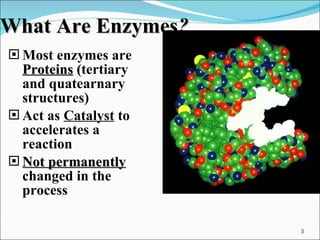
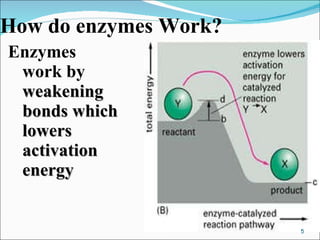
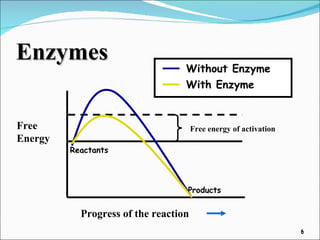
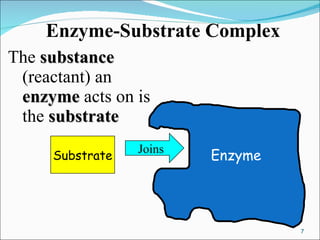
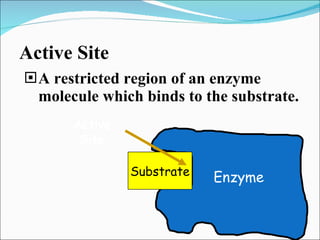
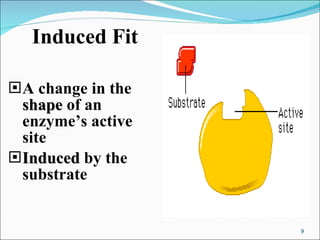
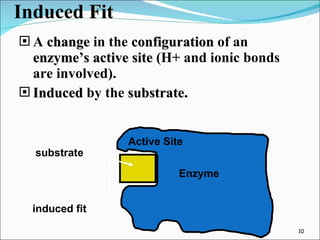
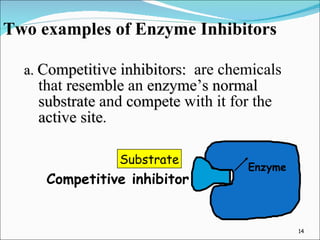
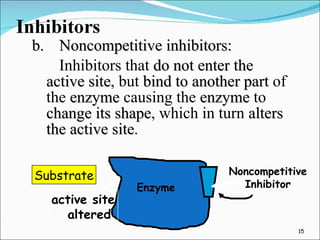
Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being permanently altered. They work by weakening bonds between reactants to lower the activation energy needed for the reaction. Enzymes have an active site that binds specifically to substrates. When the substrate binds, an induced fit may occur where the active site changes shape to better accommodate the substrate. Environmental conditions like temperature and pH can affect enzyme activity, as can cofactors that are sometimes required for proper function. Enzyme inhibitors can also decrease activity by competing for the active site or binding elsewhere and inducing a shape change in the enzyme.