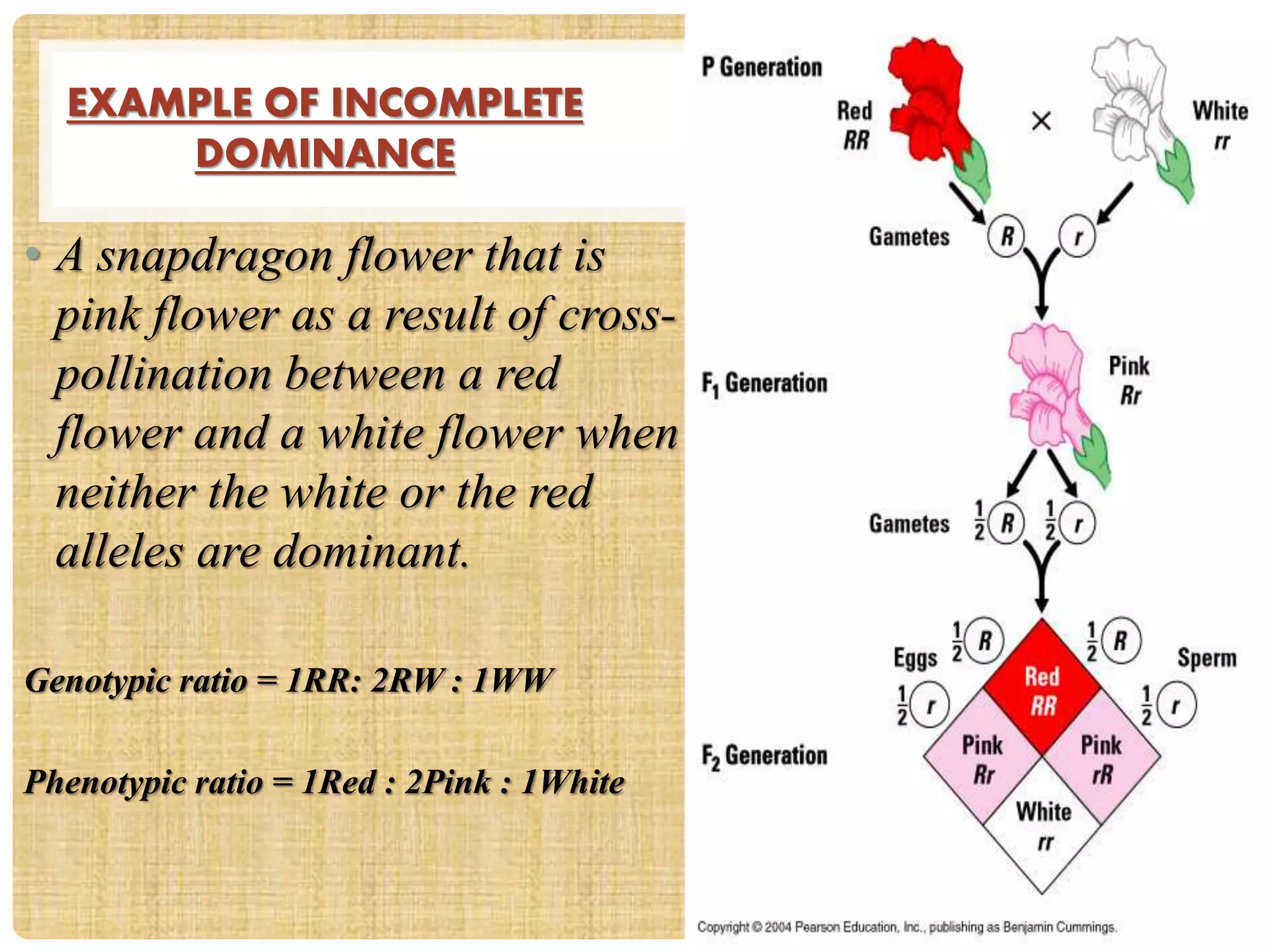
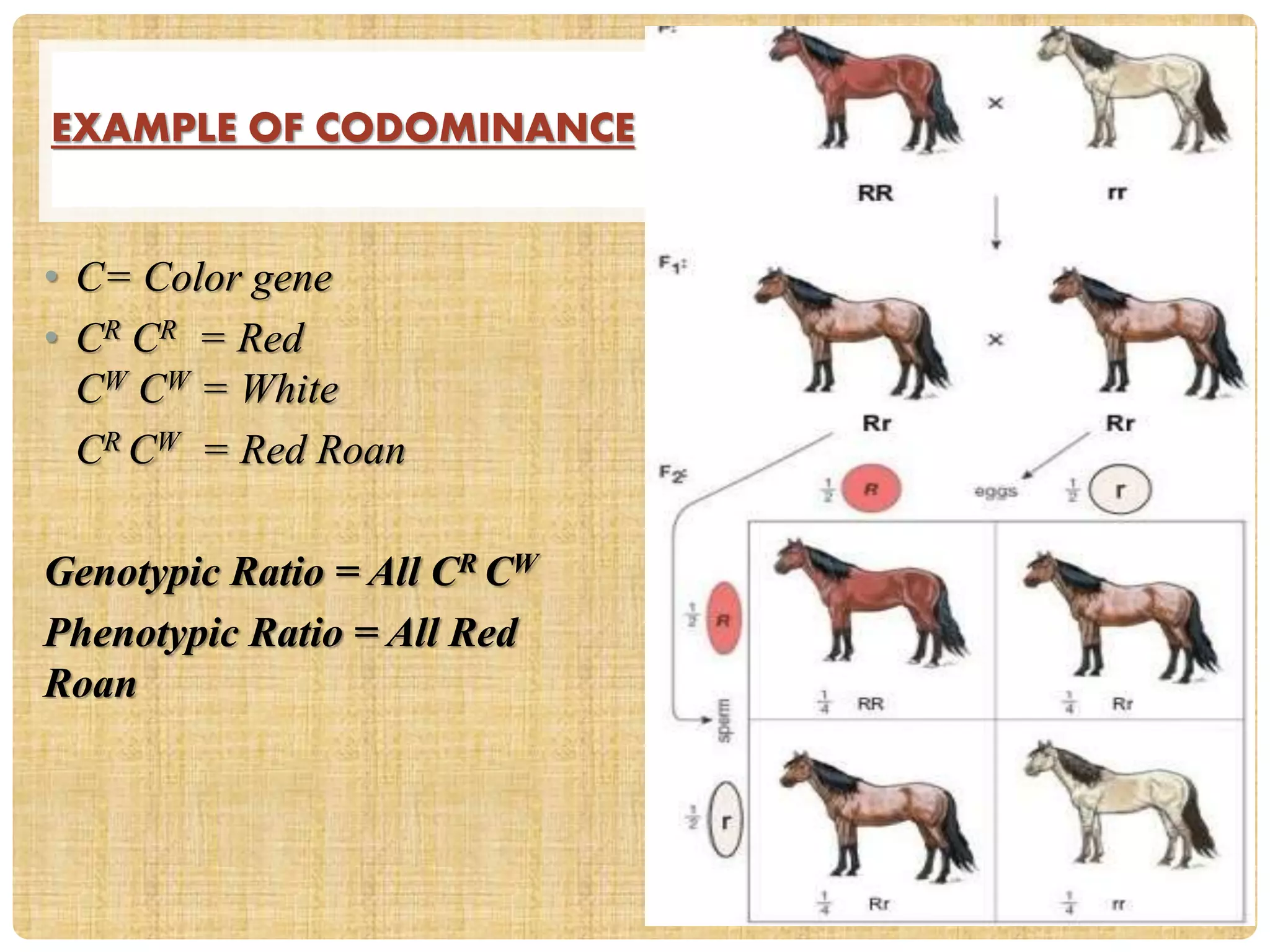
This document discusses three genetic inheritance patterns: dominance, incomplete dominance, and co-dominance. Dominance occurs when one allele is expressed over the other. In incomplete dominance, the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes. Examples include flowers and hair color. Co-dominance occurs when both alleles are fully expressed in the heterozygote, so the phenotype shows traits of both. Examples given are coat color in horses and cattle, and chestnut and white coat colors producing a palomino horse.