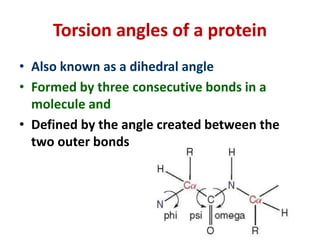
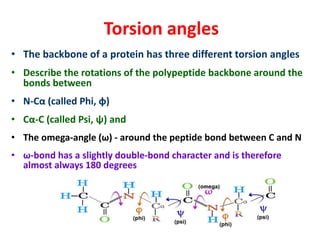
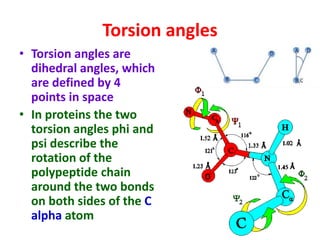
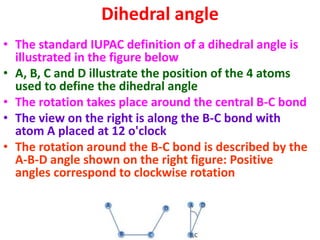
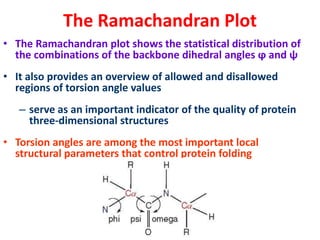
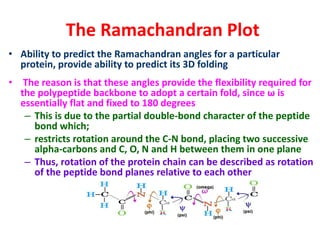
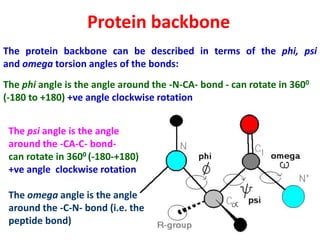
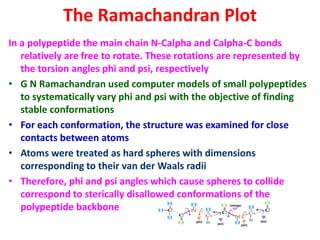
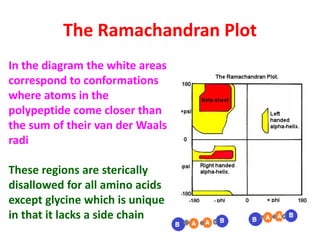
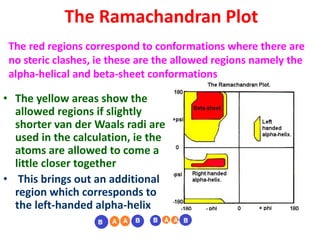
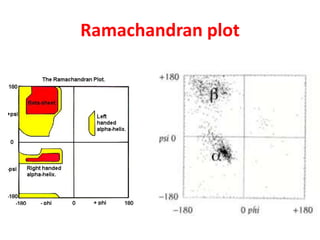
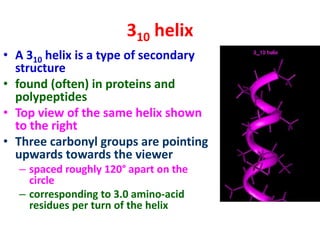
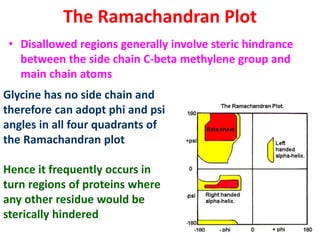
The document discusses the Ramachandran plot, which shows statistically probable combinations of the phi and psi backbone torsion angles in proteins. It describes how these two angles describe rotations around bonds in the polypeptide backbone and influence protein folding. The plot reveals allowed and disallowed regions based on steric clashes between atoms at different angle combinations. Common structures like alpha helices and beta sheets correspond to allowed regions in the plot.