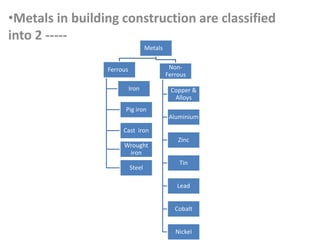
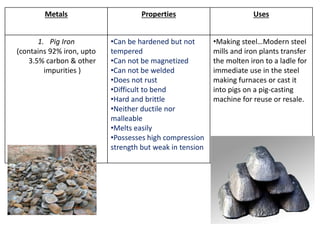
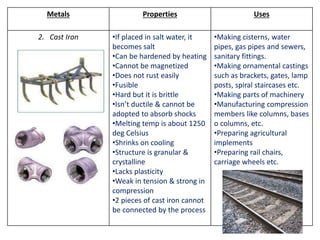
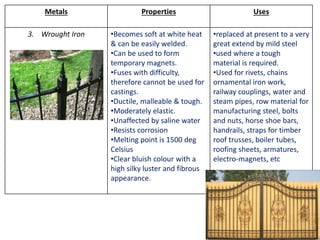
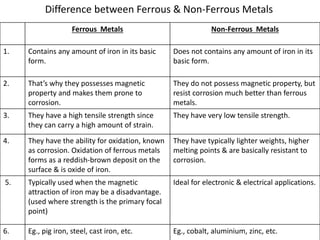
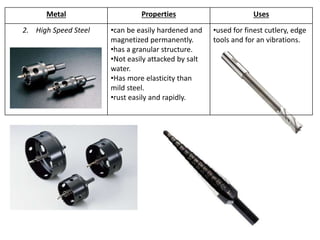
Metal is classified into ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Ferrous metals contain iron while non-ferrous do not. The key ferrous metals are pig iron, cast iron, wrought iron and steel. Pig iron is very hard and brittle while cast iron is also hard but brittle. Wrought iron is ductile, malleable and tough. Steel is an alloy of iron with 0.2-2.1% carbon and includes types like mild steel, high speed steel and stainless steel. The document discusses the properties and uses of various metals.