This document summarizes several principles of Mendel's laws of inheritance:
1. Mendel conducted hybridization experiments on peas from 1856-1863 and proposed the basic laws of inheritance in organisms.
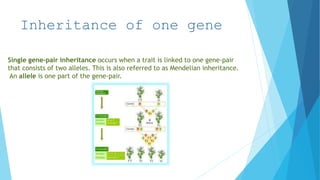
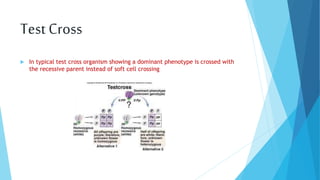
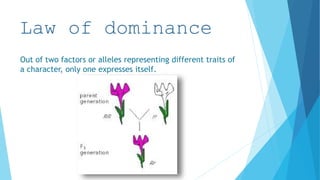
2. Inheritance follows patterns of dominance, with one allele expressing itself over the other in a gene pair. Mendel also described the law of segregation where alleles do not blend but are recovered unchanged in subsequent generations.
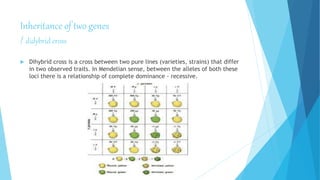
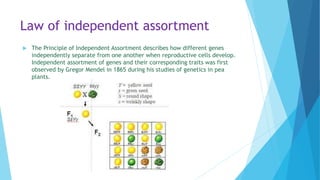
3. The principle of independent assortment holds that different genes independently separate from one another during the formation of reproductive cells, as Mendel first observed in his pea plant experiments.