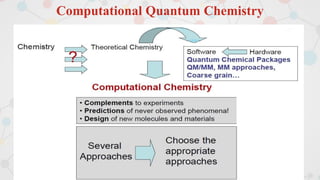
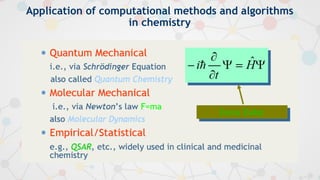
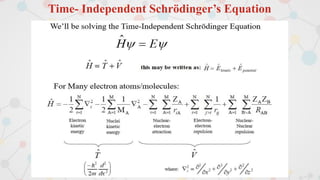
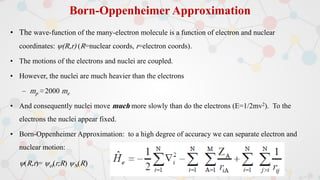
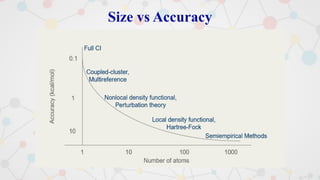
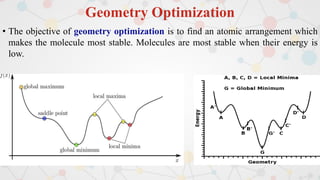
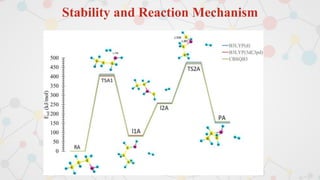
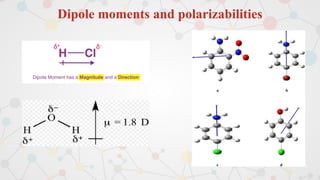
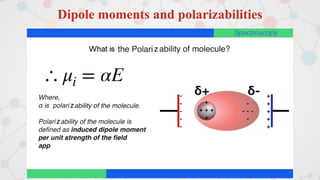
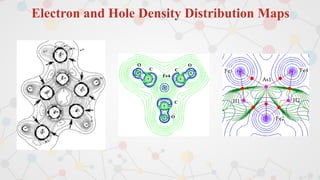
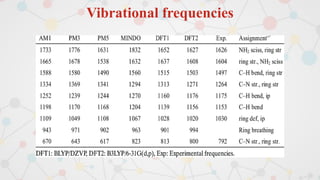
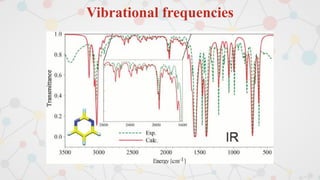
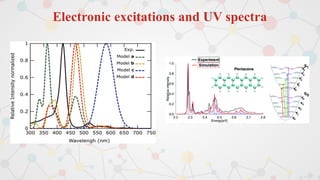
The document presents an overview of computational quantum chemistry, a branch of chemistry that utilizes mathematical methods and computer simulations to analyze chemical processes, particularly focusing on the Schrödinger equation. It discusses various calculation types, modeling approaches, and the use of approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, along with the trade-offs between accuracy and computational efficiency. Furthermore, it highlights applications in fields such as nanotechnology, drug discovery, and the study of molecular properties.