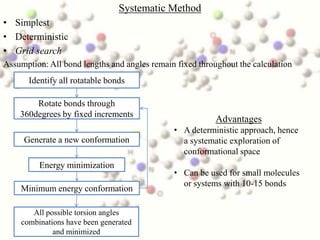
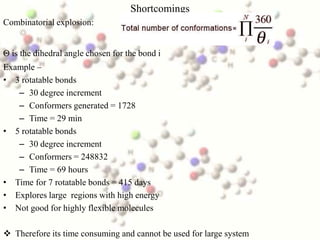
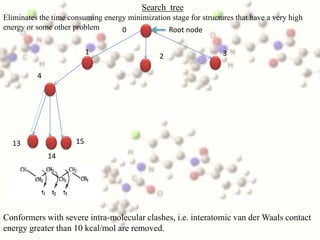
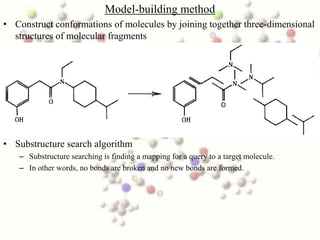
This document discusses methods for conformational analysis of molecules, which is needed to identify a molecule's lowest energy conformation. It describes systematic search methods that systematically explore all torsion angles combinations but are limited by computational time. It also describes model-building methods that construct conformations by joining molecular fragments. Available technologies for conformational analysis include software tools from Accelrys, Molecular Networks, OpenEye, Schrodinger, and Tripos.