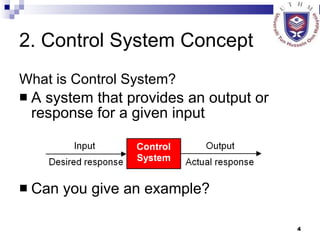
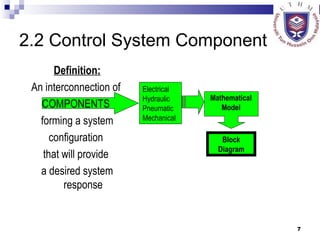
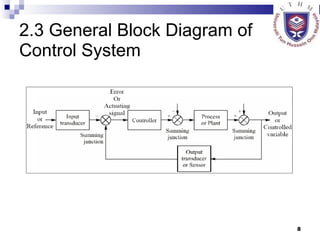
This document provides an overview of control systems, including:
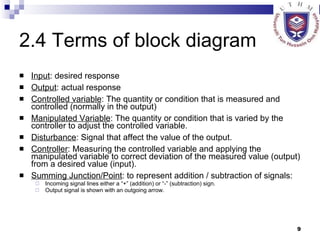
- Defining the basic components and configurations of control systems
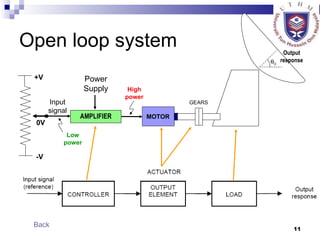
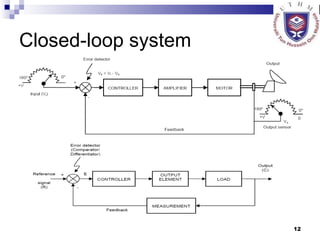
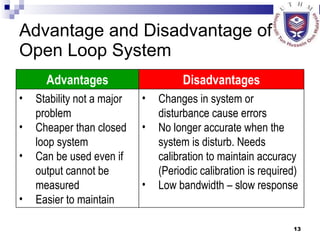
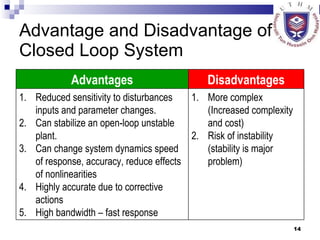
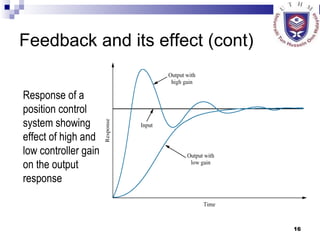
- Describing open-loop and closed-loop systems, their advantages and disadvantages
- Classifying control systems as single-input single-output, multiple-input multiple-output, linear, non-linear, time-variant, or time-invariant
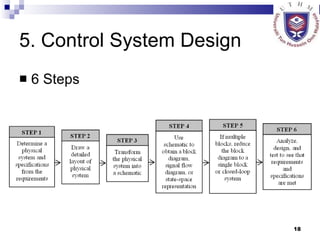
- Outlining a 6-step general process for designing a control system
- Assigning an activity for students to describe the operation of a control system from a selected sector by reverse engineering it according to the design steps
![Chapter 1 – Overview of Control System Eddy Irwan Shah Bin Saadon Dept. of Electrical Engineering PPD, UTHM [email_address] 019-7017679](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetingw1-chapter1-111011043444-phpapp02/85/Meeting-w1-chapter-1-1-320.jpg)