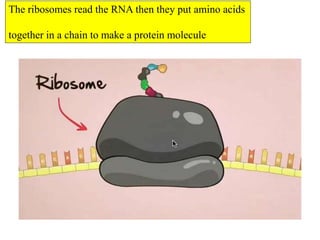
DNA is a complex information storage molecule that functions similarly to a computer program by controlling cellular operations. It is made of nucleotides, which contain a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base, and the sequence of these bases forms the genetic code essential for protein synthesis. The document discusses DNA structure, replication, and compares its data storage capacity to modern computer technology.