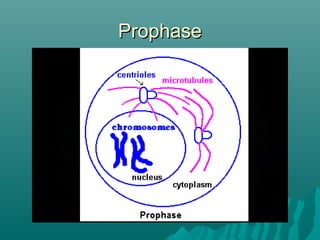
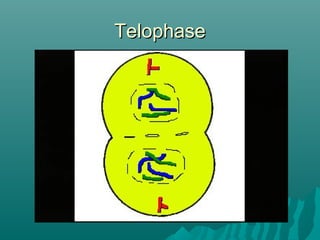
Cell division occurs through mitosis and cytokinesis to form two daughter cells. Mitosis involves four phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase - where chromosomes condense and separate. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm. Most of a cell's life is spent in interphase, which prepares the cell for division. Cell division allows for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction.