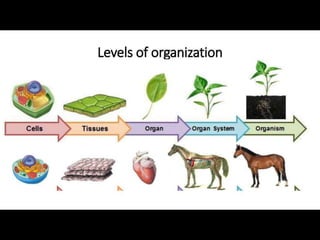
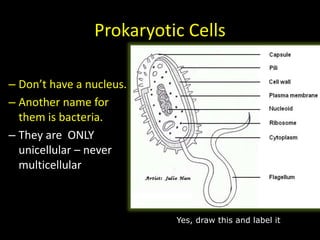
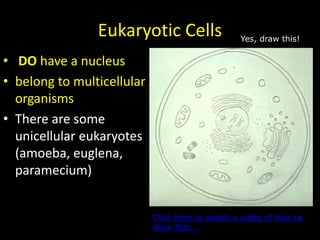
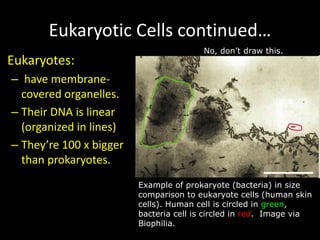
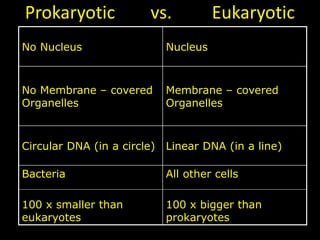
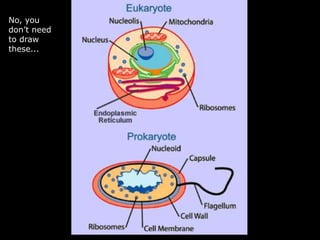
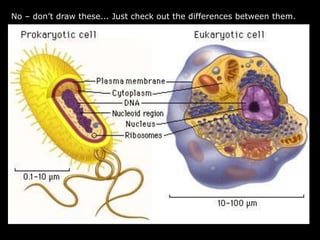
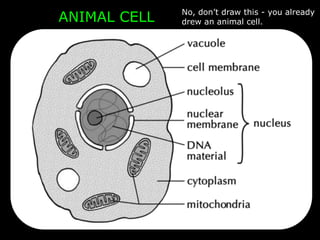
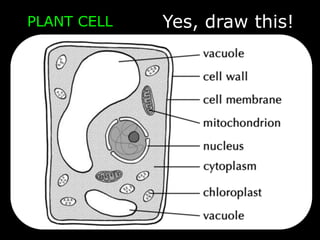
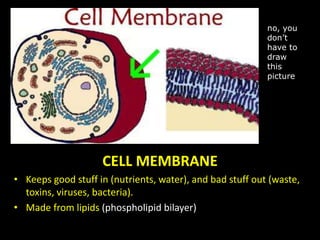
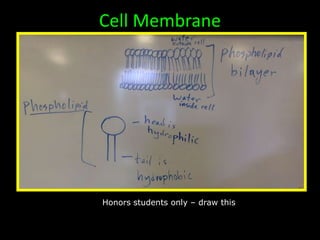
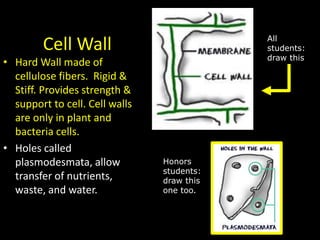
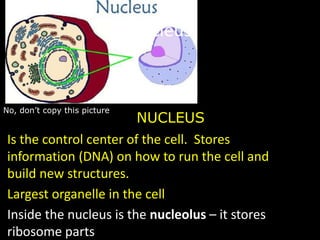
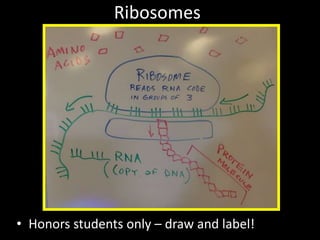
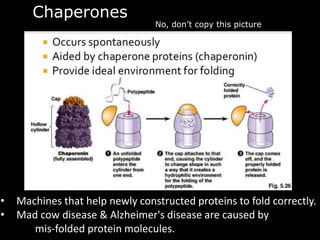
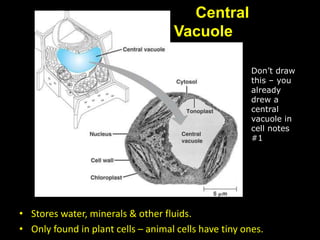
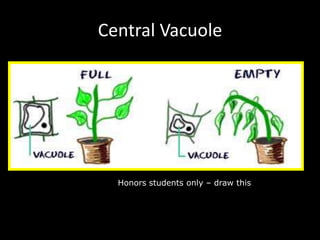
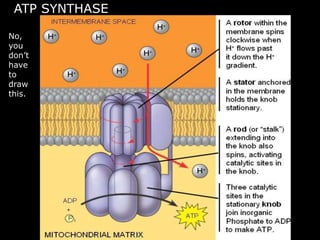
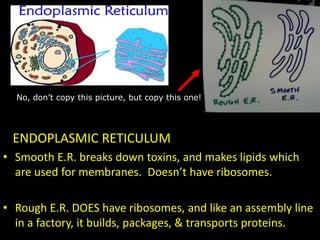
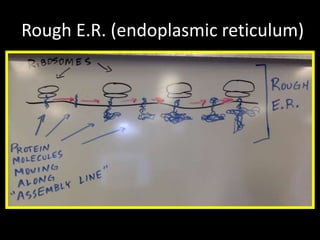
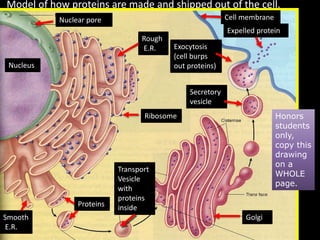
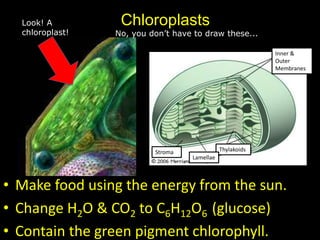
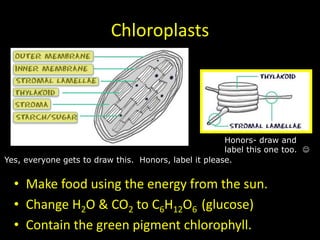
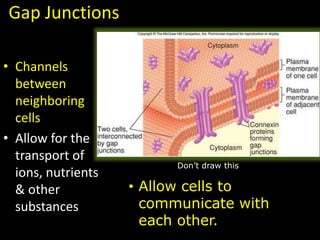
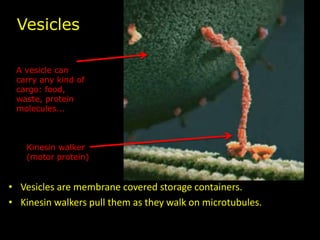
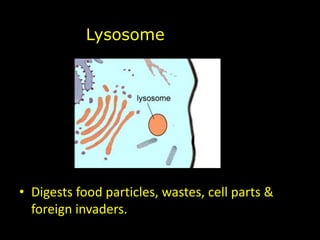
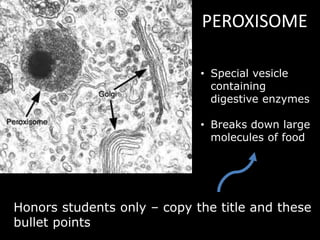
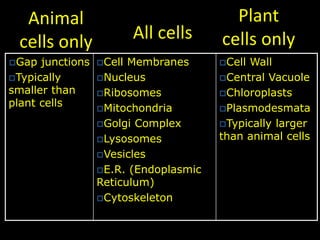
The document comprises detailed notes on cell biology, including information on unicellular and multicellular organisms, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and various organelles and their functions. It outlines key concepts such as the cell theory, the structure and function of cell membranes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and the cytoskeleton. It also includes prompts for students to engage with reflection activities and prepare for future test questions.