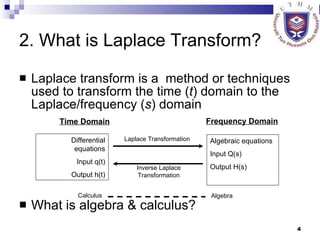
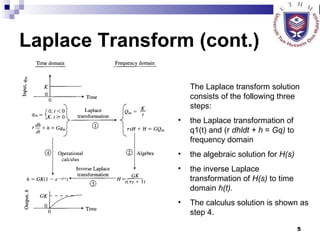
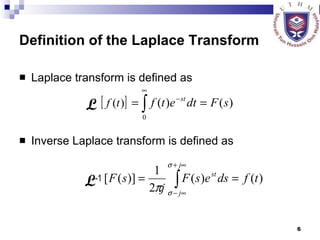
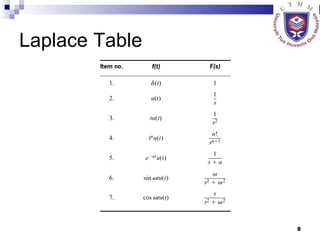
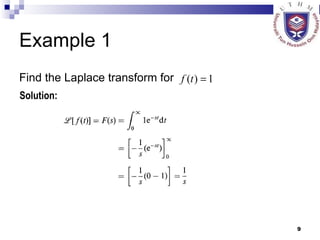
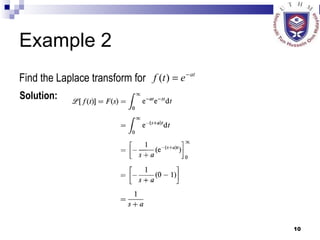
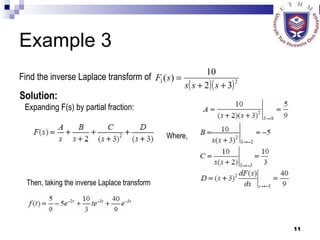
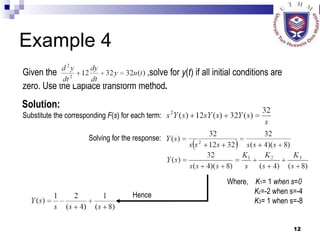
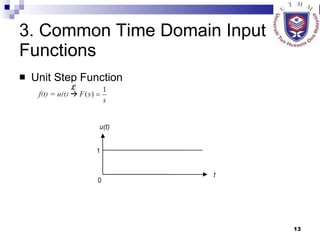
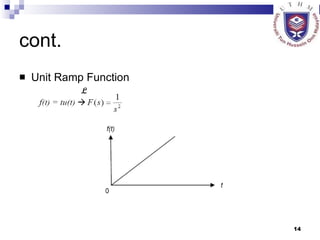
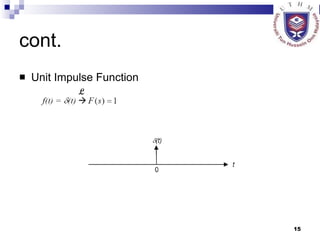
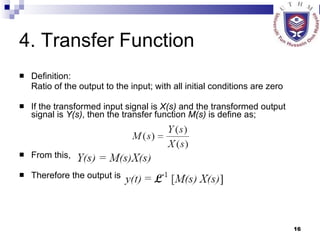
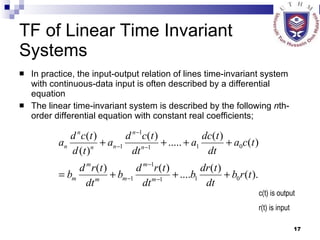
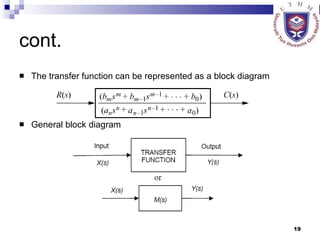
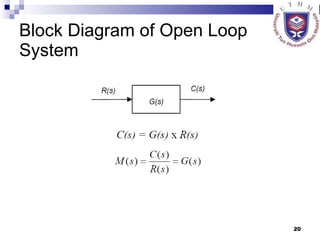
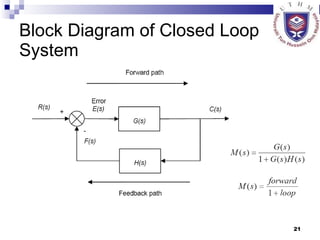
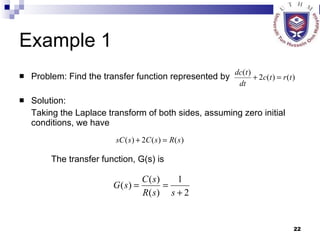
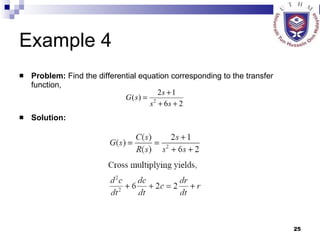
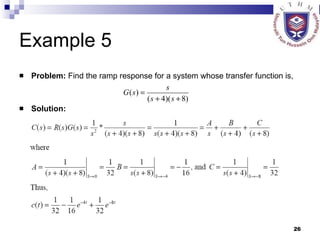
This document provides an overview of analog control systems and Laplace transforms. It introduces key concepts like Laplace transforms, common time domain inputs, transfer functions, and modeling electrical, mechanical and electromechanical systems using block diagrams and mathematical models. Examples are provided to illustrate Laplace transforms, transfer functions, and analyzing system response using poles, zeros and stability analysis.
![Chapter 2 Analog Control System Eddy Irwan Shah Bin Saadon Dept. of Electrical Engineering PPD, UTHM [email_address] 019-7017679](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetingw3-chapter2part1-110627223239-phpapp02/75/Meeting-w3-chapter-2-part-1-1-2048.jpg)