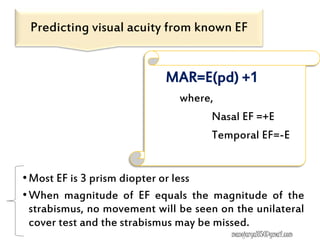
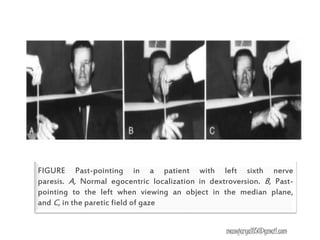
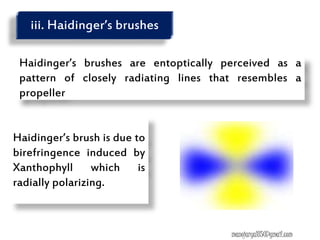
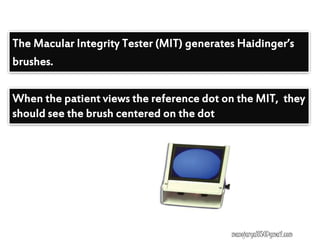
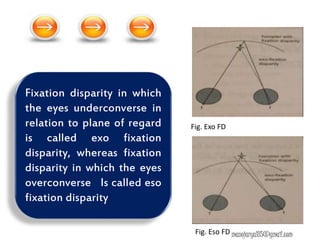
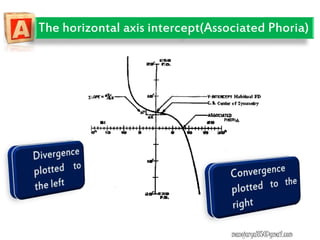
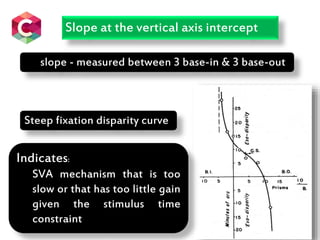
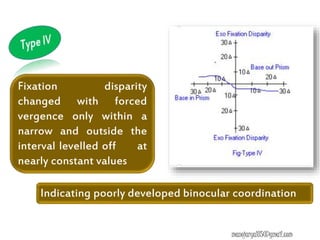
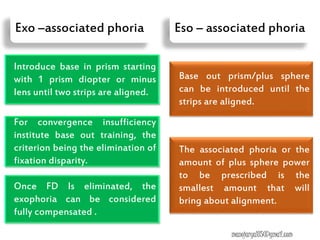
This document contains information about various tests used to evaluate monocular fixation, including past pointing, visuoscopy, Haidinger's brush, and fixation disparity tests. It provides details on how each test is performed and what it evaluates. For example, it explains that past pointing detects abnormal visual localization in patients with recent eye muscle paralysis by having them point to where an object is located. Visuoscopy uses a modified ophthalmoscope to project a target on the retina to assess fixation point. Haidinger's brush and Maxwell's spot can also be used to determine the direction and magnitude of any eccentric fixation.