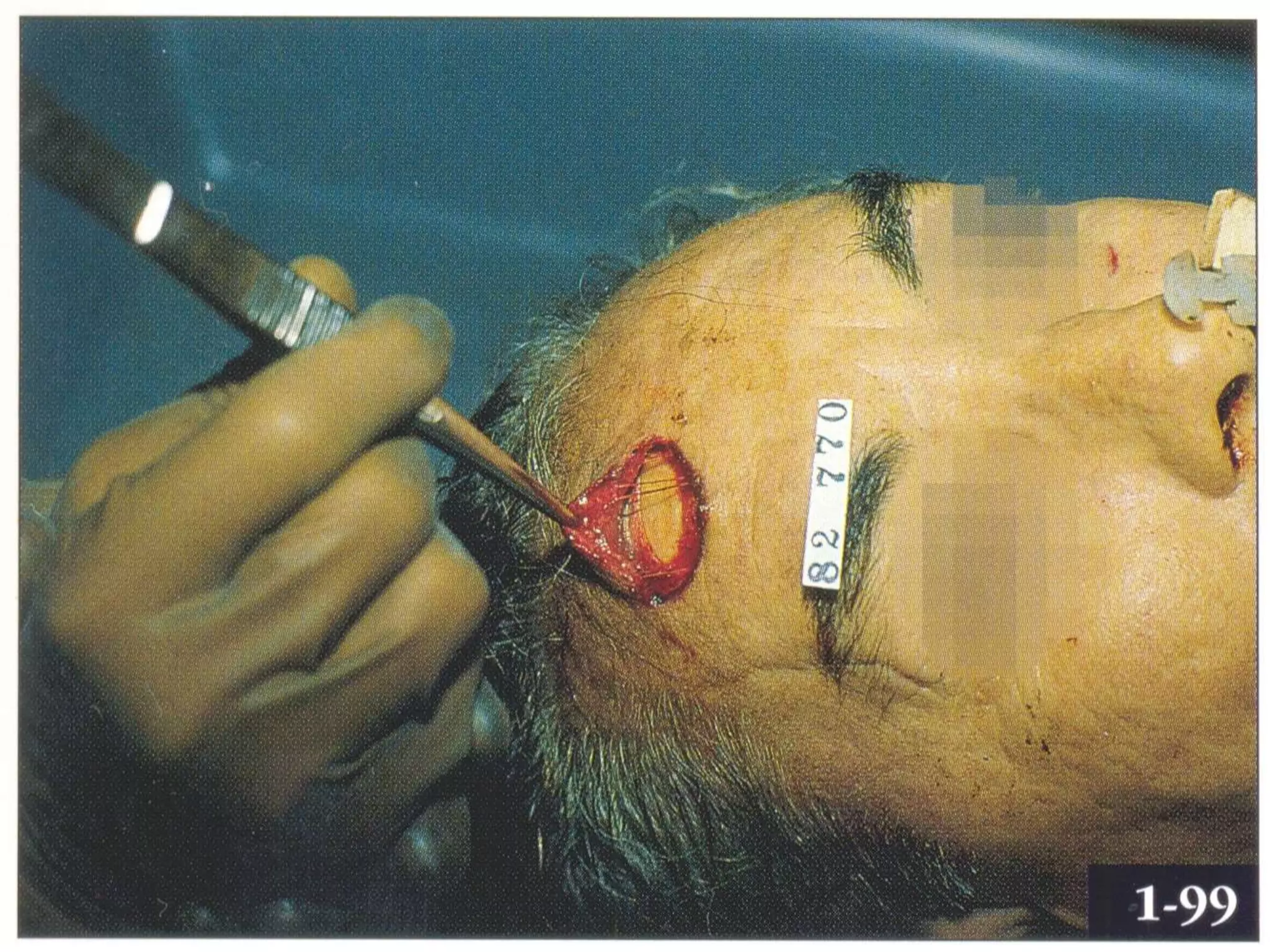
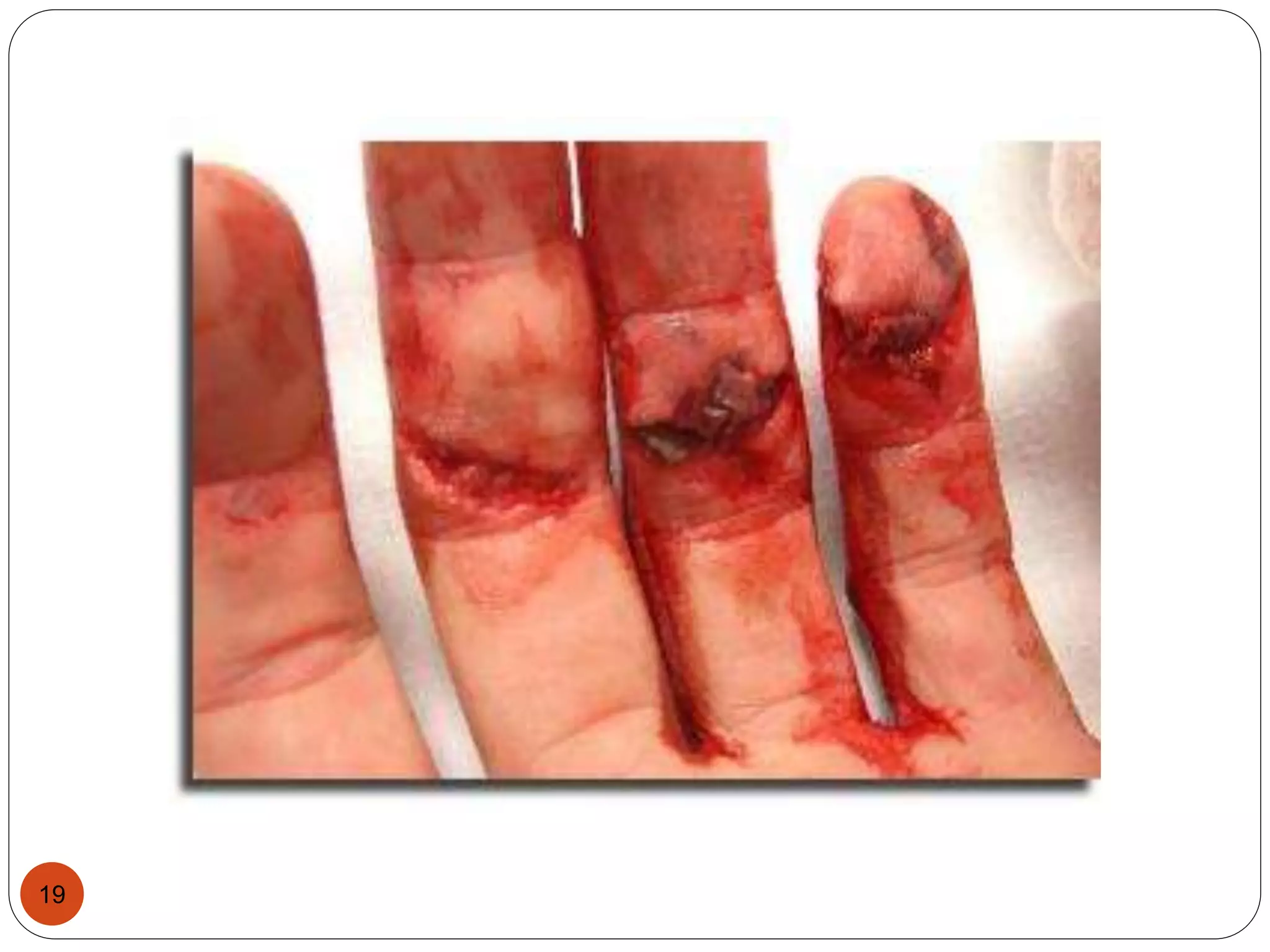
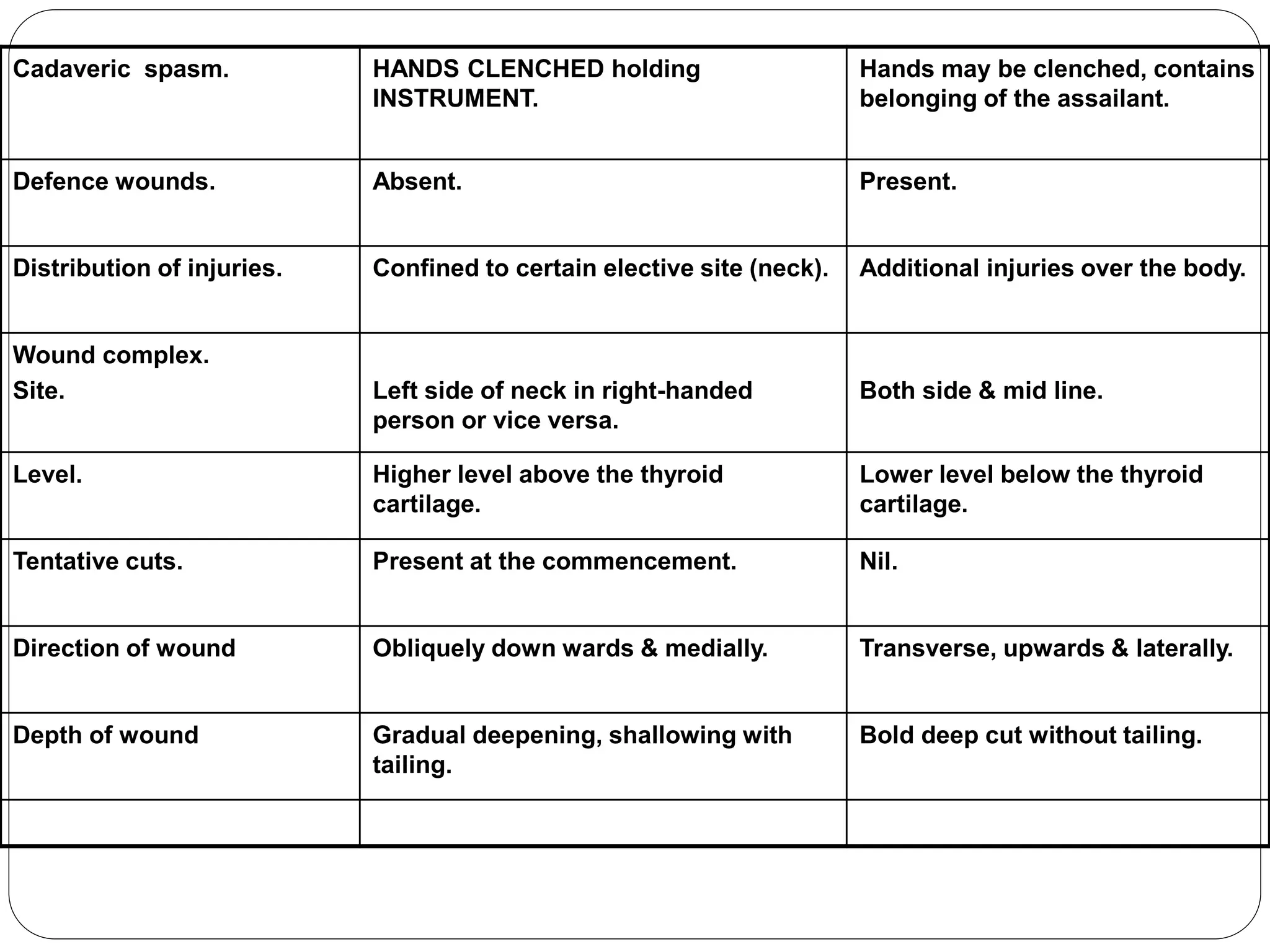
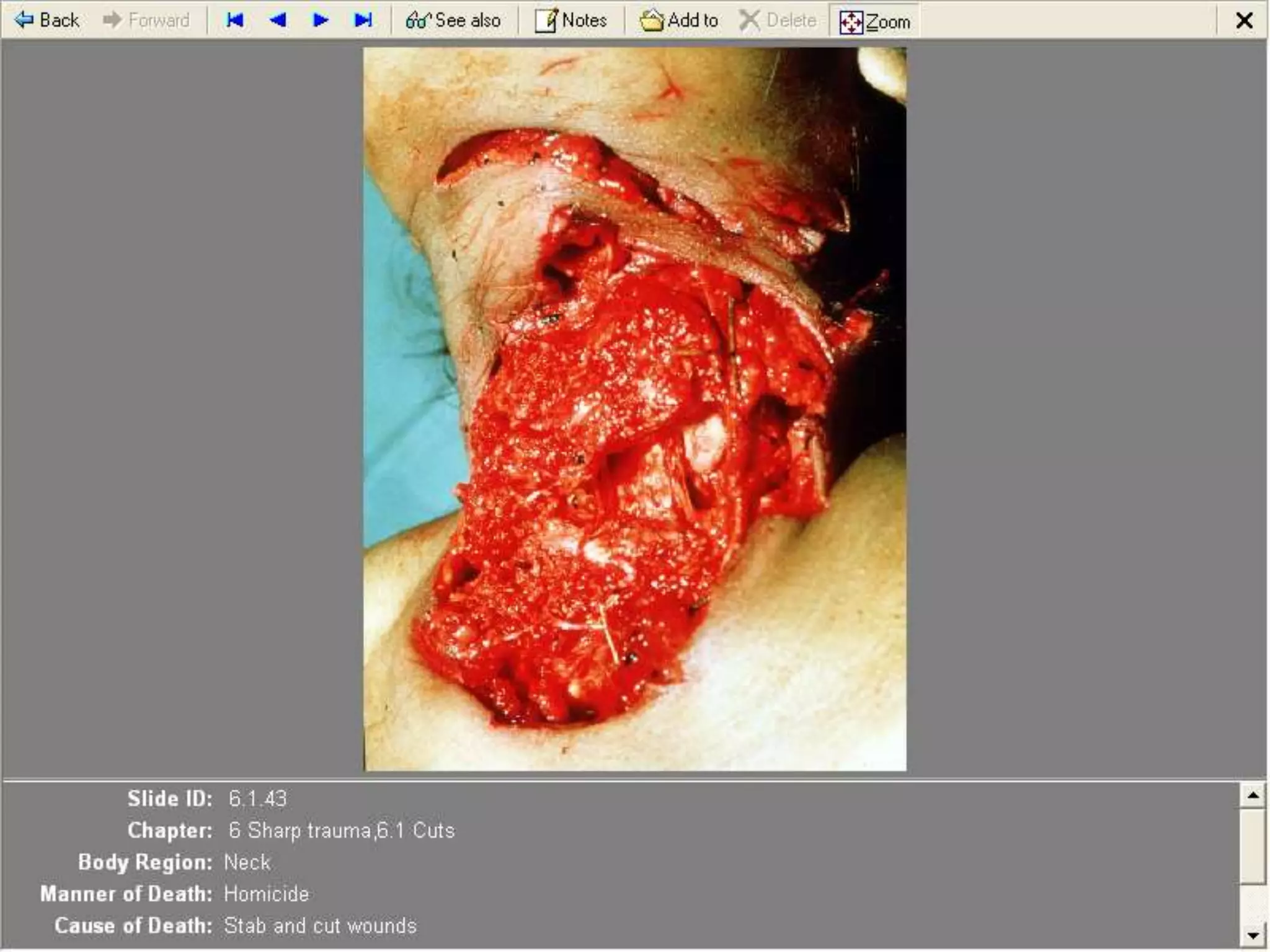
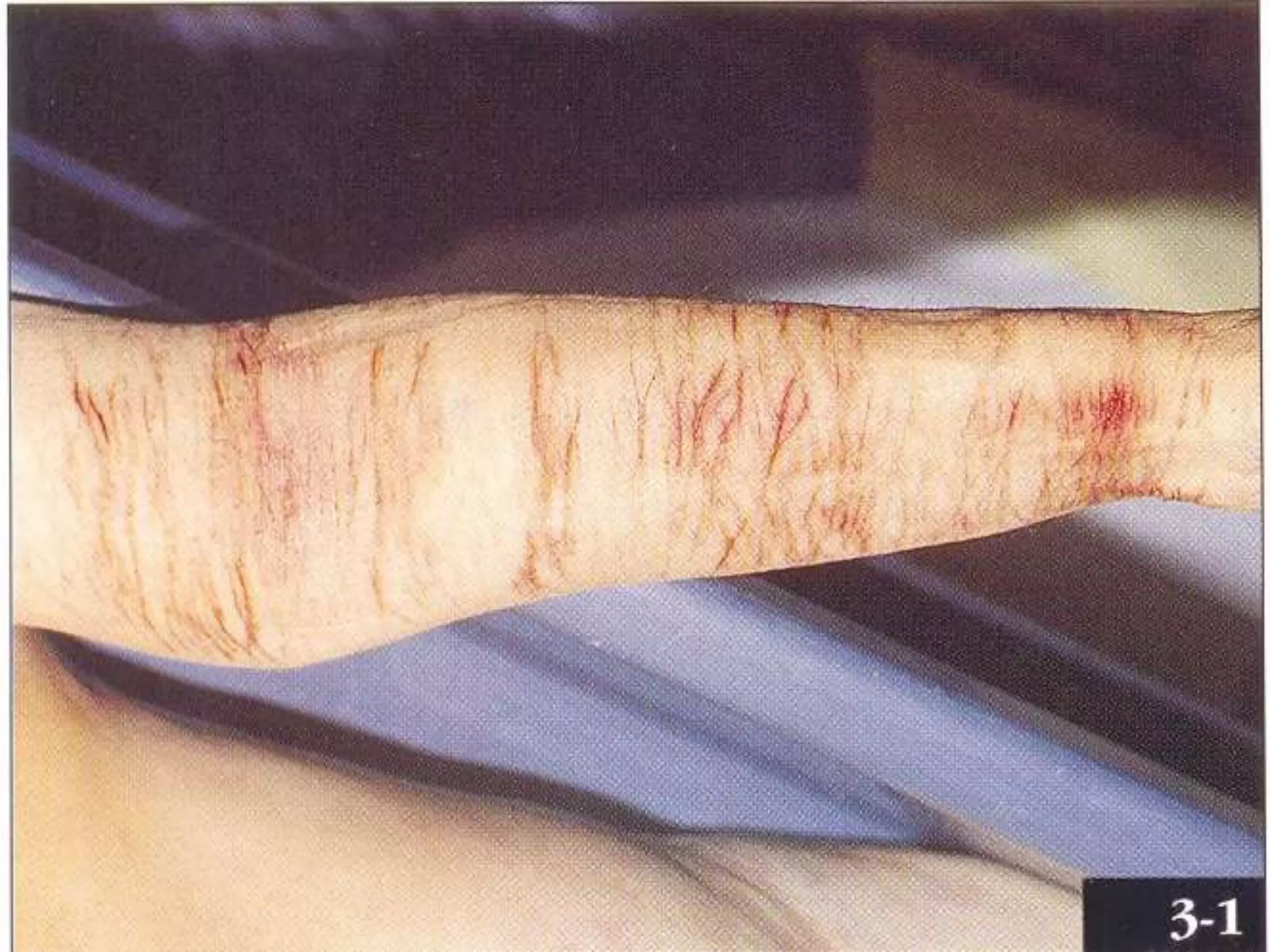
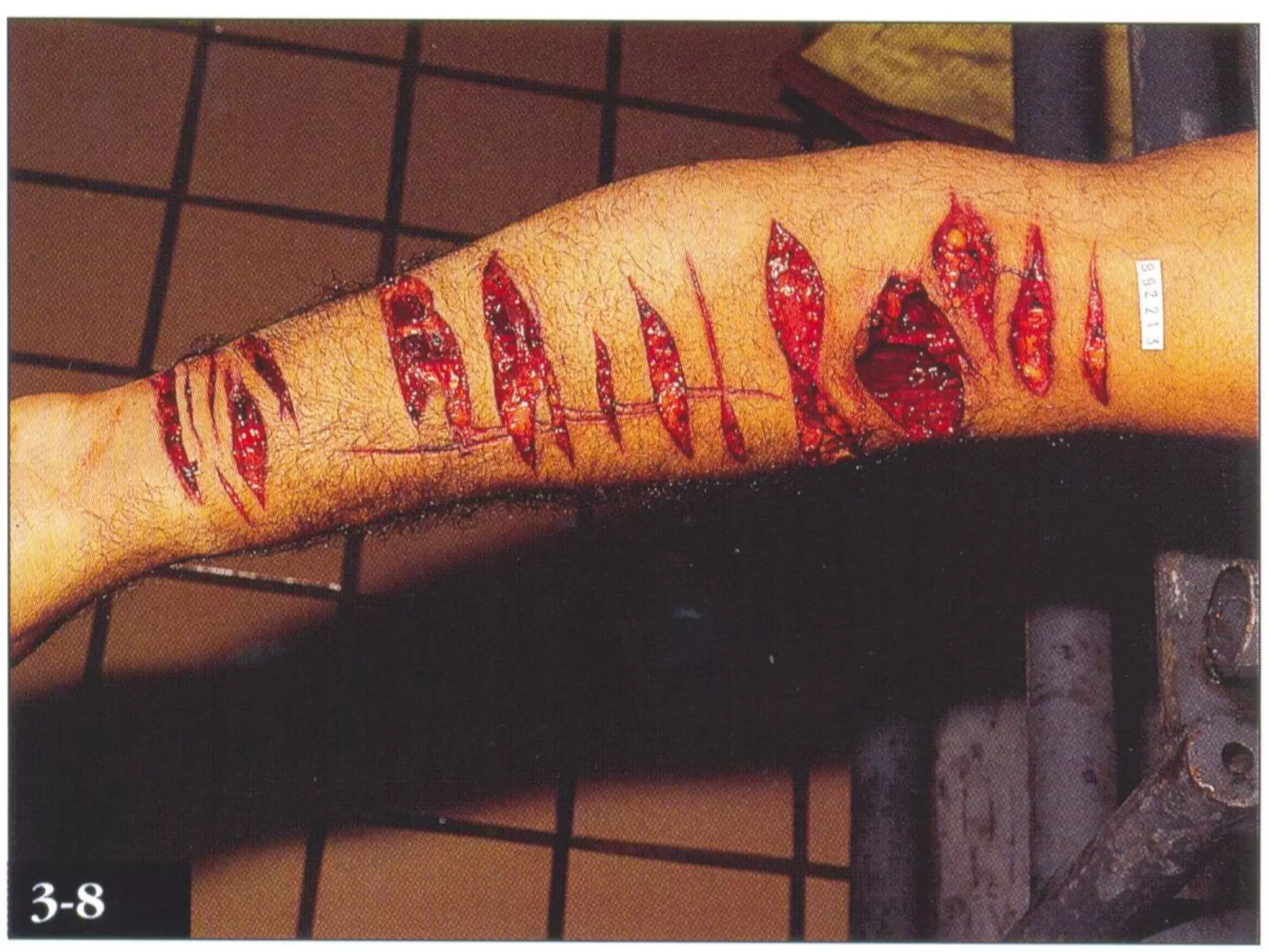
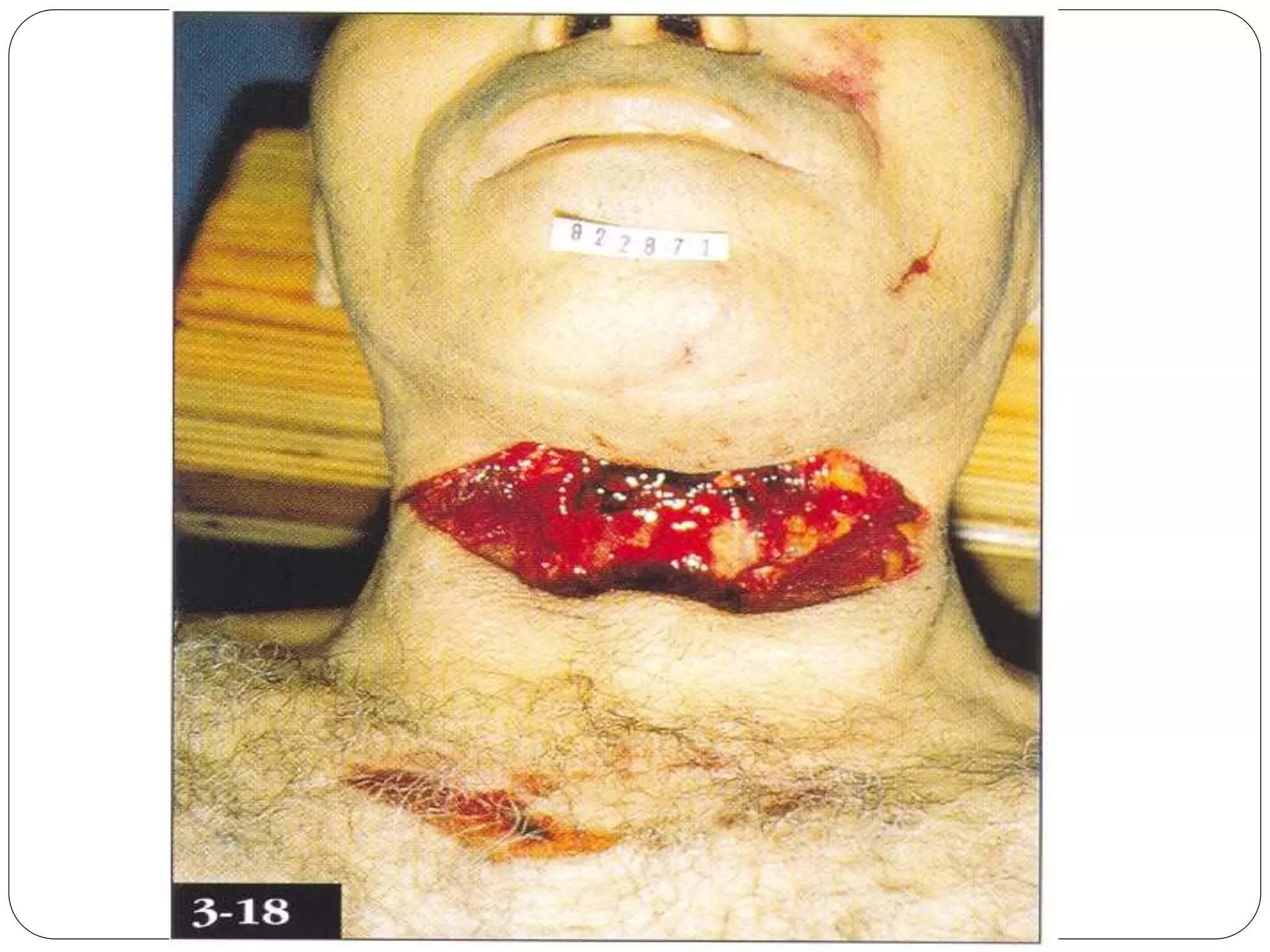
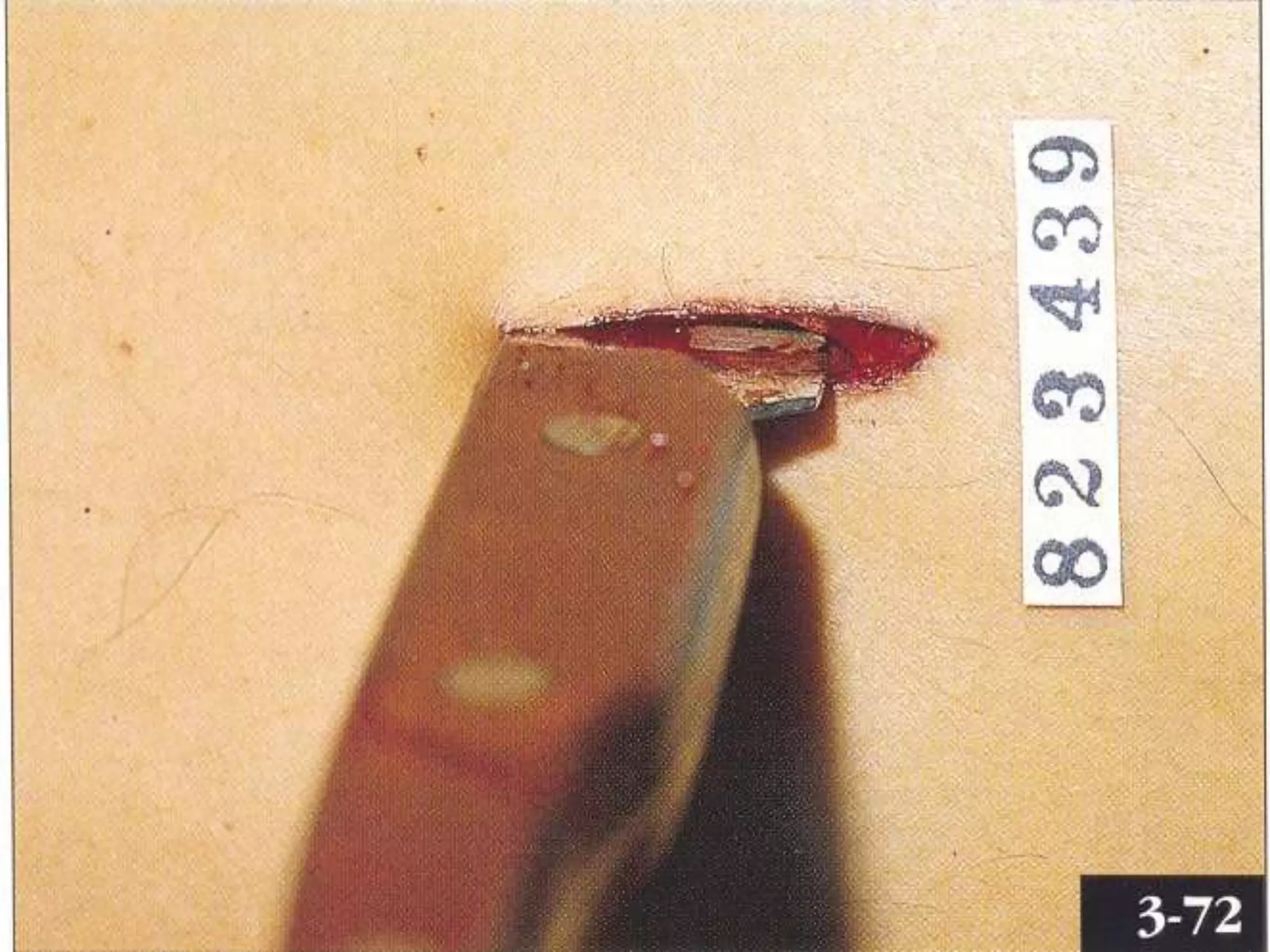
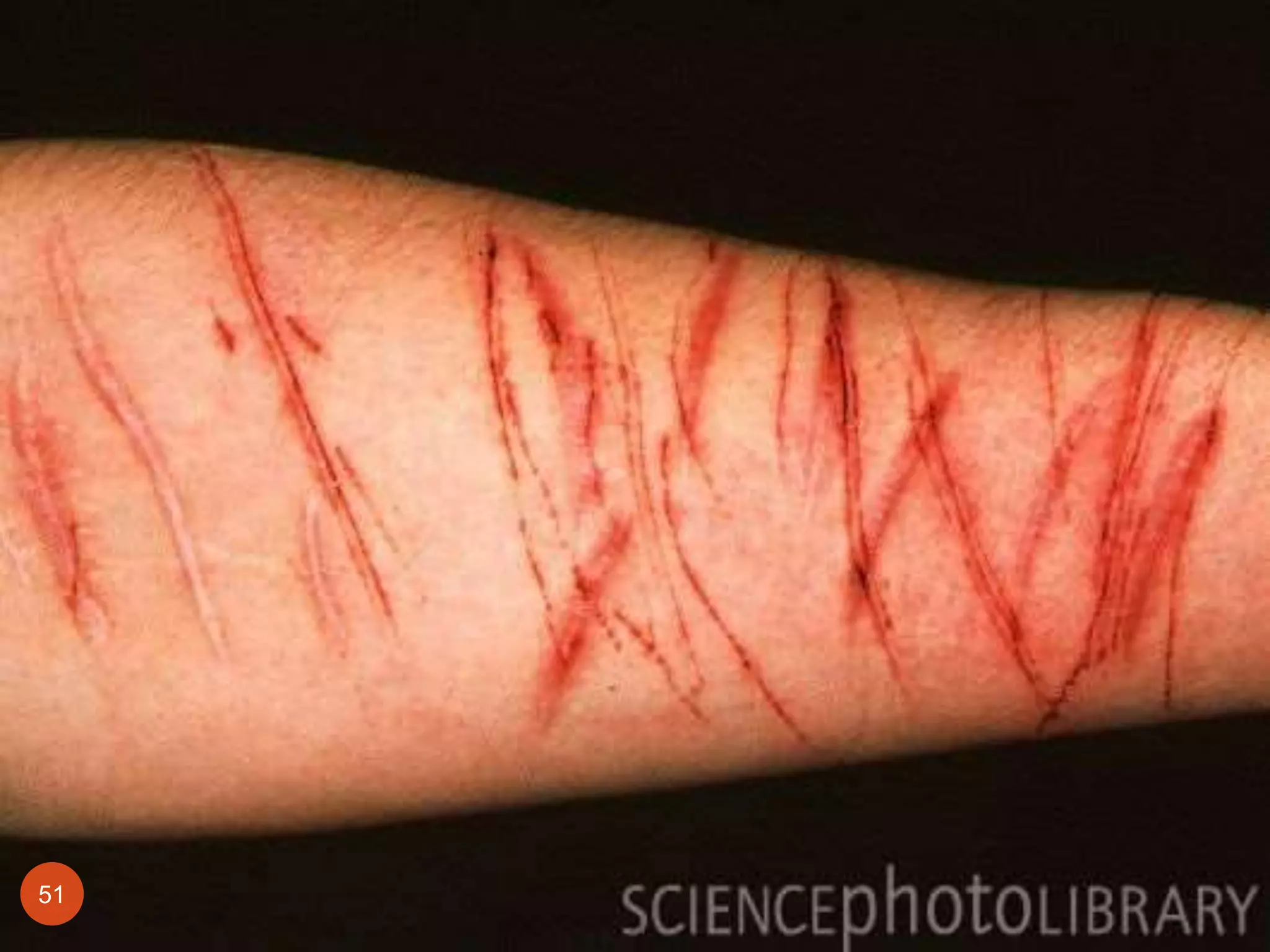
This document discusses different types of wounds including lacerations, incised wounds, stab wounds, and fabricated wounds. Lacerations are caused by blunt force and result in tears in the skin with irregular edges. Incised wounds are clean cuts caused by a sharp blade with regular edges. Stab wounds are penetrating injuries caused by a sharp pointed weapon. Fabricated wounds are self-inflicted or inflicted by another to mislead investigators and may involve superficial cuts or insertion of pellets. Key diagnostic features help determine the weapon and manner of different wound types.