Embed presentation


















































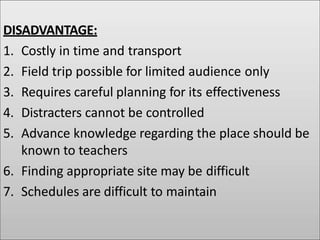








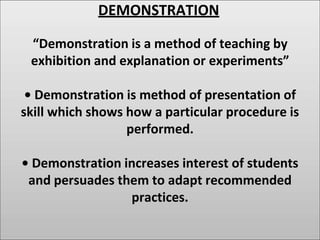













Group discussion, seminar, symposium, role play, project method, field trip, workshop are teaching methods discussed. Group discussion involves planning, active participation and evaluation. Seminar involves preparation, presentation and evaluation of a topic. Symposium involves separate speeches on an aspect of a question. Role play allows acting out real life situations. Project method involves importing real life problems into school. Field trips provide direct experience. Workshops involve experts finding solutions through discussion.







































































