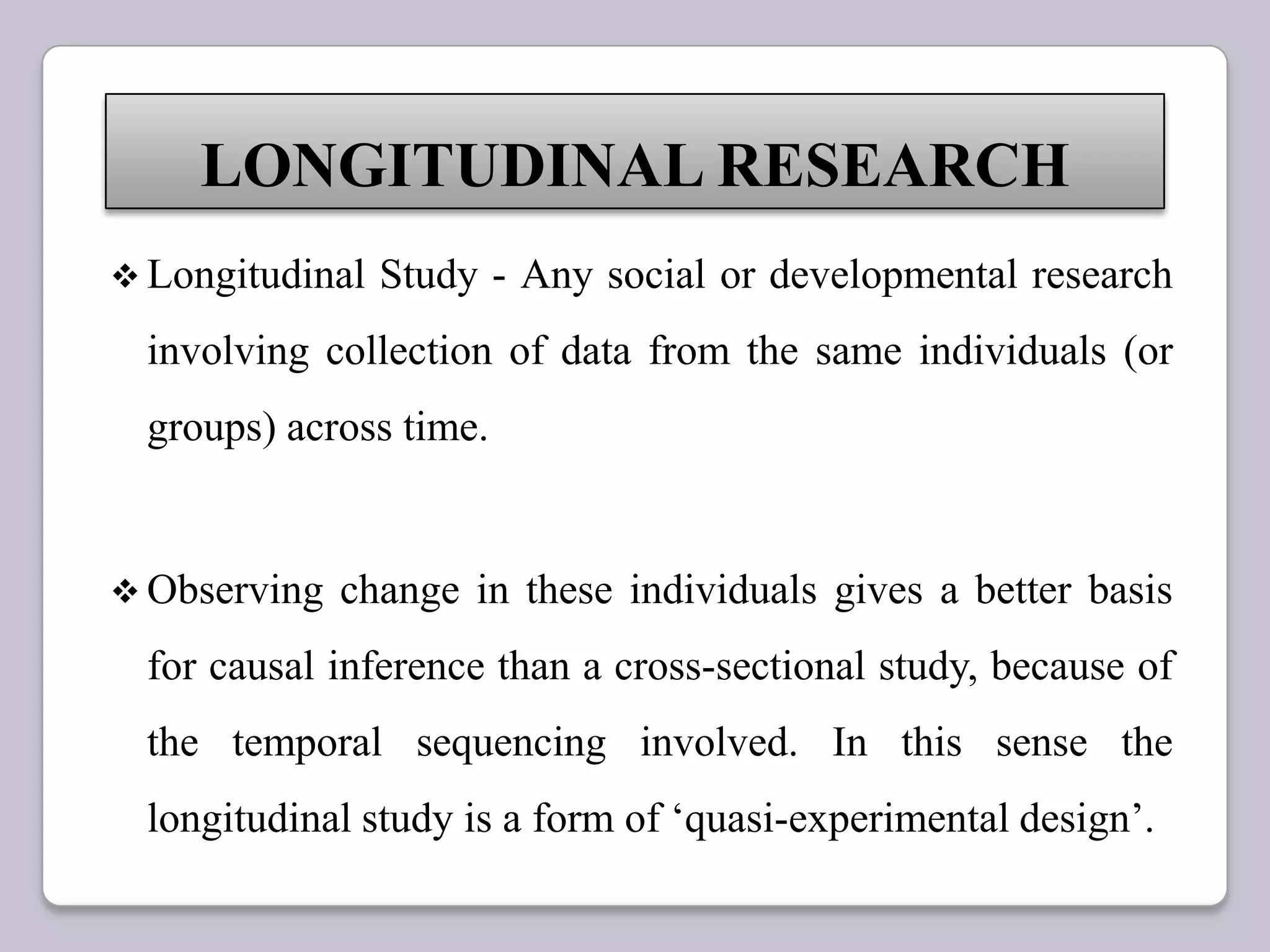
This document discusses one time and longitudinal research. One time research involves studying a sample at a single point in time, such as population surveys. Longitudinal research studies the same sample at multiple points over an extended period. It allows observation of changes in individuals or groups. Cross-sectional studies collect data from a population sample once, while longitudinal studies revisit the same sample multiple times, making longitudinal research better for understanding causation. The document also defines descriptive research and different types of longitudinal research designs like cohort and panel studies.