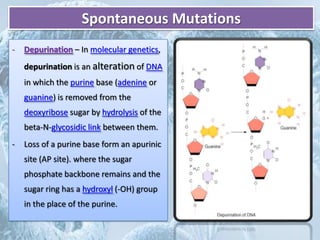
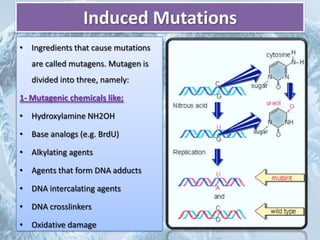
Mutations are any changes in the DNA sequence of an organism. They can be caused spontaneously during DNA replication or repair, or can be induced by mutagens like chemicals, radiation, or viruses. Mutations are classified as point mutations, which change a single DNA base, or frameshift mutations, which insert or delete DNA bases. Cells have DNA repair mechanisms to correct mutations, such as base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, and mismatch repair. Unrepaired mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or have no effect on the organism.