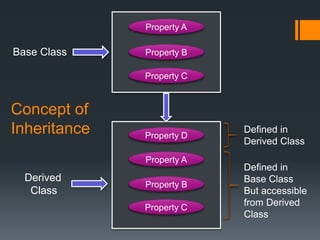
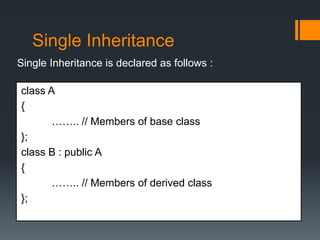
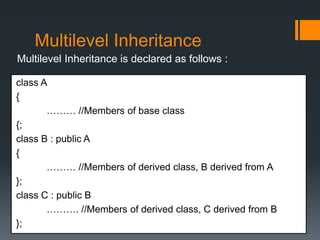
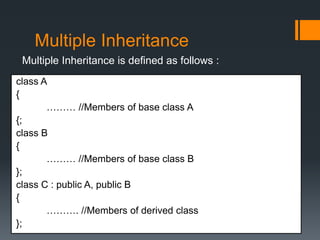
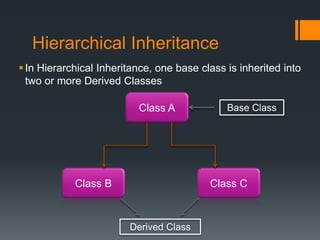
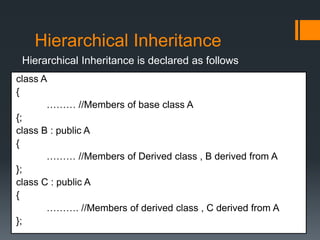
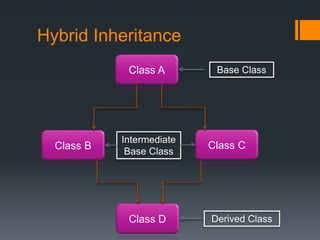
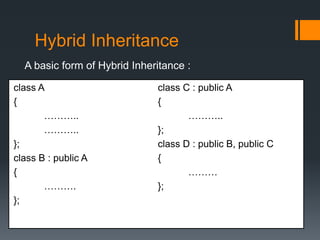
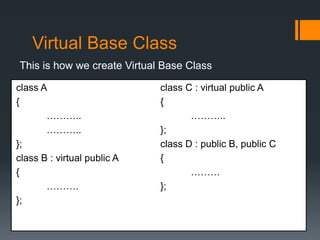
Inheritance allows a derived class to inherit properties from a base or parent class. A derived class inherits attributes and behaviors of the base class and can add its own attributes and behaviors. There are different types of inheritance including single, multilevel, multiple, hierarchical, and hybrid inheritance. Inheritance promotes code reuse and reduces development time.