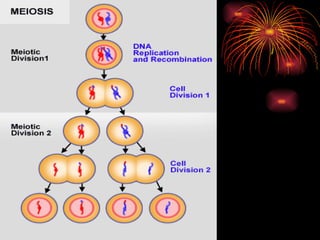
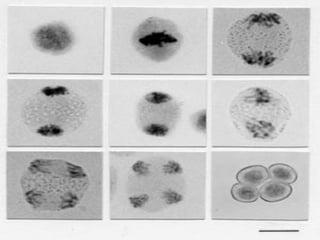
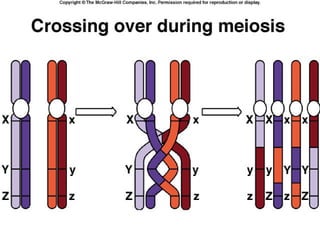
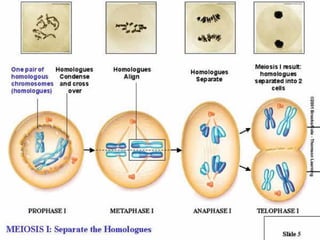
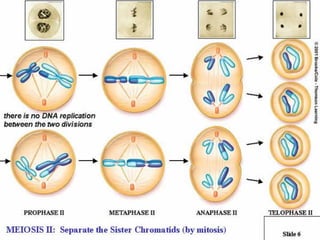
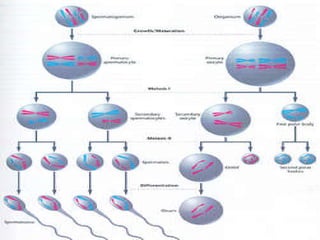
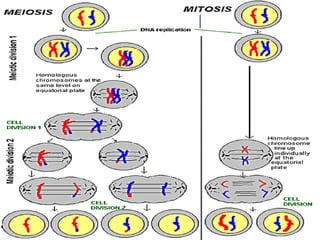
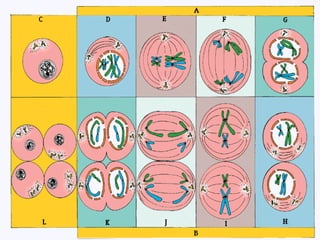
Meiosis is the process by which diploid cells in organisms undergo two cell divisions to produce four haploid gametes. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo crossing over, then separate so each daughter cell has one of each type of chromosome. Meiosis II then separates the sister chromatids, resulting in four haploid cells each containing one set of chromosomes. This allows for genetic variation between gametes and offspring through independent assortment of chromosomes and new combinations from crossing over during meiosis I.