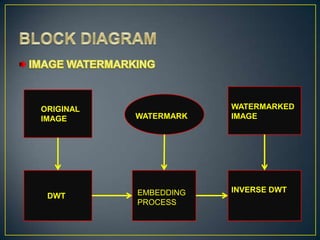
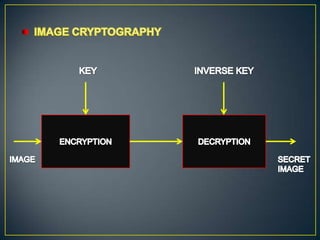
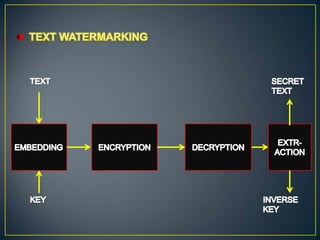
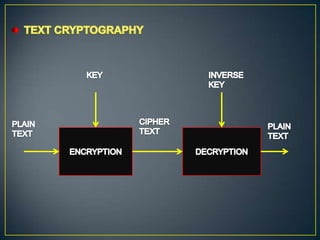
This document compares watermarking and cryptography. It discusses that watermarking involves hiding secret information in digital images while cryptography transforms information into an unreadable format. Watermarking provides security and an extra layer of authentication while cryptography focuses on protecting the meaning of documents. The document also outlines some advantages and disadvantages of each technique such as watermarking being more resistant to attacks but cryptography providing better security through encryption.