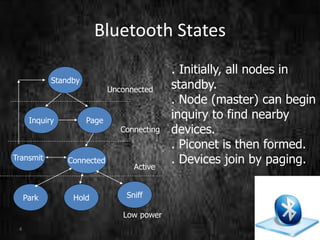
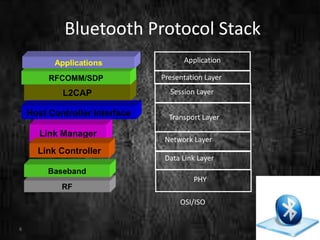
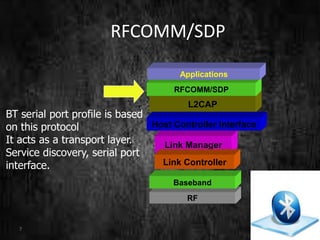
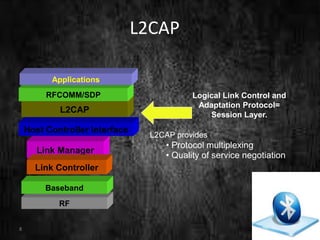
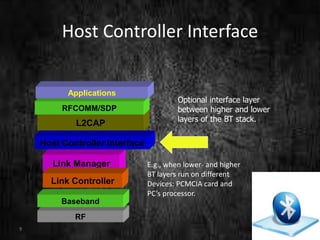
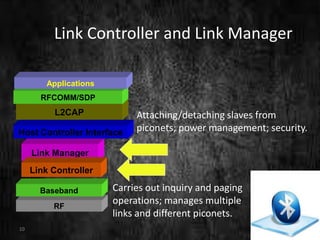
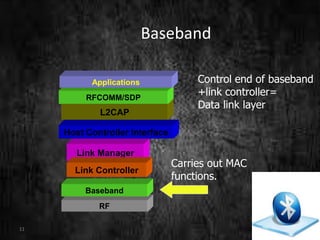
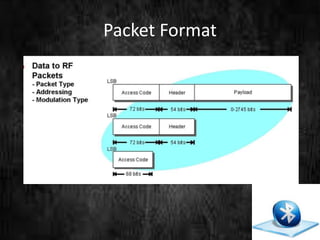
This document summarizes a technical seminar presentation on Bluetooth technology. It includes an agenda covering an introduction to Bluetooth, its states, features, protocol stack including layers like RFCOMM, L2CAP, and the link controller. It describes Bluetooth's short-range wireless communication, various states like standby and connected, its layered protocol stack, and security features. The presentation concludes by asking if there are any questions.