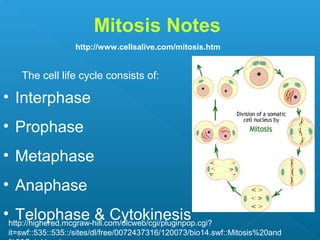
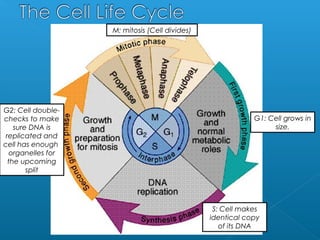
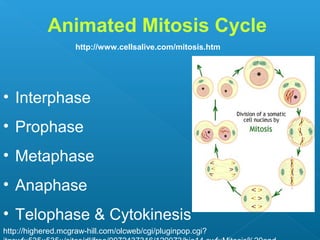
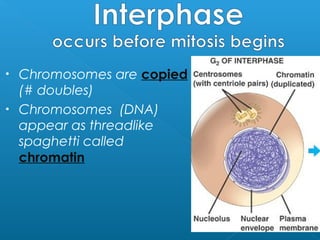
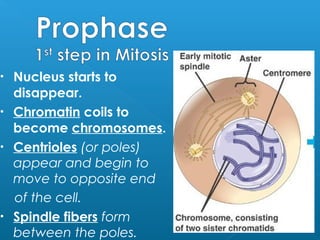
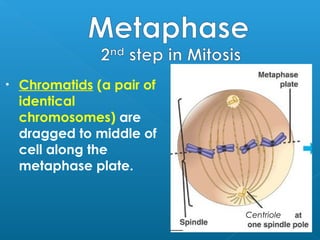
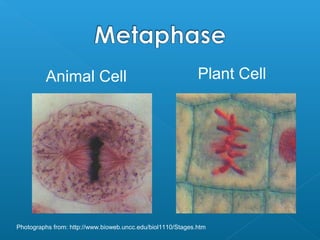
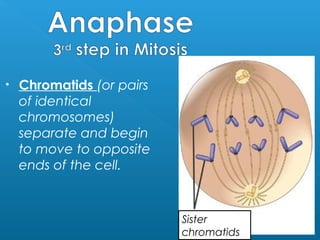
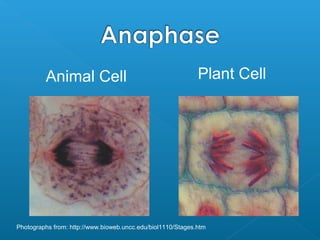
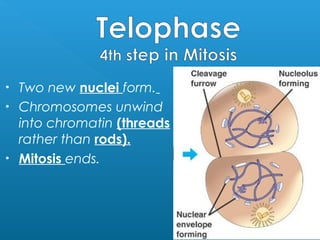
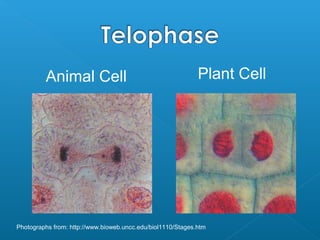
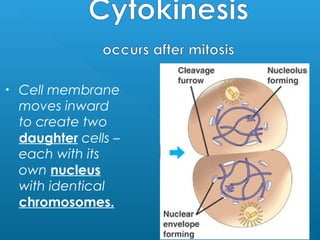
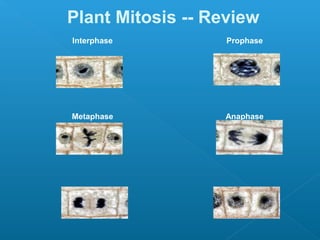
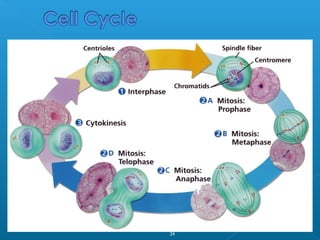
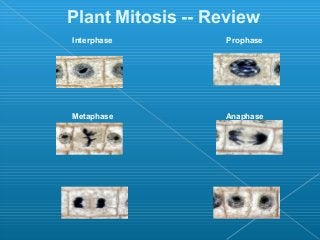
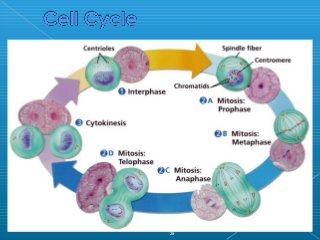
Little elephants grow up to be big elephants through cell growth and division. Cells multiply through mitosis, where the cell makes an identical copy of its DNA and divides into two daughter cells. This cell growth and division allows the elephant to increase in size as it matures, rather than cells individually increasing in volume. The document provides information about the cell cycle and process of mitosis.