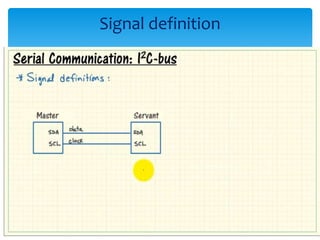
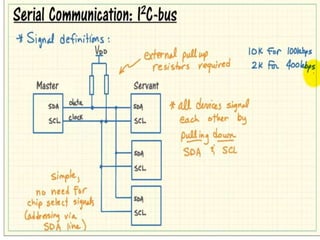
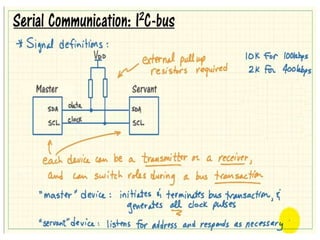
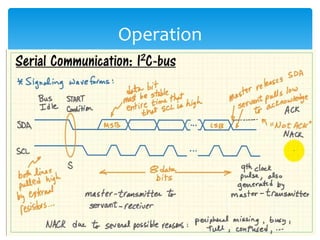
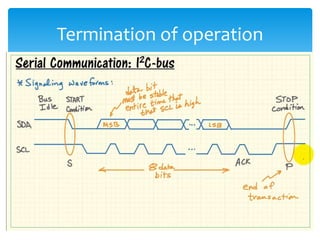
The document discusses the I2C protocol, which uses just two bidirectional serial data lines (SDA and SCL) to allow multiple devices to communicate on the same bus. It supports synchronous communication at various speeds up to 5 Mbps. Devices are addressed using 7- or 10-bit addresses. Data is transferred in bytes, with start and stop conditions defining the beginning and end of each transmission. All data transitions must occur when the clock signal SCL is low.