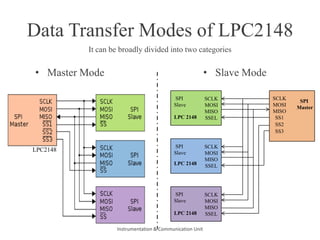
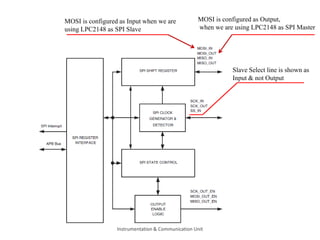
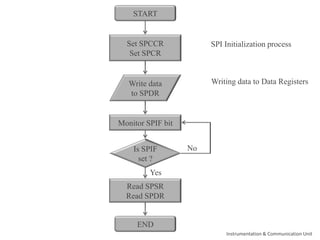
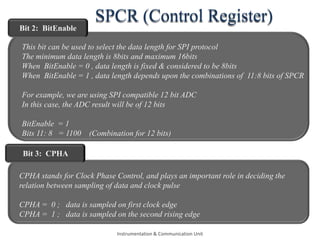
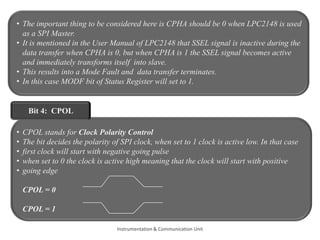
The document discusses the SPI protocol used in the LPC2148 microcontroller. It describes the SPI communication modes of master and slave. It explains the various SPI registers used for configuration - SPCCR for clock settings, SPCR for control settings like CPHA and CPOL, SPDR for data transfer, and SPSR for status. It provides steps for initialization and data transfer in both master and slave modes. The document also discusses factors like clock frequency, data length, and interrupt handling related to SPI communication using LPC2148.