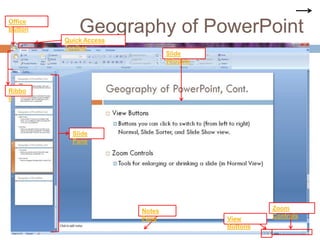
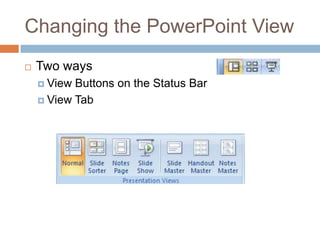
This document provides an overview and introduction to using Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 for beginners. It defines key terms like presentations, slides, notes, and handouts. It describes the basic interface elements of PowerPoint like the ribbon, slide pane, and view buttons. It explains how to perform basic tasks like creating a new presentation, inserting slides, selecting layouts, and changing the view. It also defines the different view types like Normal, Slide Sorter, Notes Page, and Slide Show views.