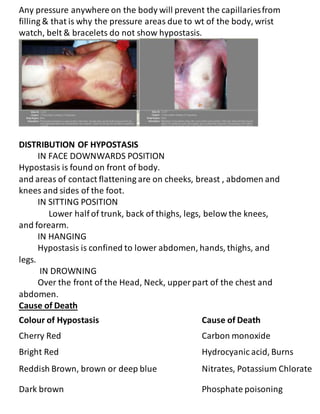
1. Death is defined as the complete and irreversible stoppage of respiration, circulation, and brain functions. It is a continuous process rather than a single event. 2. There are two phases of death - somatic death, which is the irreversible loss of integrated functioning of the organism, and molecular death, which is the death of individual organs and tissues. 3. Immediate changes that occur after death include insensibility, loss of reflexes, cessation of respiration and circulation, and a flat EEG rhythm. Early changes include eye changes, skin changes, muscular flaccidity, algor mortis, and postmortem lividity.