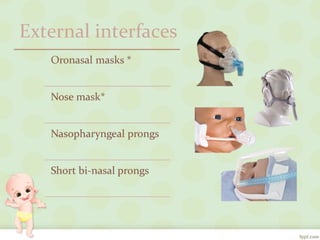
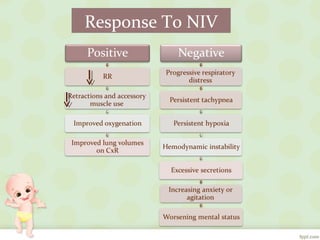
The document discusses various noninvasive ventilation (NIV) techniques for neonates, including CPAP, BiPAP, SNIPPV, and HHFNC, along with their clinical indications and contraindications. Evidence suggests that HHFNC and other NIV strategies are effective for treating respiratory distress syndrome and hypoxic respiratory failure, with favorable outcomes compared to traditional methods. The findings indicate that NIV techniques offer similar efficacy in management, highlighting their importance in neonatal care.