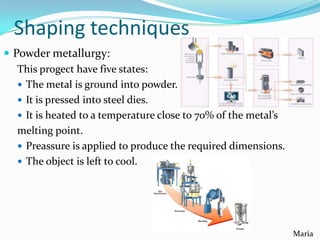
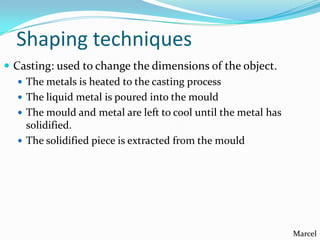
The document summarizes various properties and characteristics of metals. It discusses physical properties like strength, ductility and conductivity. It also covers chemical properties such as oxidation and toxicity. Metals are obtained through surface or underground mining. Common ferrous metals include iron, steel and cast iron. The document also describes some heavy metals like lead, tin, zinc and copper, as well as alloys like bronze and brass. It outlines techniques for shaping metals, including rolling, extrusion, forging, casting and powder metallurgy. Permanent joining is done through riveting, welding or adhesives, while temporary joins use nuts, bolts or other fasteners. Finishing techniques remove imperfections and protect surfaces.