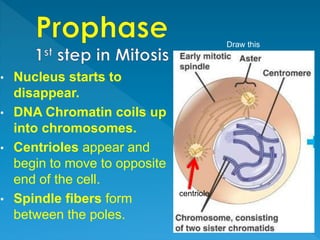
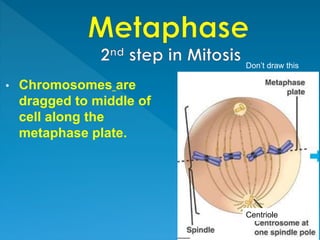
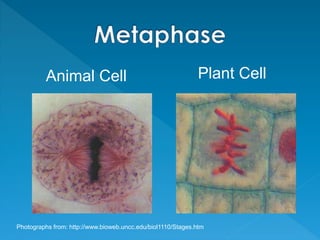
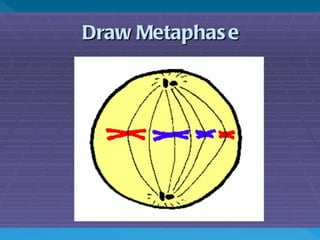
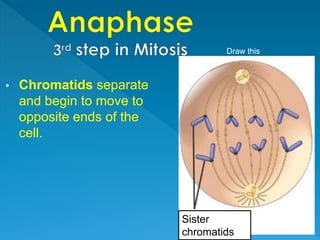
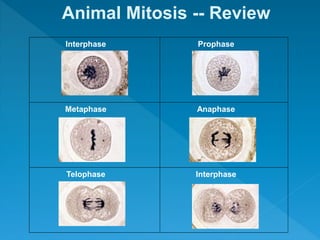
Skin cancer develops most often on skin exposed to the sun. It is the abnormal growth of skin cells that don't know when to stop multiplying, forming tumors. The cell life cycle consists of interphase, where cells perform normal functions, and mitosis, where cells divide into two daughter cells through the stages of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, followed by cytokinesis where the cell physically splits.