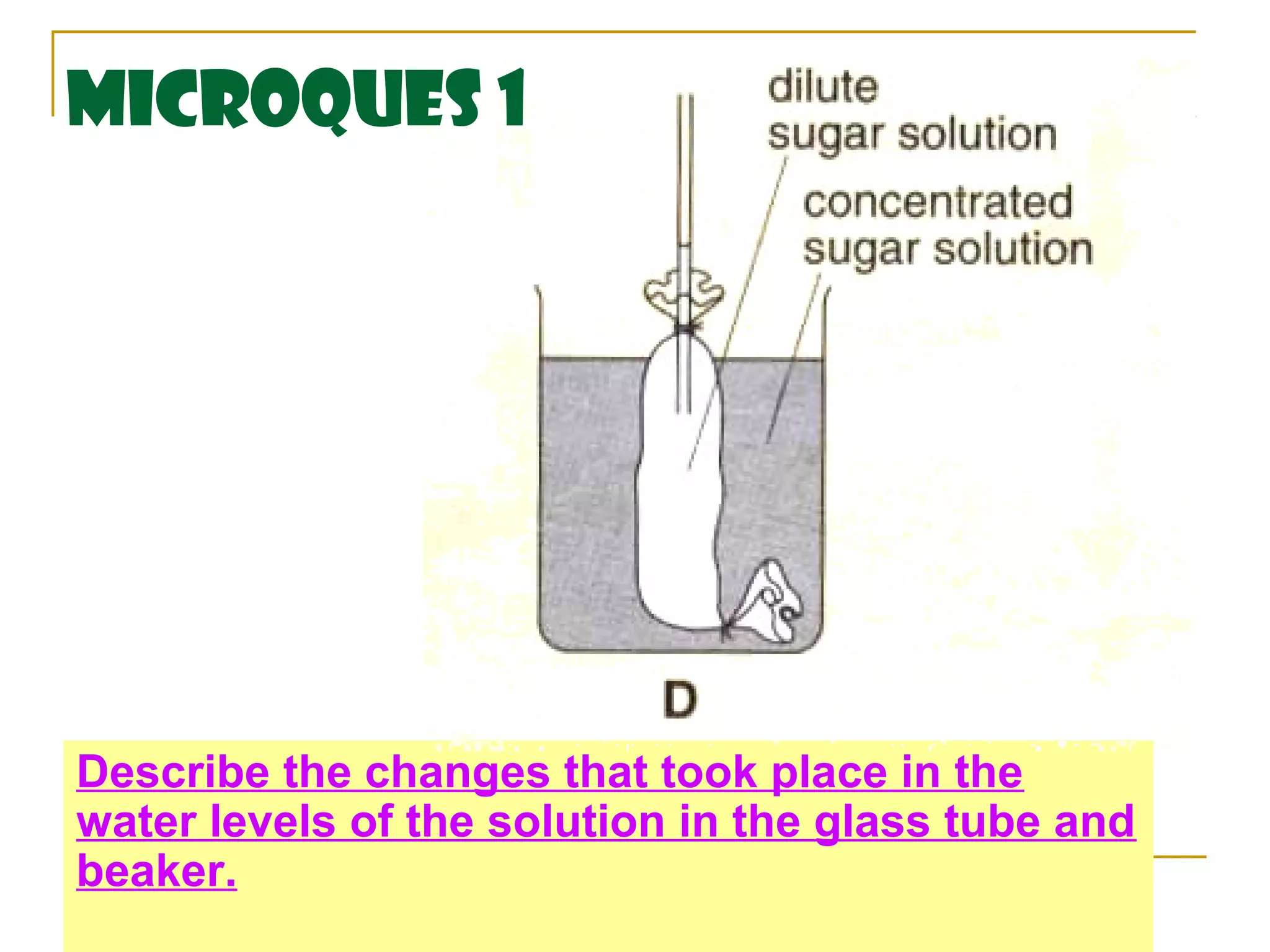
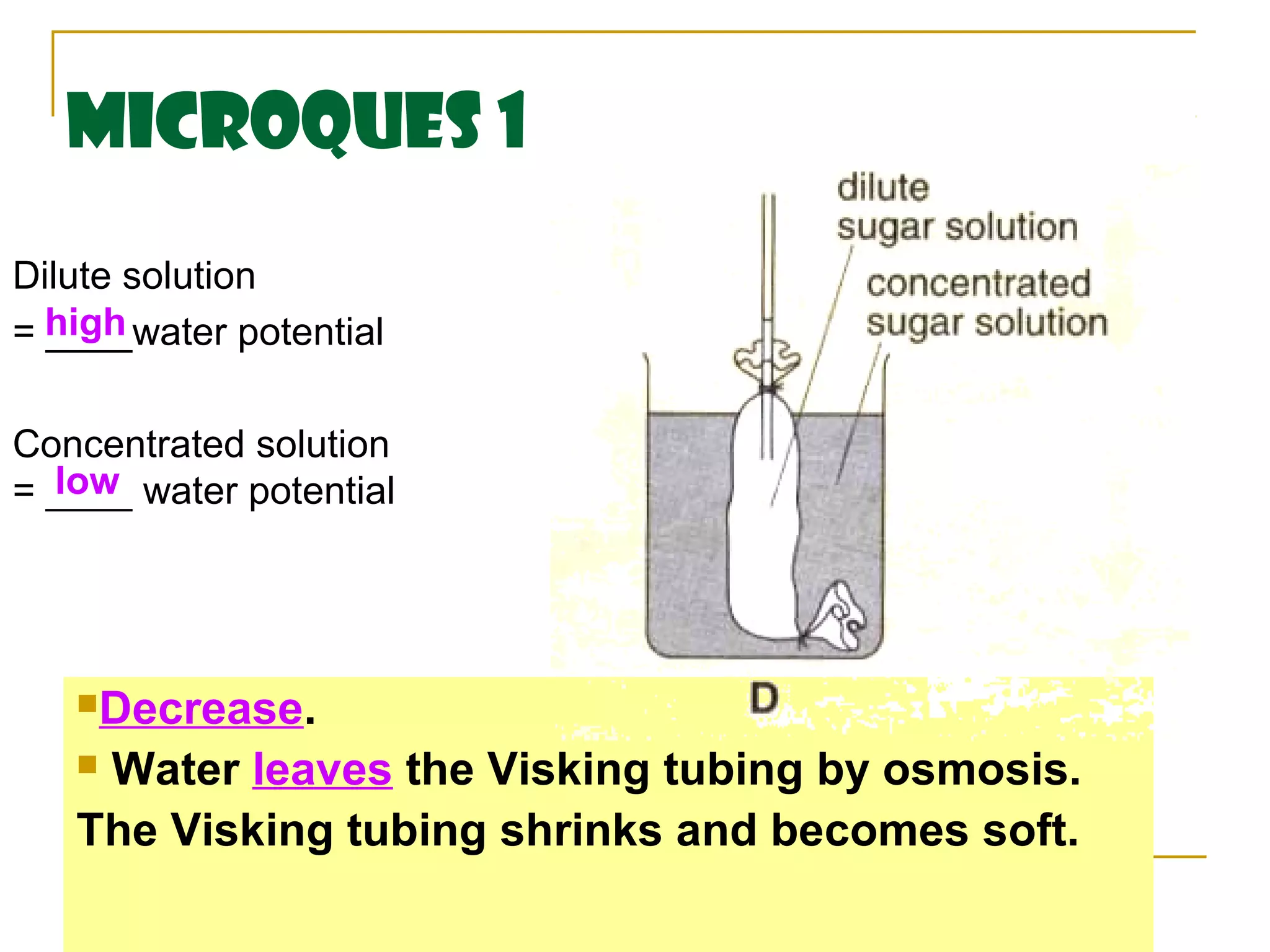
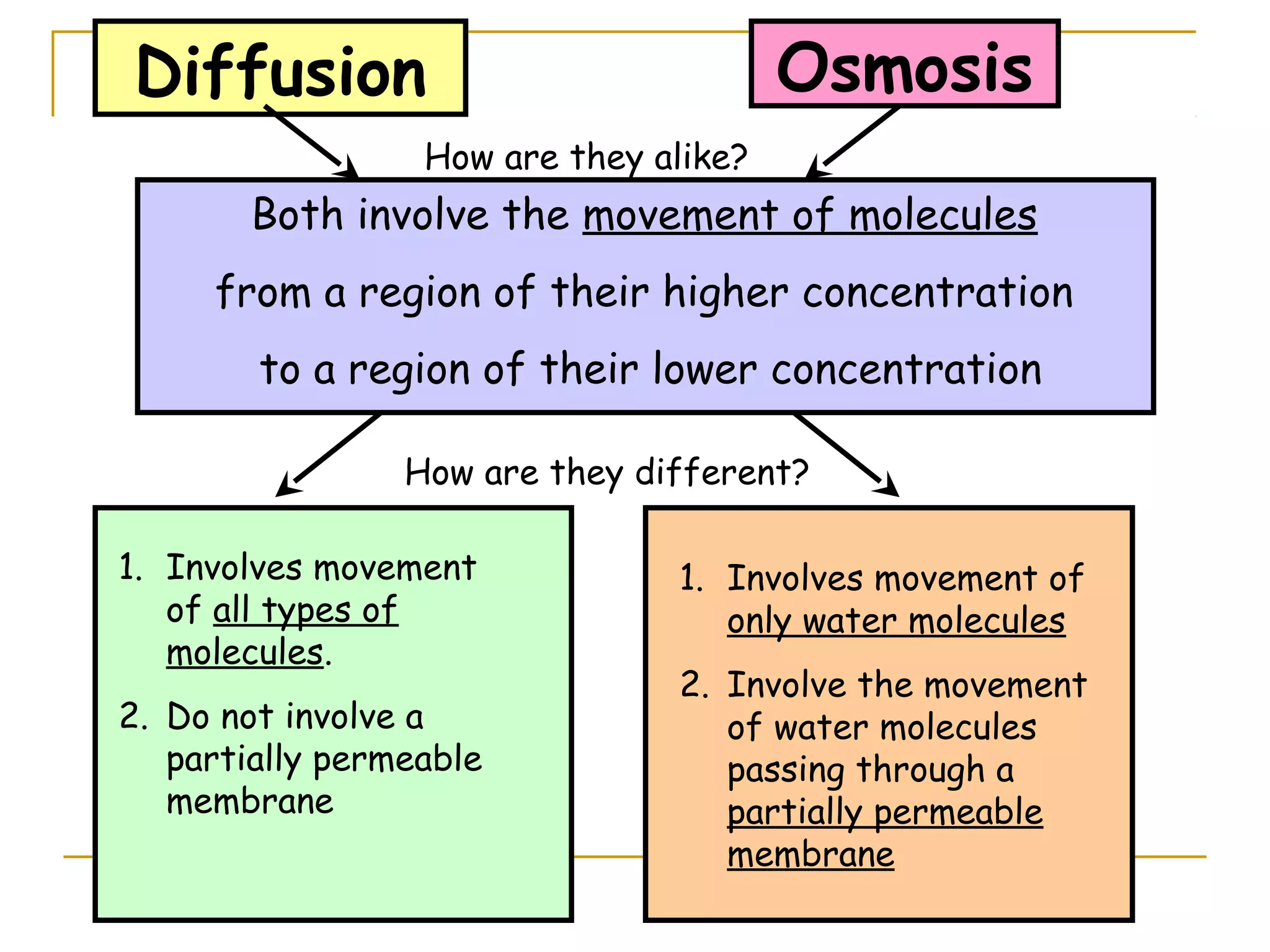
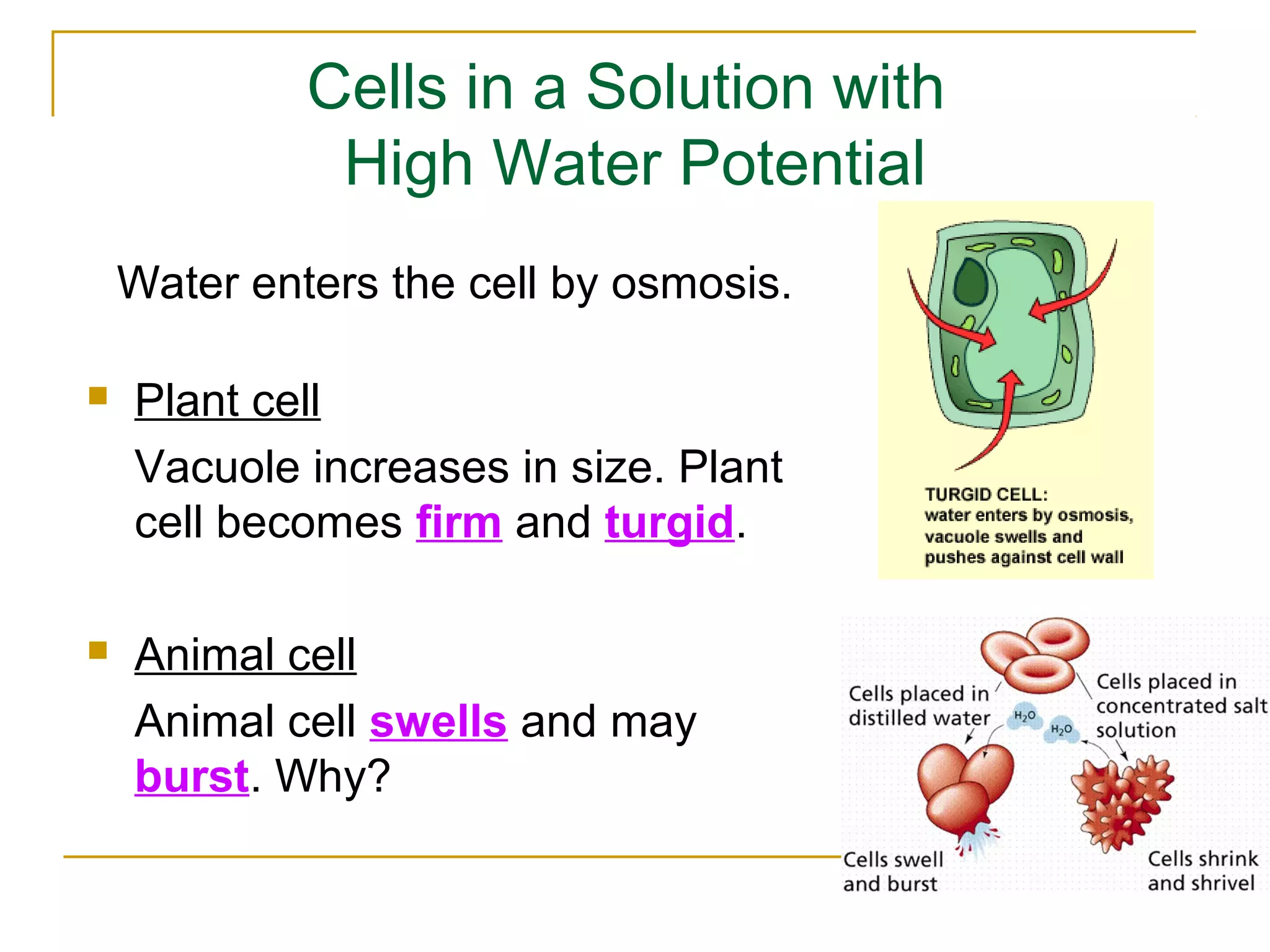
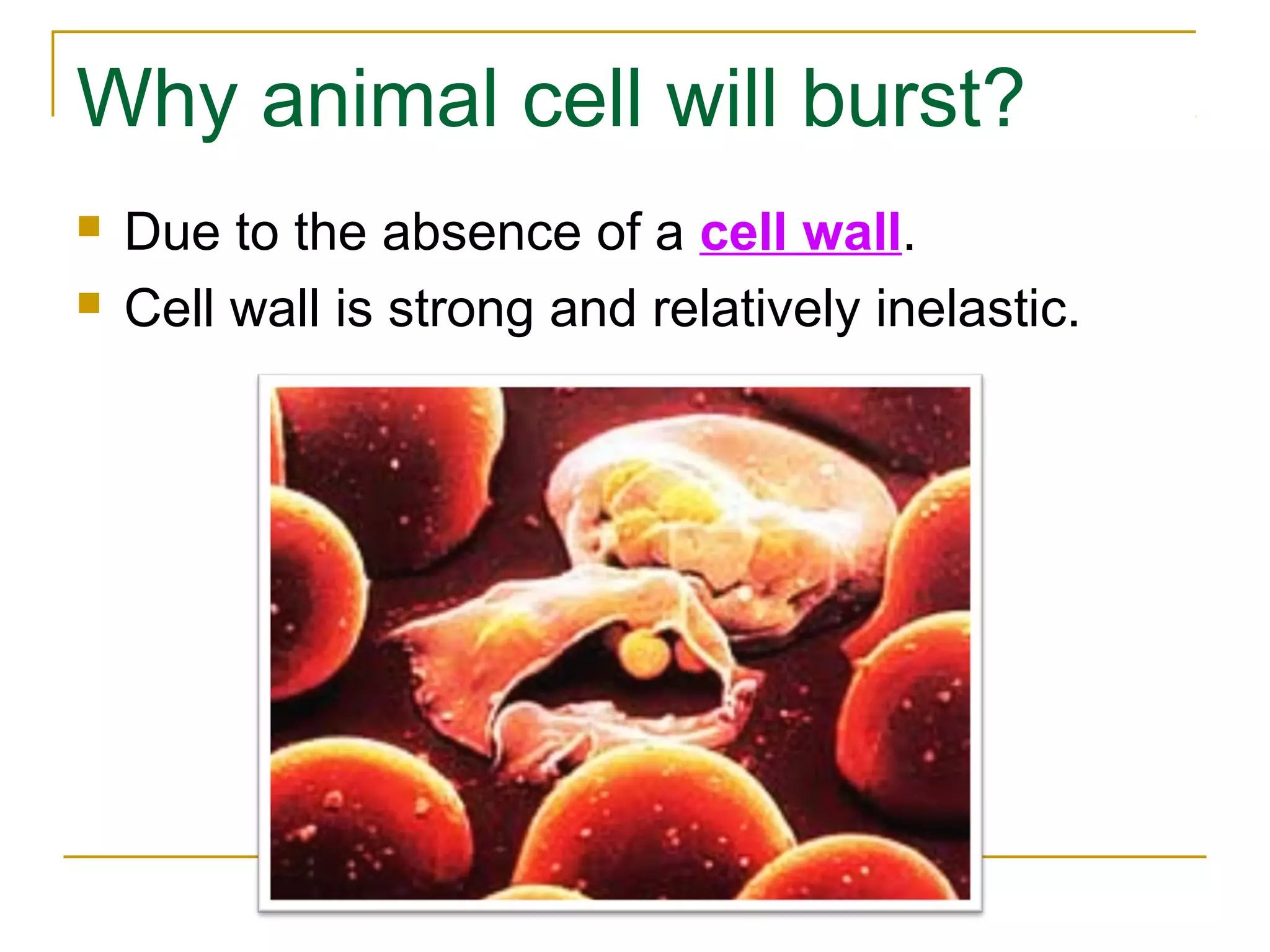
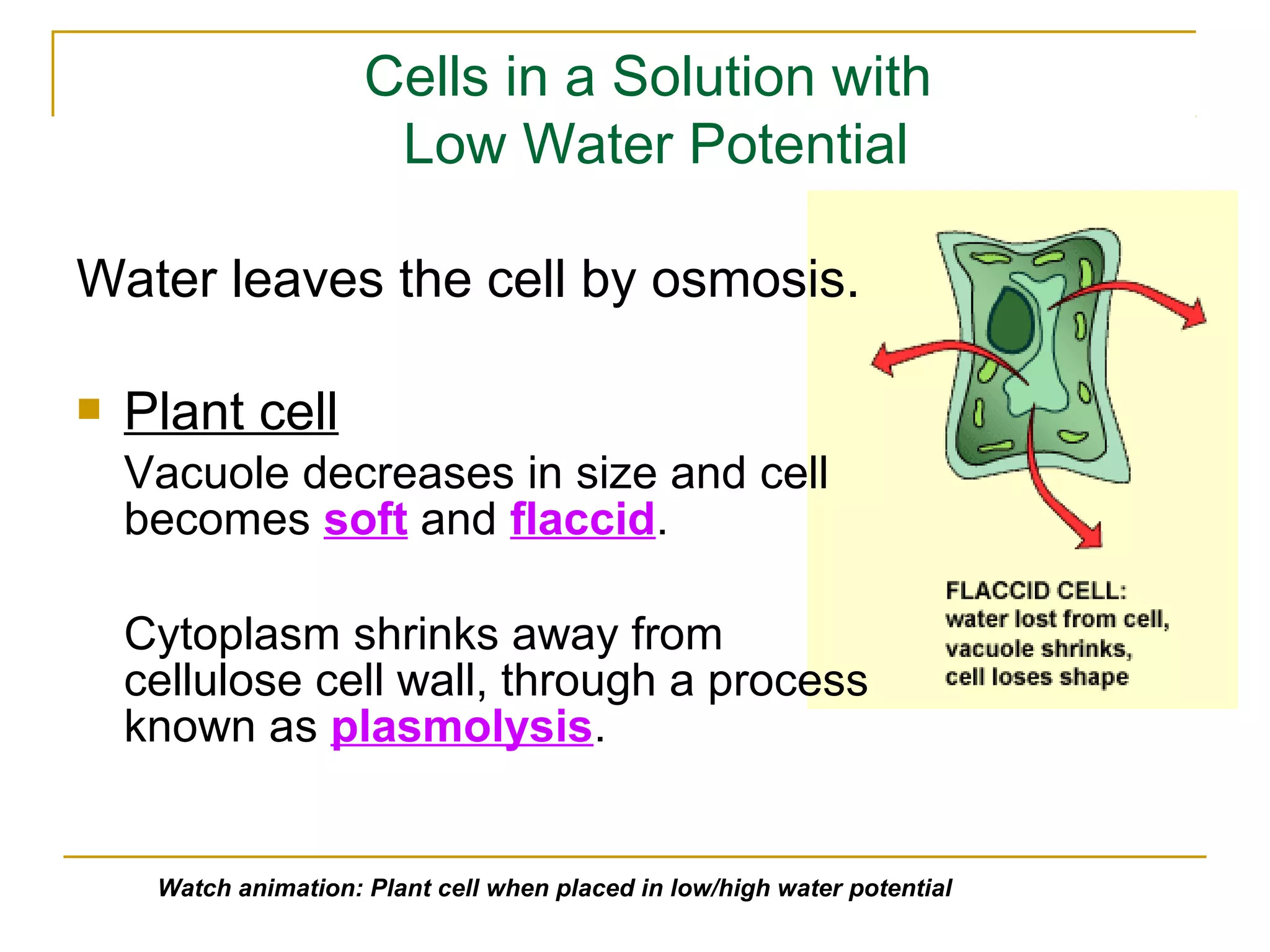
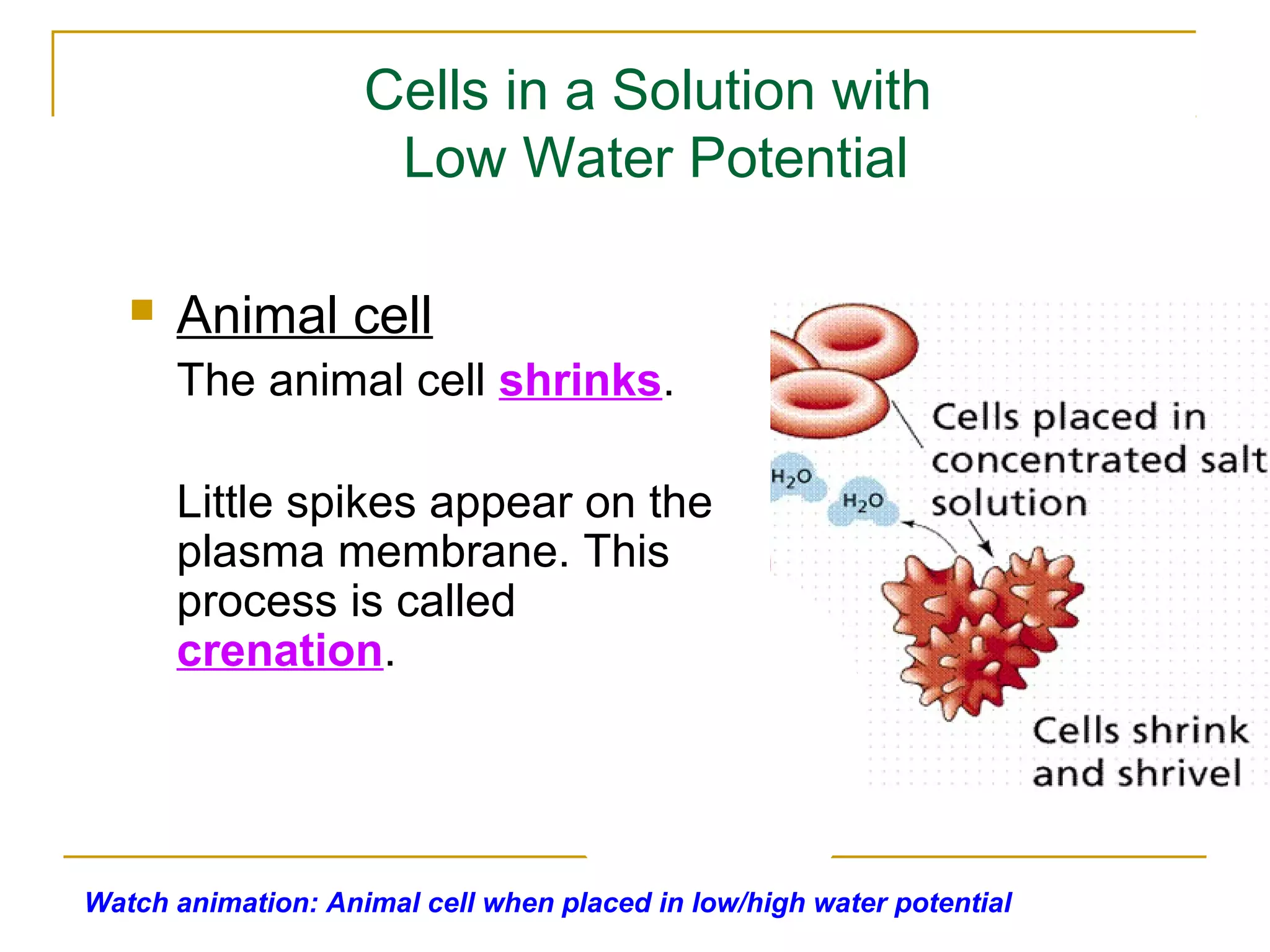
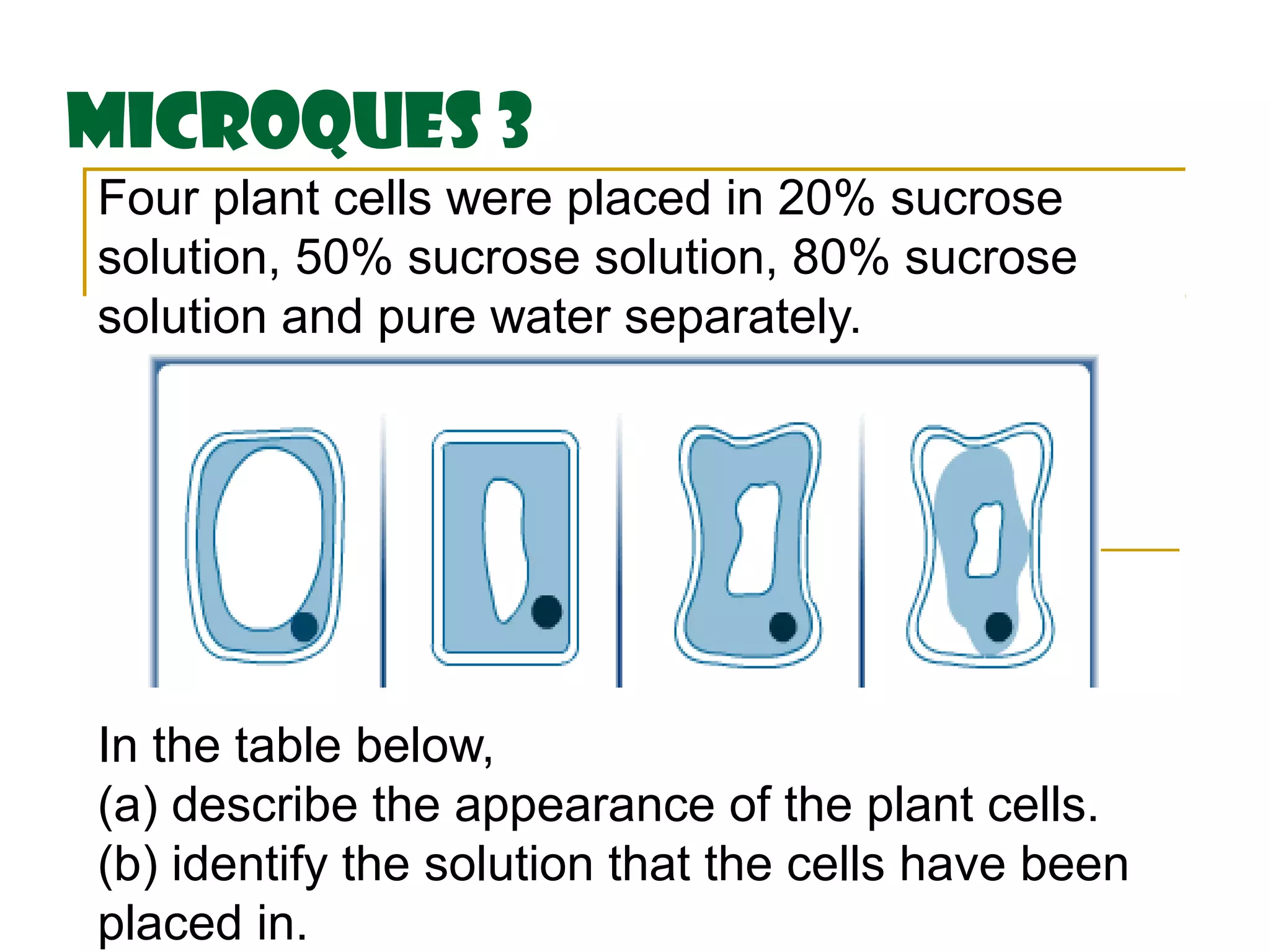
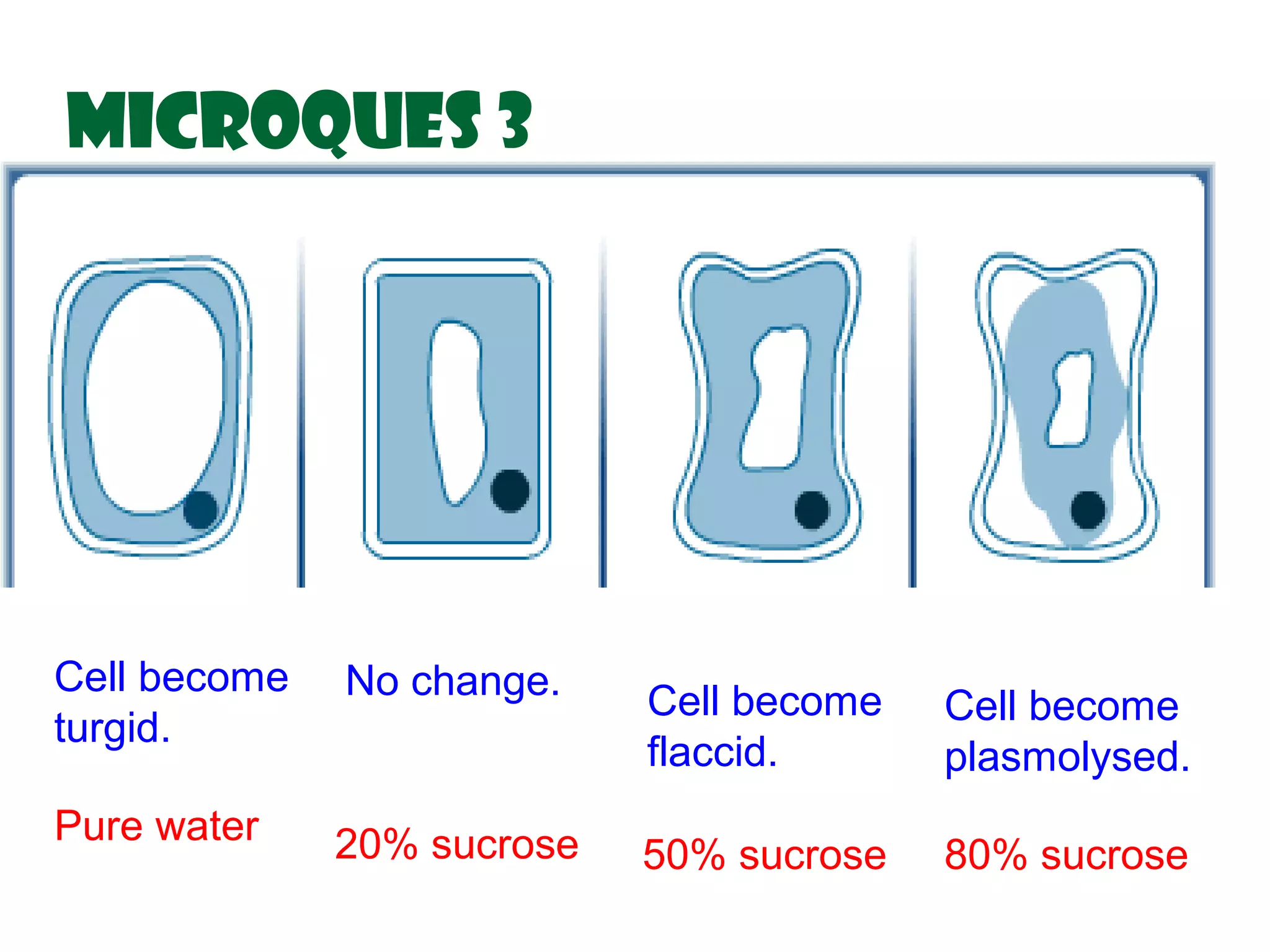
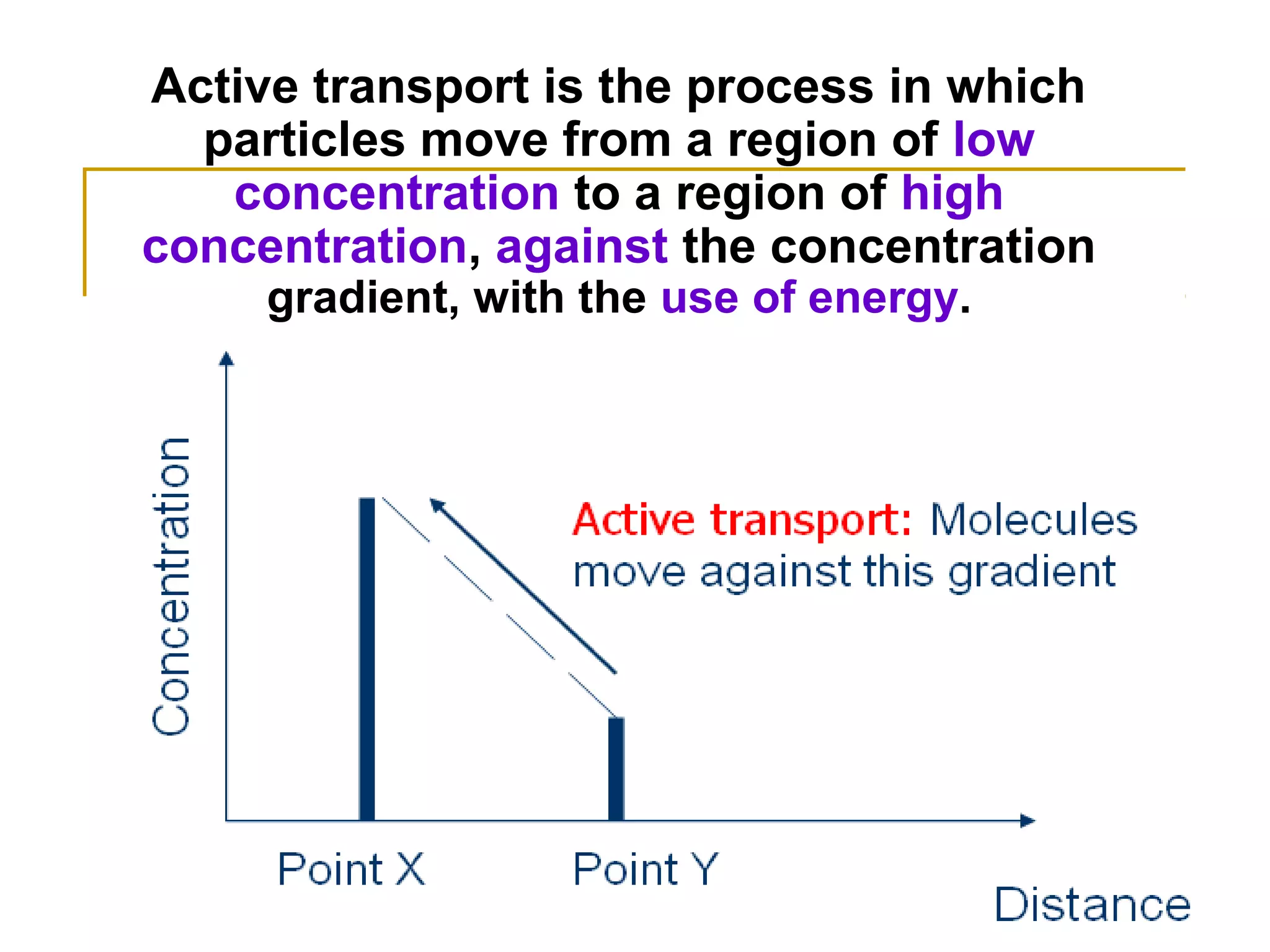
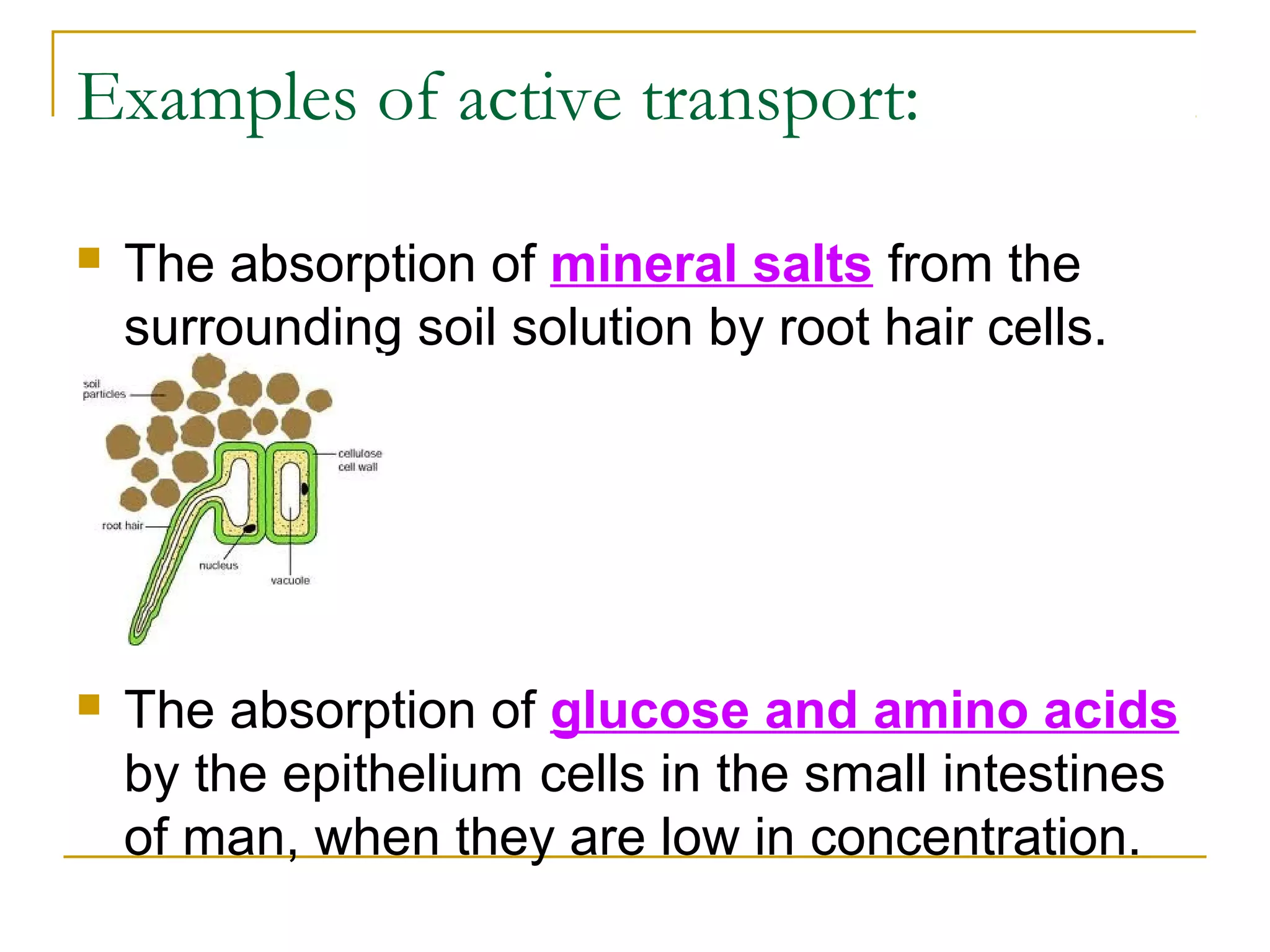
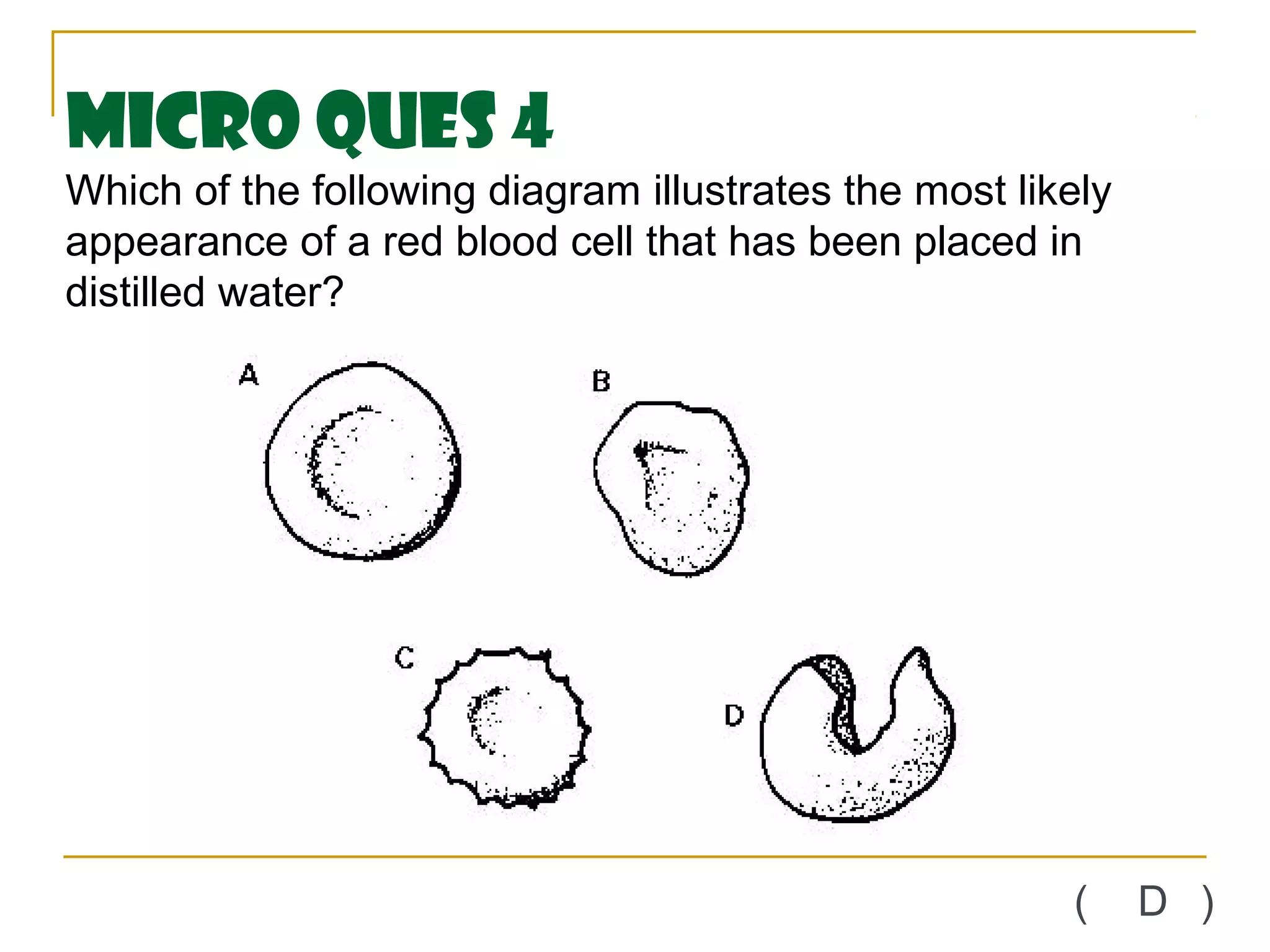
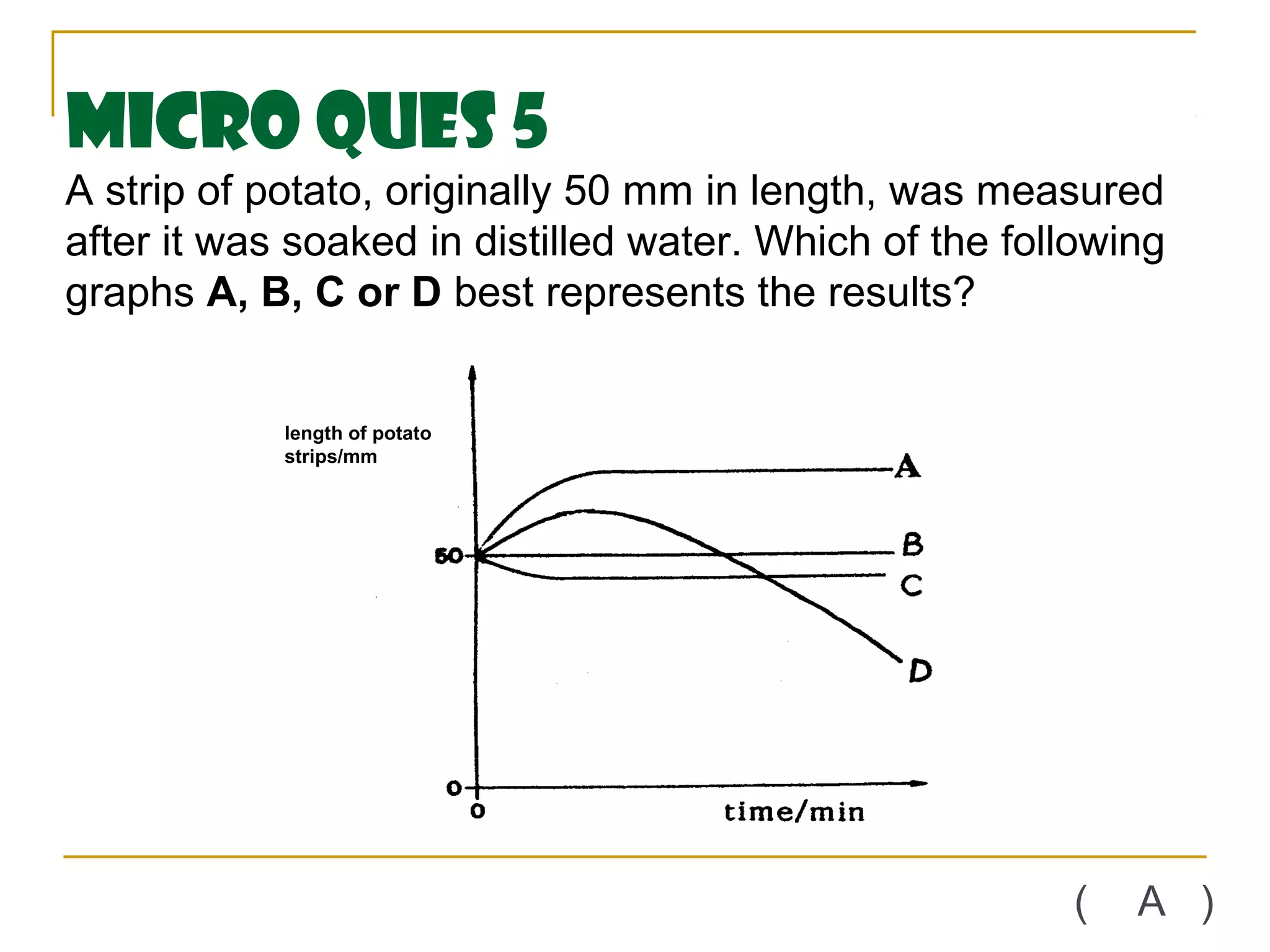
This document defines key transport processes in biology - diffusion, osmosis, and active transport - and provides examples of each in plants and humans. Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from high to low concentration down a gradient. Osmosis is the specific case of diffusion where water moves through a semi-permeable membrane from high to low water potential. Active transport moves molecules against a concentration gradient and requires energy. The document discusses the roles of these processes in nutrient/gas exchange and describes demonstrations of osmosis in plant and animal cells under varying conditions.