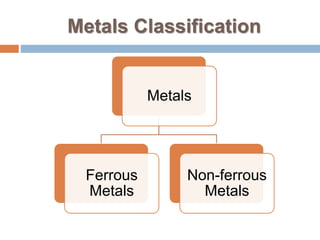
Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. They are usually shiny, malleable, and ductile. The main types of metals are ferrous (containing iron) and non-ferrous. Ferrous metals include pig iron, cast iron, wrought iron, and various types of steel depending on carbon content. Non-ferrous metals include aluminum, copper, brass, lead, and tin. Metals can be protected from corrosion through processes like tarring, painting, galvanizing, and electroplating which form protective coatings.