Embed presentation
Downloaded 715 times




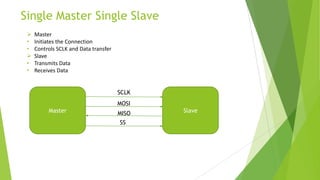
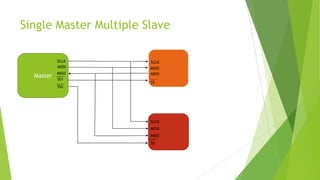





Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a communication protocol developed by Motorola for serial communication. It uses a master-slave architecture with 4 connection wires - MOSI, MISO, SCLK, and SS. The master device controls the clock signal and initiates data transfer to and from the slave devices. SPI allows for full duplex communication at high speeds and is commonly used with peripherals like converters, memories, sensors, and displays. While it provides high throughput, SPI requires more pins than alternatives like I2C and does not have hardware flow control or slave acknowledgement.









