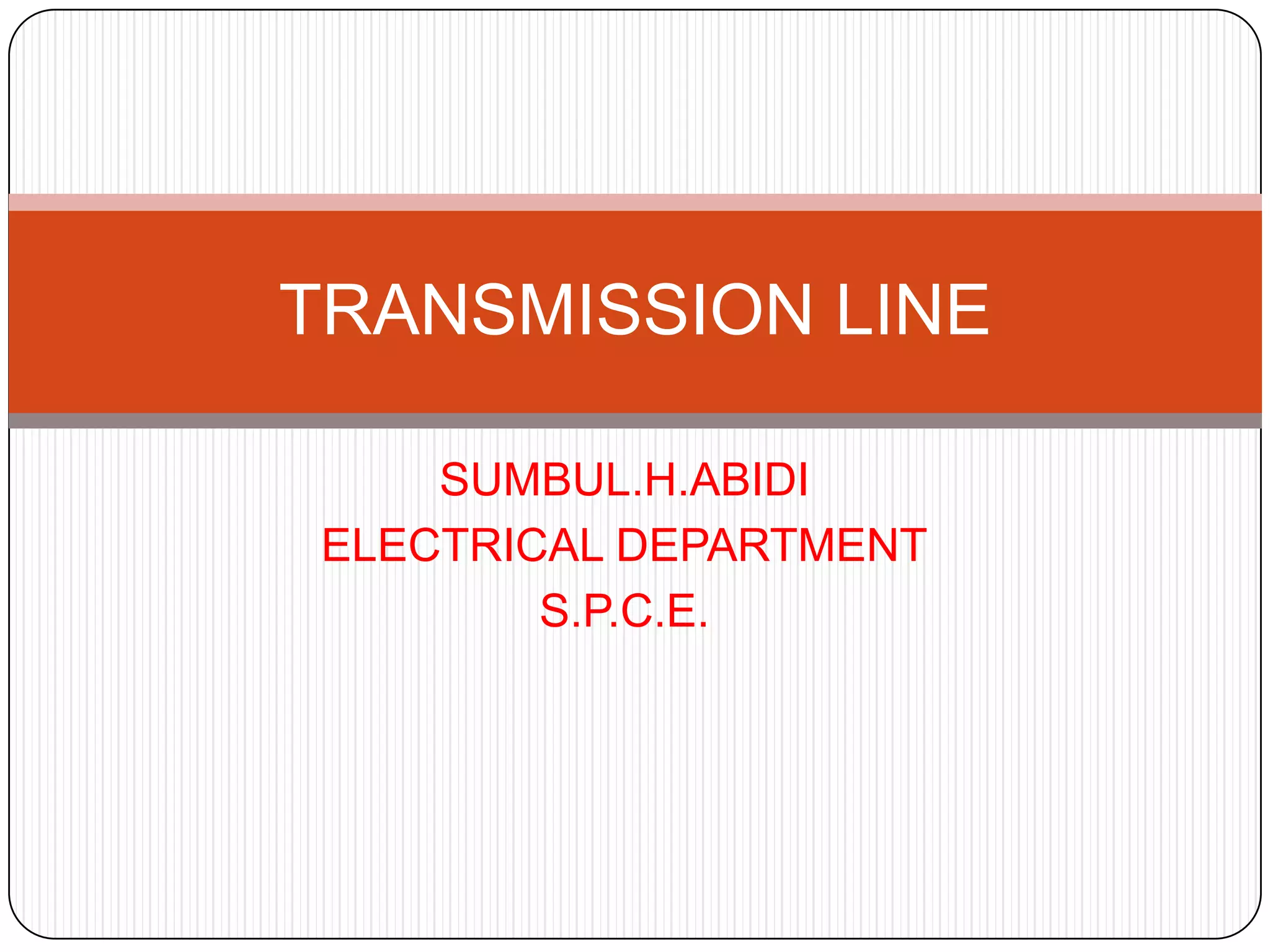
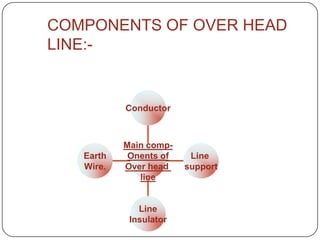
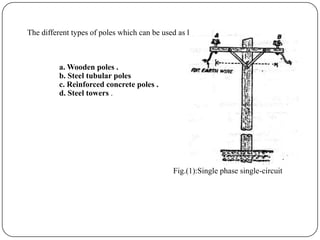
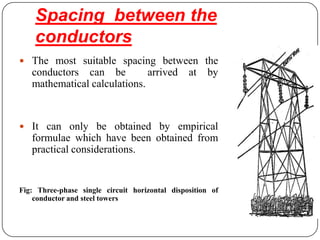
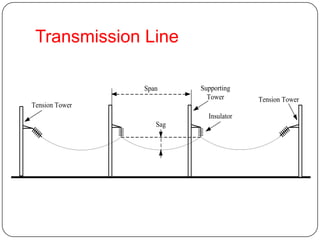
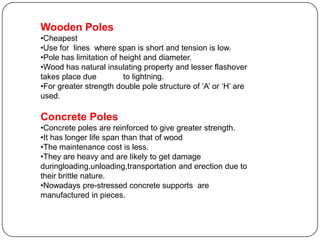
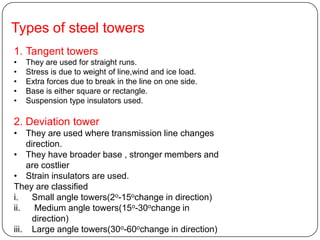
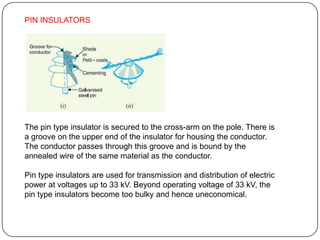
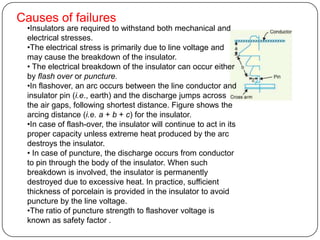
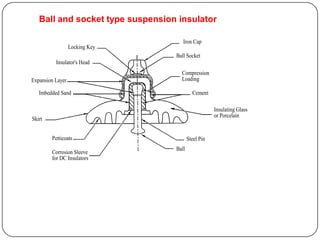
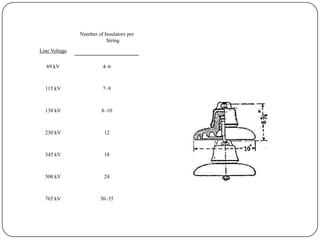
The document discusses the key components of overhead transmission lines, including conductors, earth wires, line insulators, and line supports. The main line supports discussed are wooden poles, steel tubular poles, reinforced concrete poles, and steel towers. The requirements for line supports are that they must be strong, light, require few parts, be inexpensive, have low maintenance costs, allow for easy access and erection of lines, and have a long life. The types of insulators used in overhead systems are also summarized, including pin, suspension, strain, and shackle insulators.