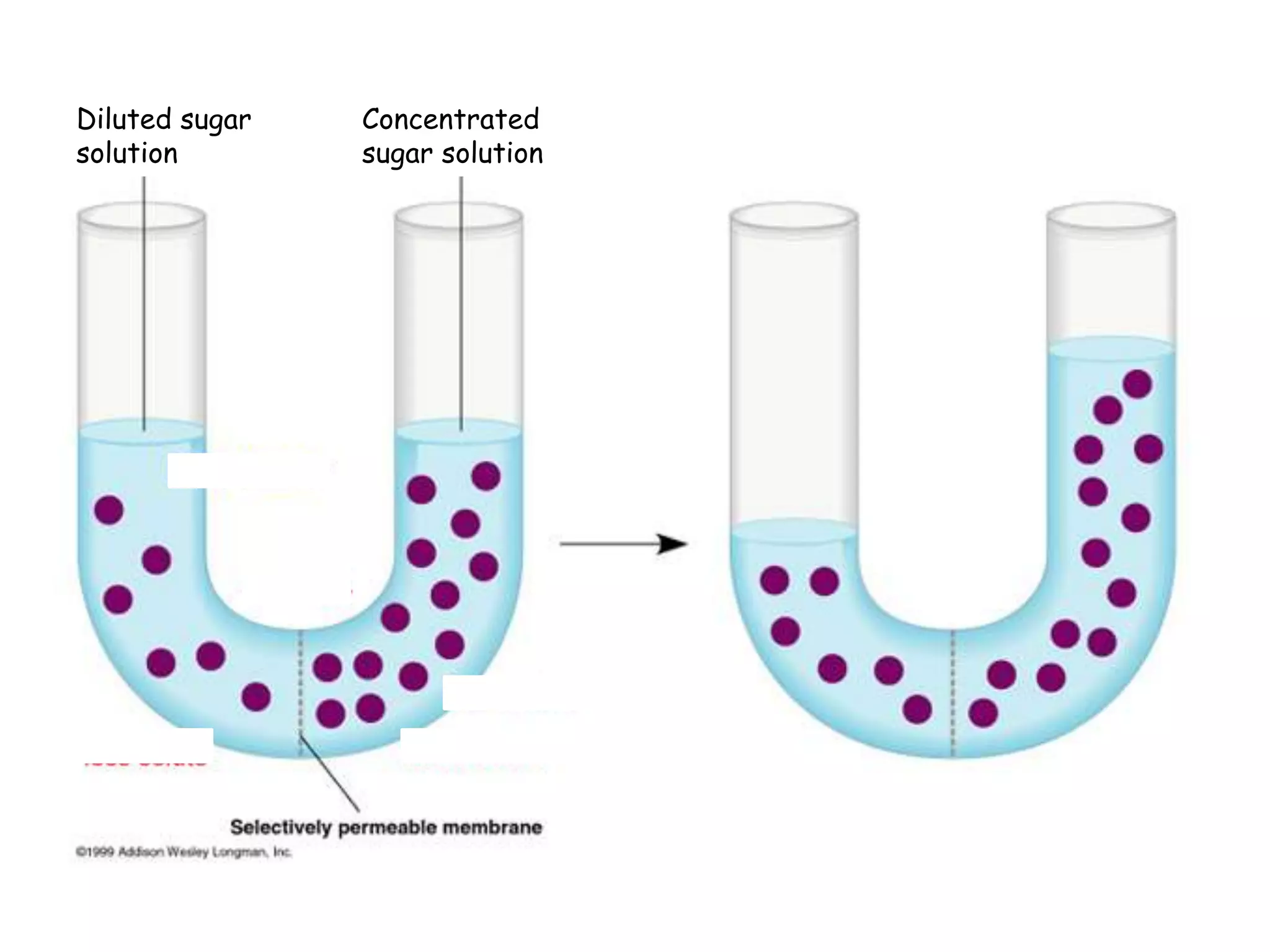
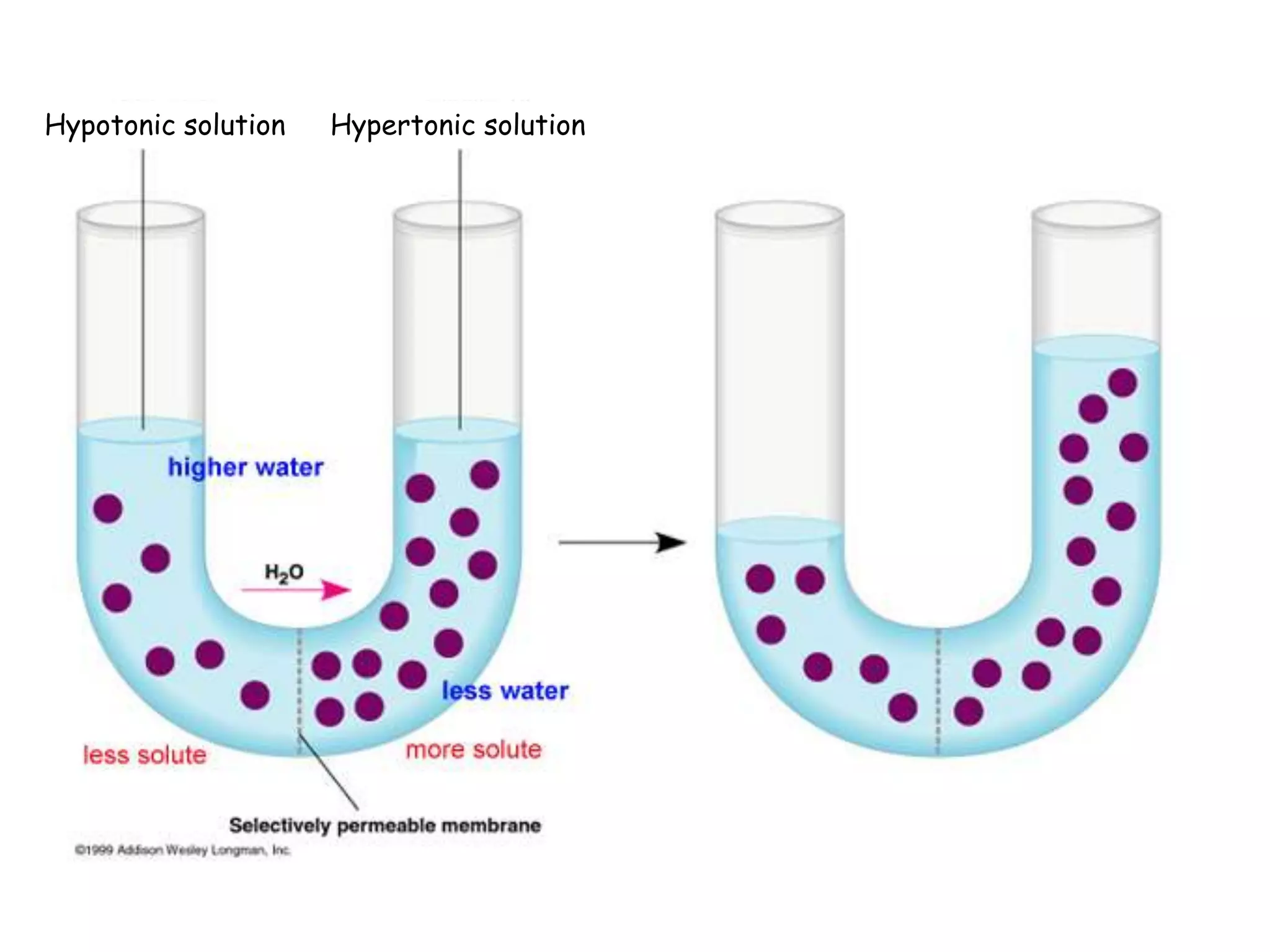
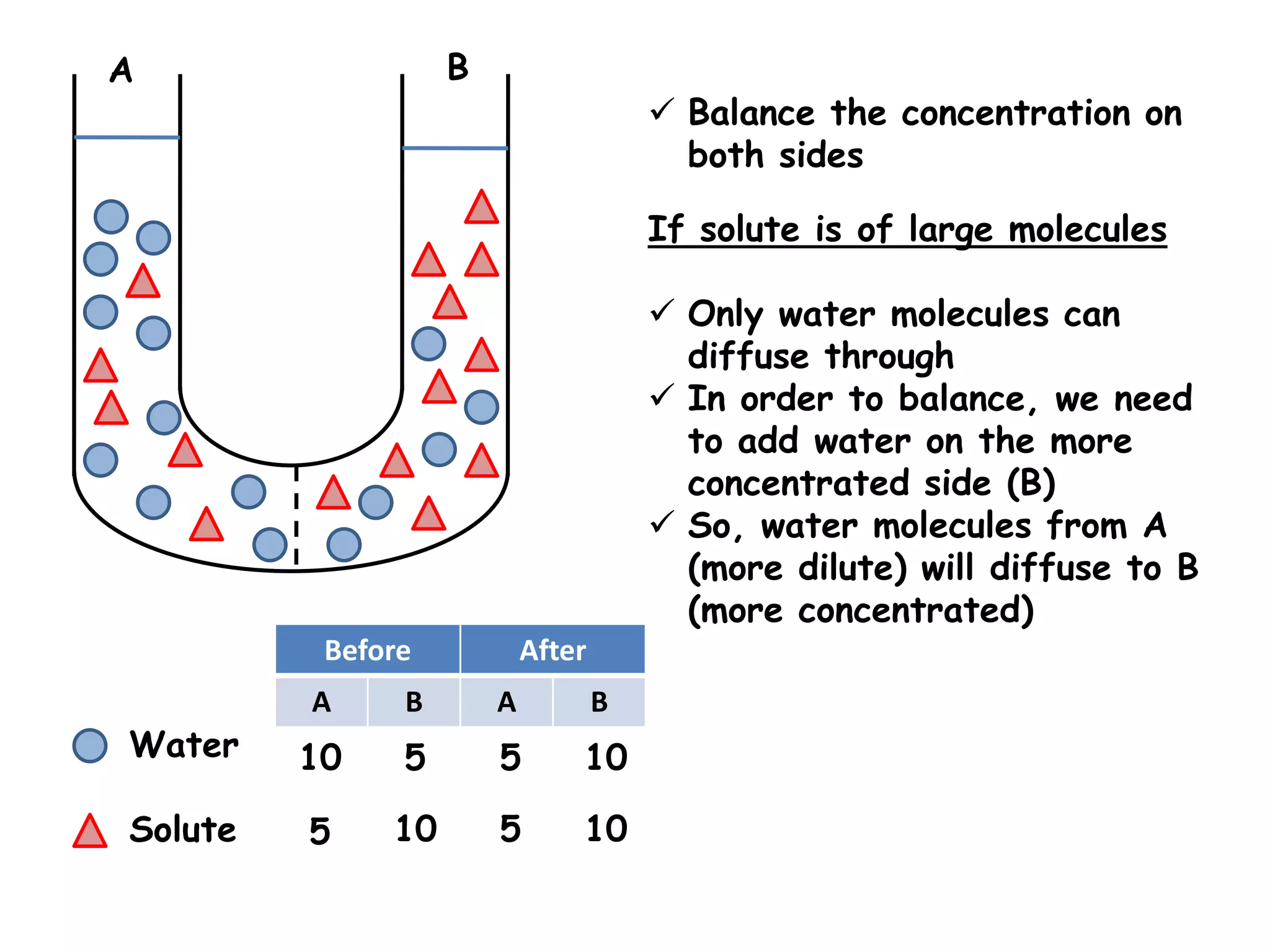
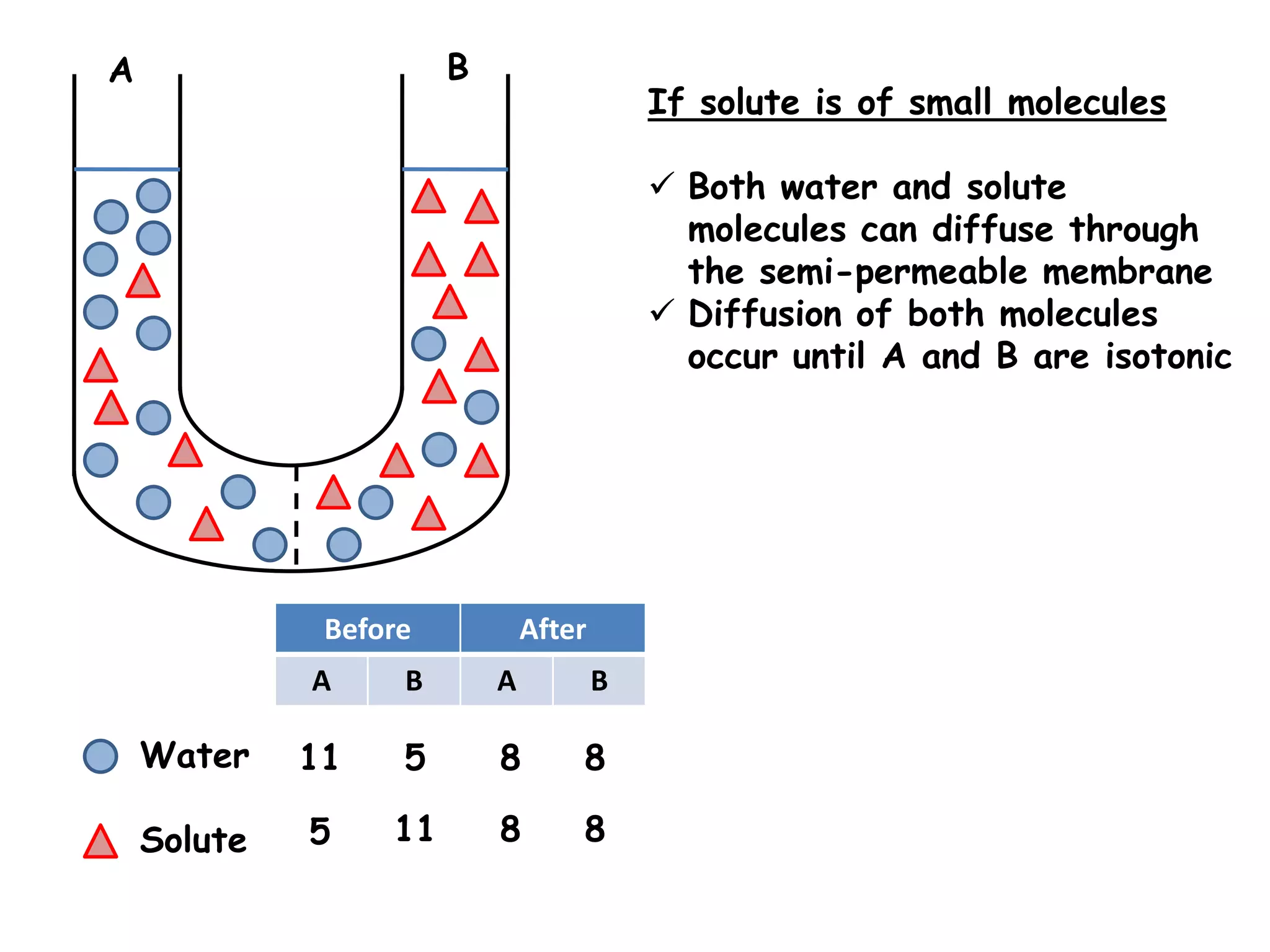
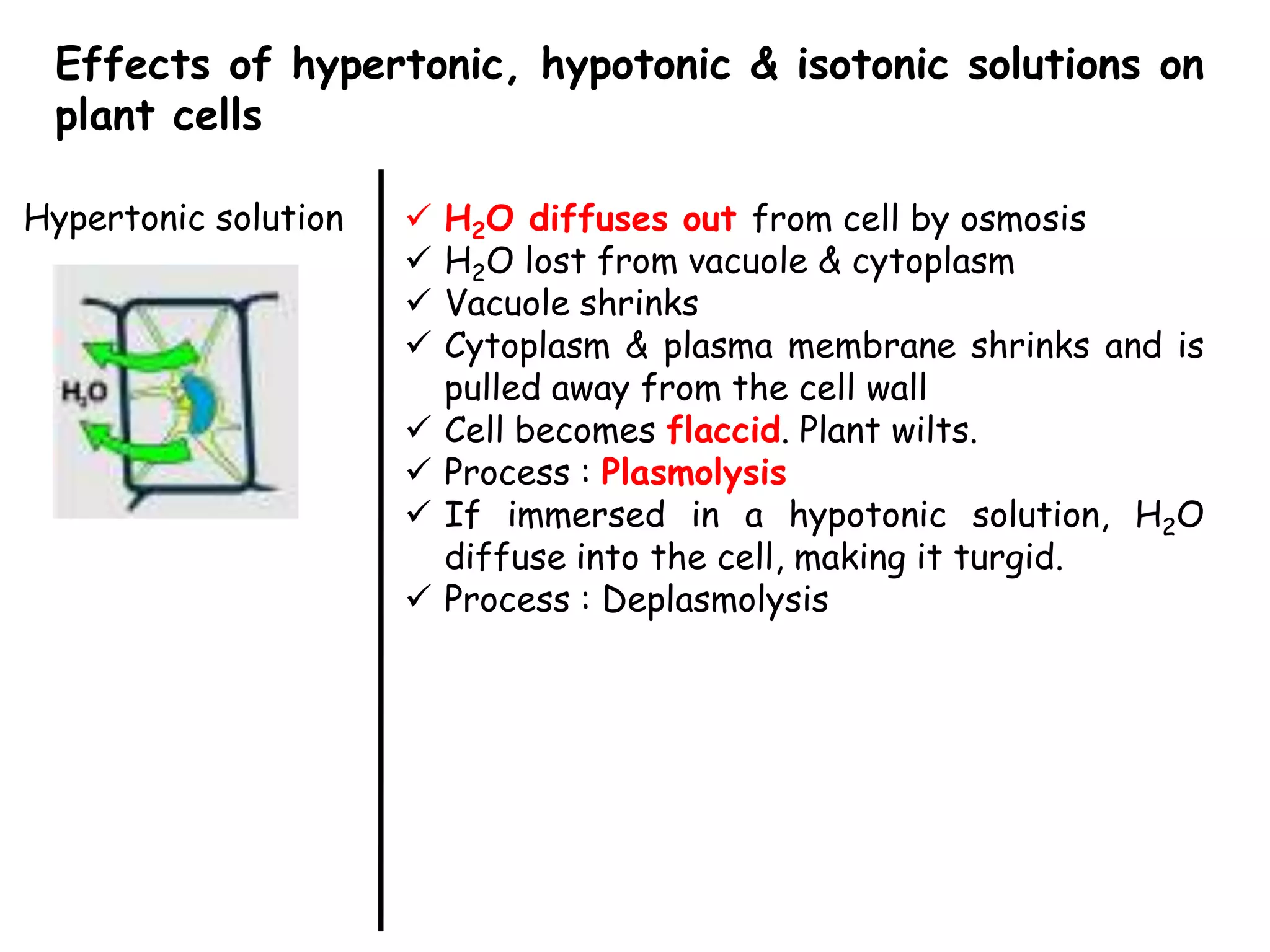
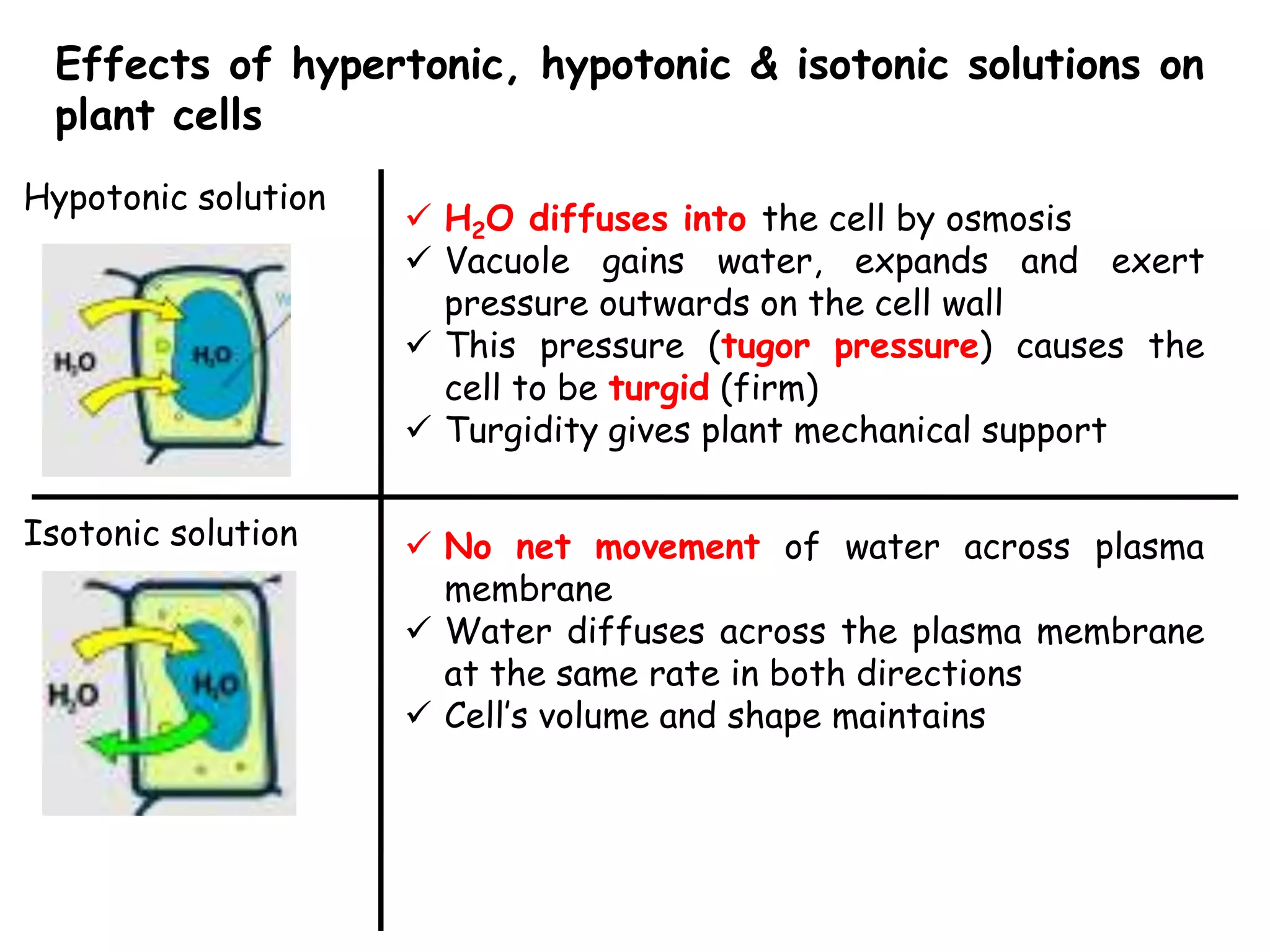
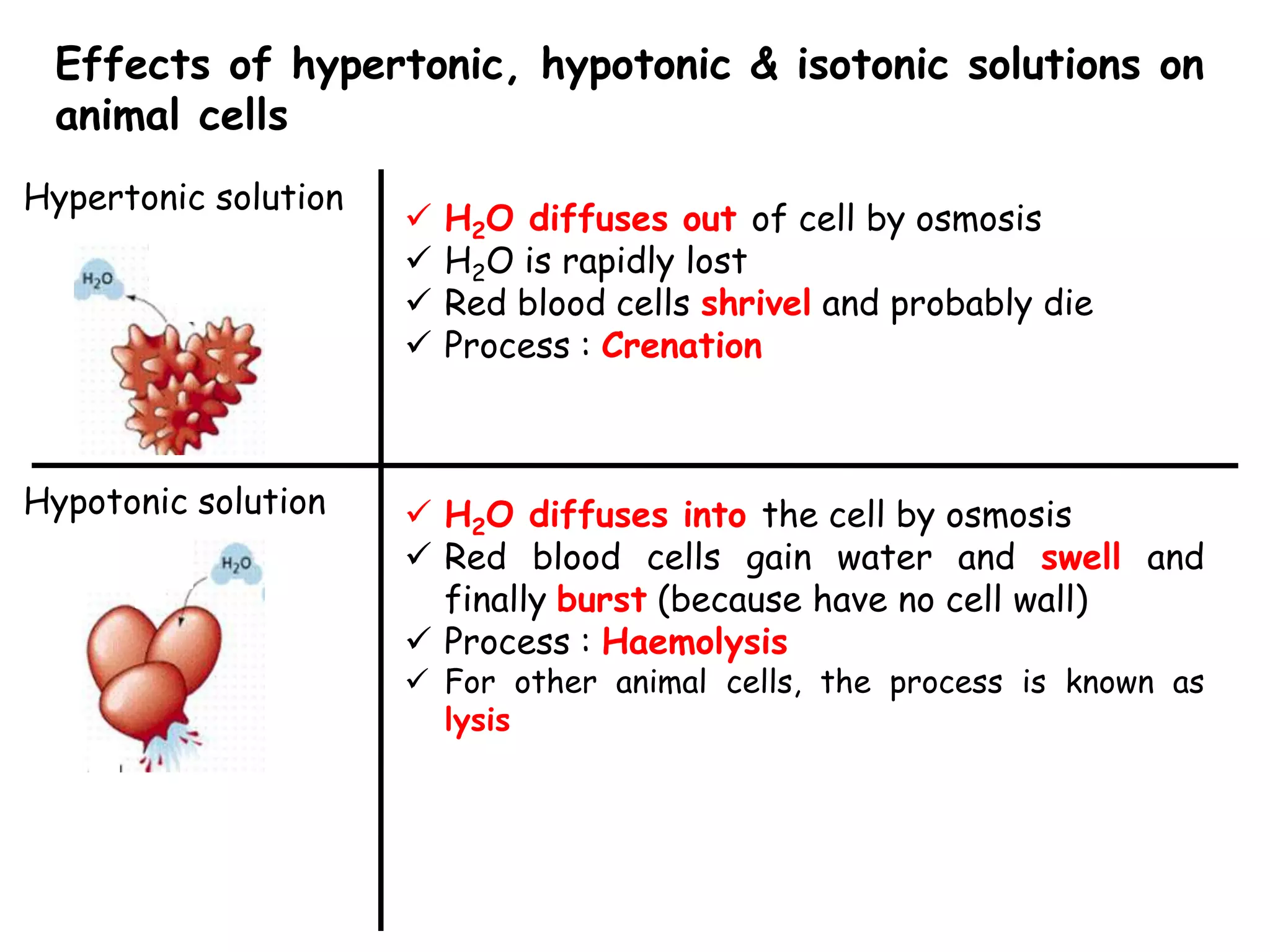
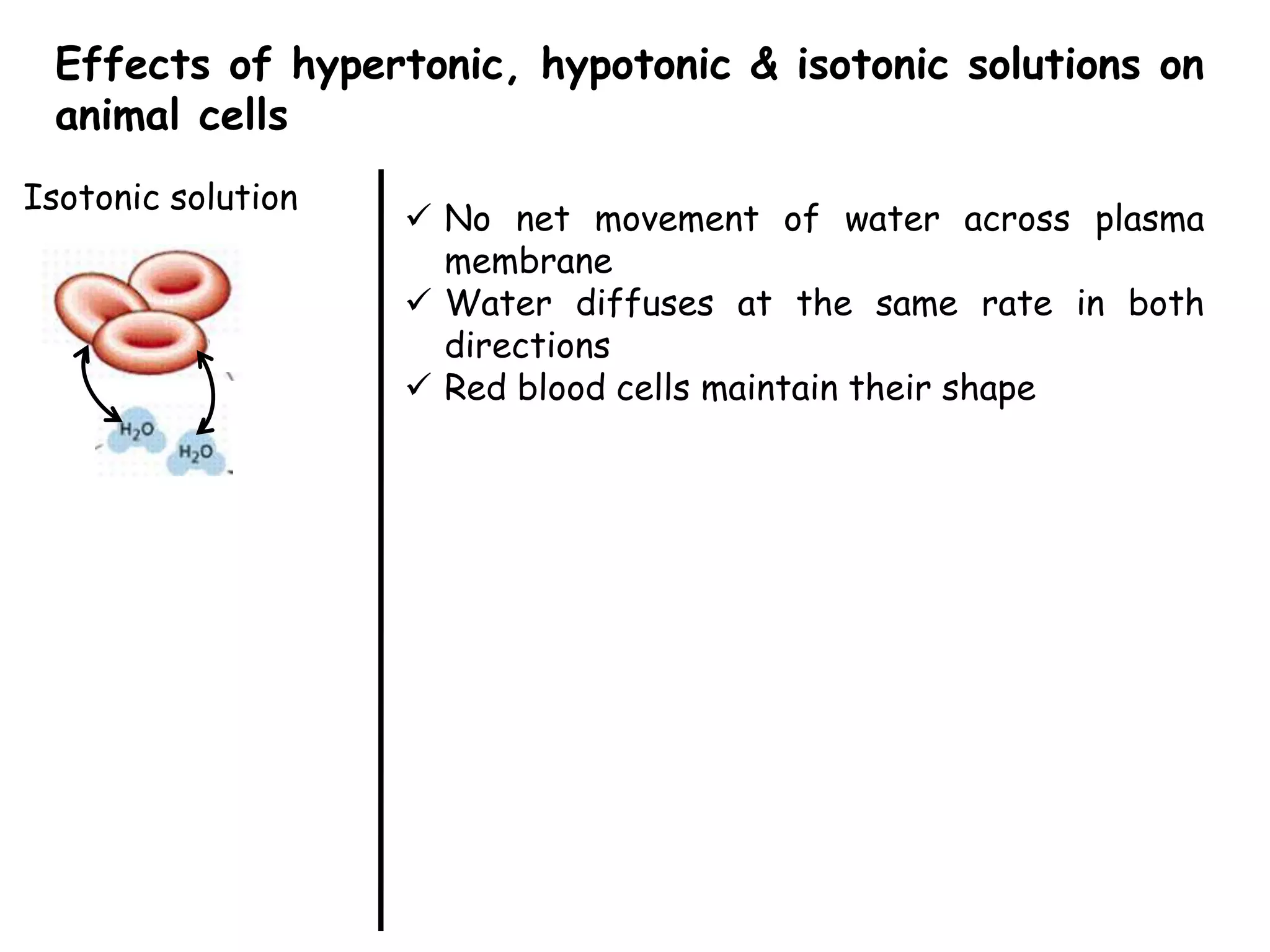
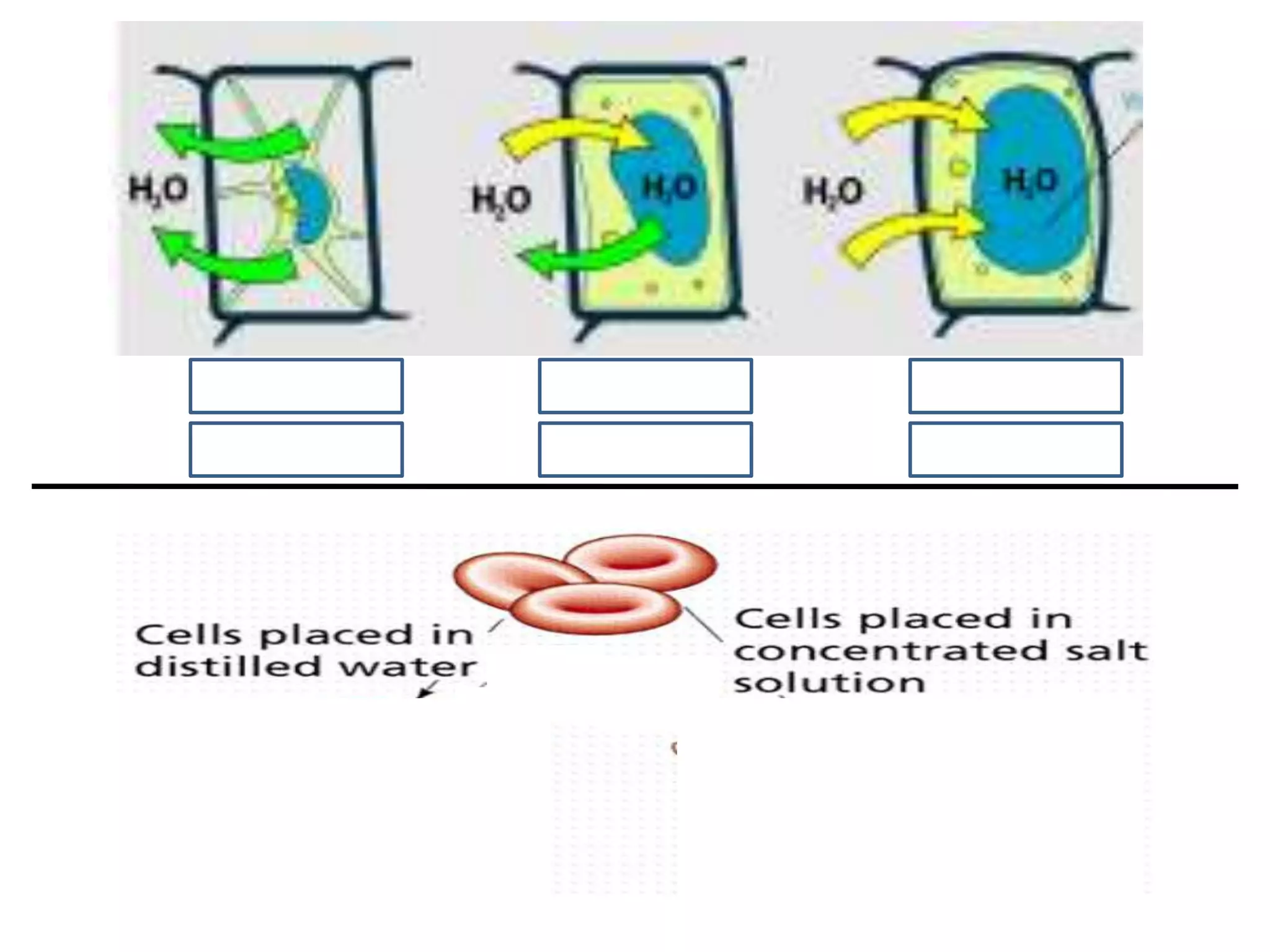
This document summarizes osmosis and the effects of hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions on plant and animal cells. It explains that in a hypertonic solution, water diffuses out of the cell, while in a hypotonic solution water diffuses into the cell. An isotonic solution does not change the cell volume as water diffuses in both directions at equal rates. It provides examples of how osmosis impacts wilting plants and food preservation.