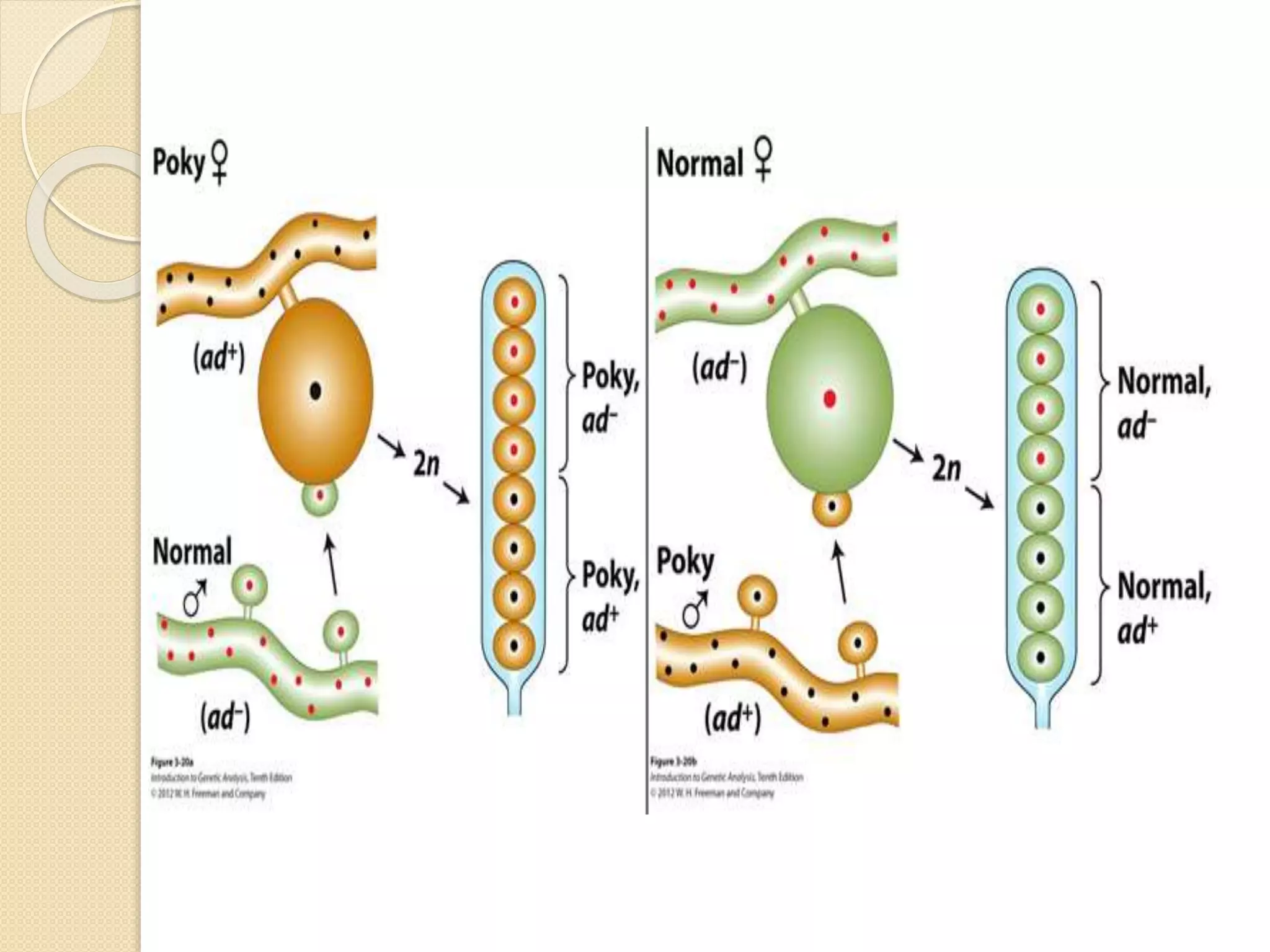
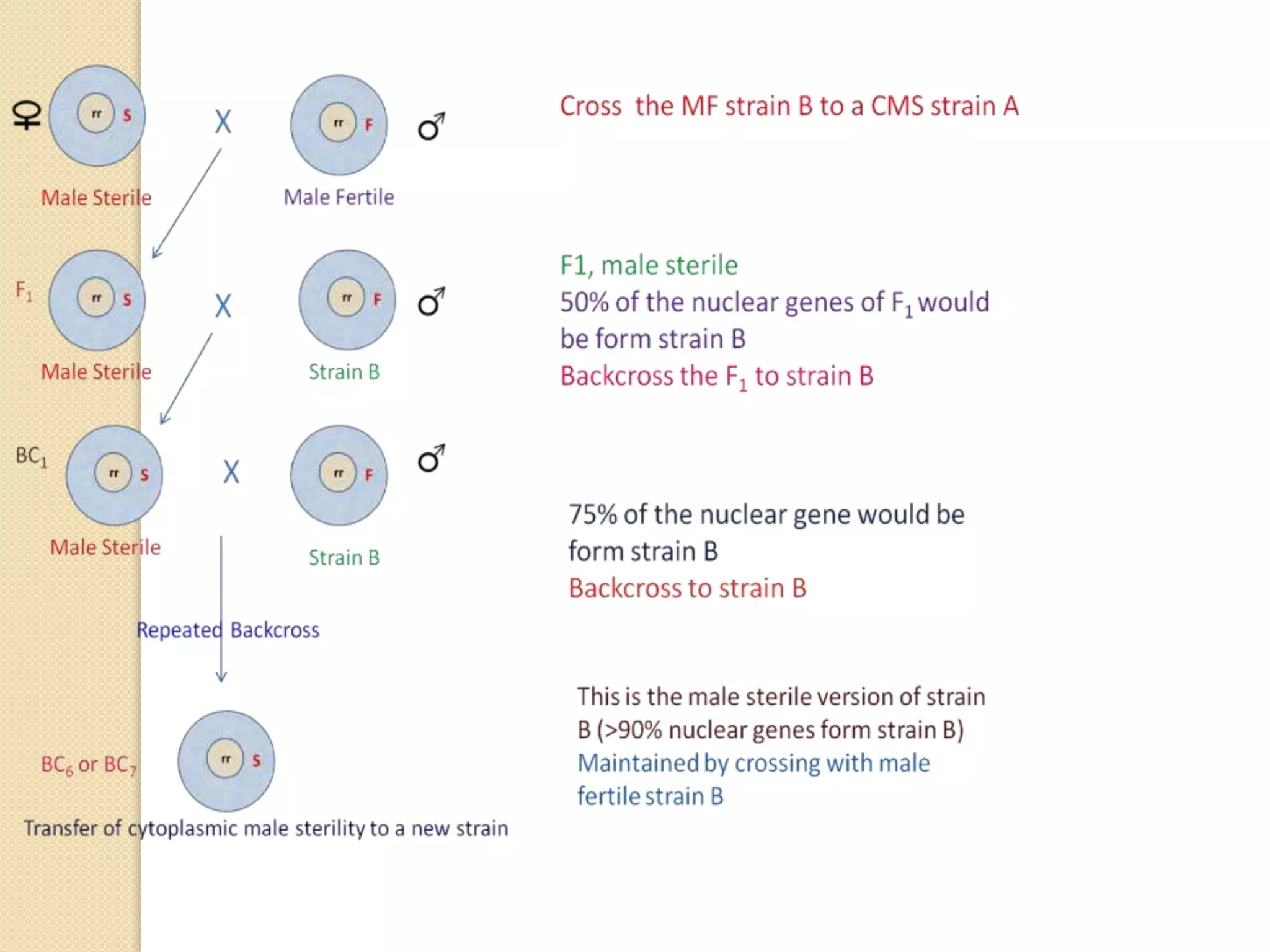
Extrachromosomal inheritance involves the transmission of genetic traits from parent to offspring through cytoplasmic organelles like chloroplasts and mitochondria, rather than through nuclear genes. Three examples are given: (1) variegated leaves in four o'clock plants are inherited cytoplasmically, (2) streptomycin resistance in Chlamydomonas is inherited through chloroplasts, and (3) "poky" phenotype and abnormal cytochromes in Neurospora are inherited maternally through mitochondria. Cytoplasmic inheritance can also cause traits like cytoplasmic male sterility in plants. Maternal effects occur when the female parent's genotype influences offspring traits regardless of the male parent's genotype.