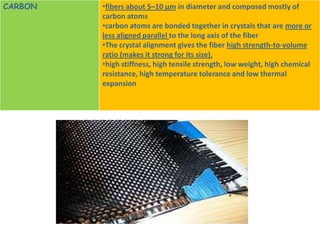
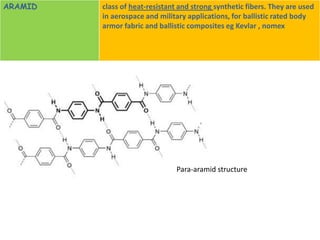
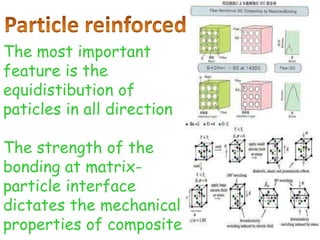
FRP is a composite material made of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers or particles. The reinforcing materials improve the strength and elasticity of the polymer. Fiber reinforced plastics specifically use fiber reinforcement. Common fiber types include glass, carbon, and aramid fibers. The properties of the FRP depend on the properties of the fibers and matrix, their relative volumes, fiber length and orientation. FRPs are used in applications requiring high strength, stiffness, stability and resistance to heat, chemicals and abrasion.