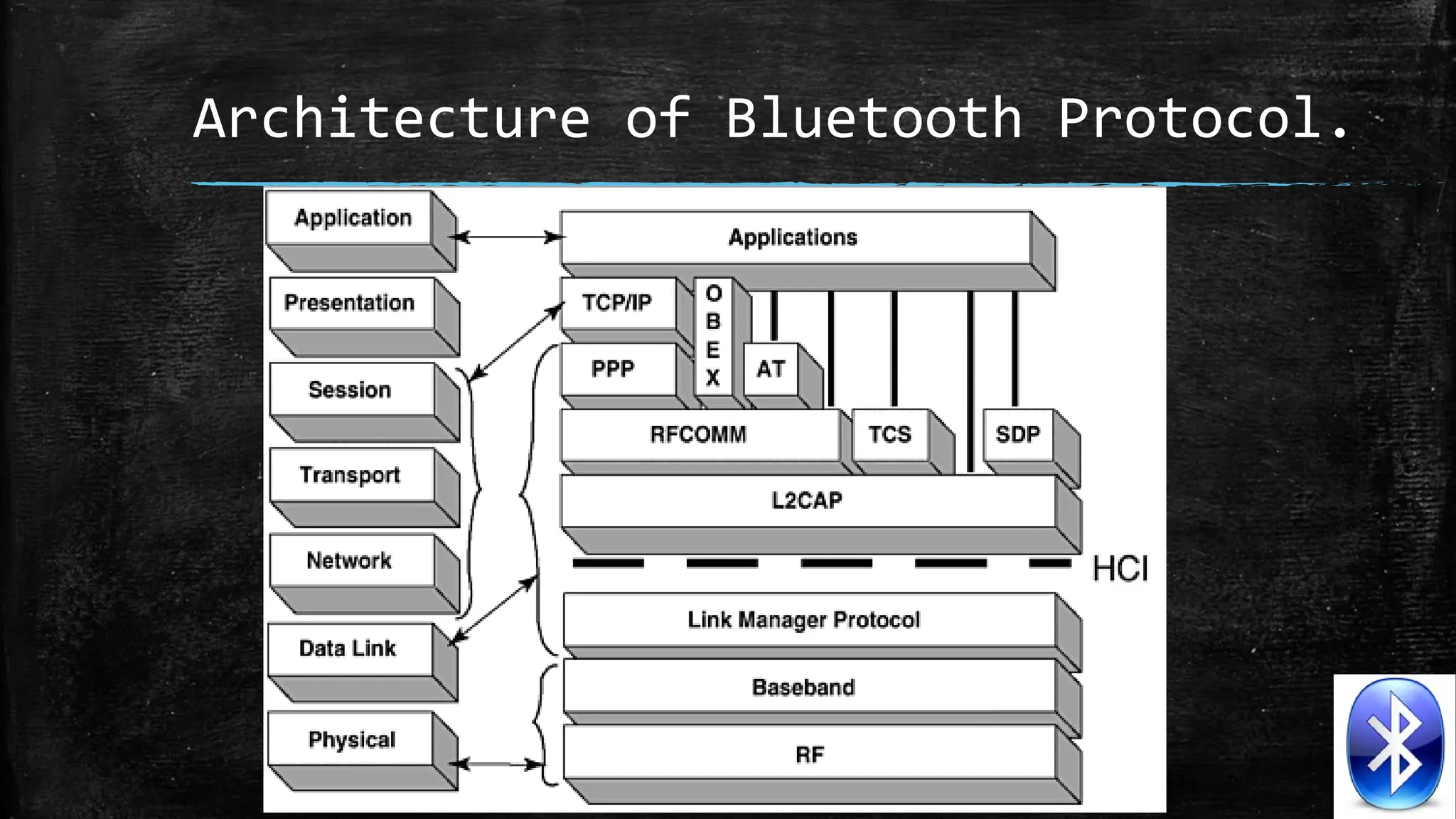
The document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology, detailing its history, architecture, and various protocols used within its stack. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of Bluetooth, emphasizing its role in short-range wireless communication and ongoing developments to enhance security and speed. Additionally, the content highlights future prospects for Bluetooth technology, indicating a strong demand for advancements in wireless applications.