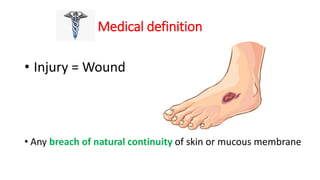
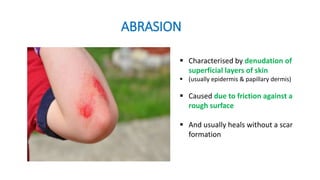
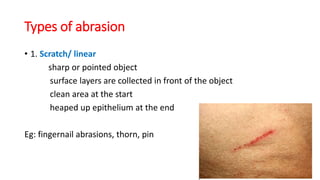
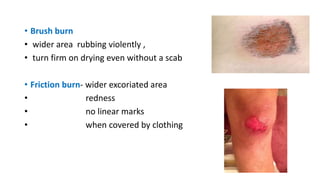
This document discusses various types of mechanical injuries including abrasions, contusions, lacerations, and their distinguishing features. It defines abrasions as denudation of superficial skin layers caused by friction against a rough surface. Contusions are characterized by extravasation of blood into subcutaneous tissue due to blunt force trauma. Lacerations are tears or splits of skin/tissue caused by blunt force stretching tissues beyond their limits. The document outlines the classification, appearance, healing process, differential diagnosis and medicolegal importance of each type of mechanical injury.











![• Medico Legal Importance of Abrasions
• (1) Direction of force – can be estimated from tissue tags
• (2) Force of impact – can be judged
• (3) Foreign matter sticking over abrasions –
may give an idea of scene of crime
[eg grass, gravel, sand etc]
• (4) Imp and only sign – of internal injury sometimes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-16-320.jpg)









![Factors Modifying Size and Shape
• 1. Age Children and old people bruise
• 2. Sex Women bruise more easily than men [more s/c fat]
• 3. Obesity Fat people bruise more easily [greater amount of s/c fat]
• 4. Color of skin Fair skin- better appreciated visually
• 5. Effect of embalming dark pigment complex with blood
• 6. Condition and type of tissue
(i) Vascular and loose tissue (eg face, vulva, scrotum)
(ii) Good muscle tone (boxers, athletes
(ii) Resilient areas (abdomen, buttocks) bruise less.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-26-320.jpg)




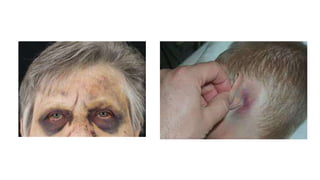
![Examples:
(i) Spectacle hematoma –
(a) Blunt injury to the forehead collects around the eye
(b) Blunt injury to skull / fracture of anterior cranial fossa
known as spectacle hematoma, panda eyes or raccoon eyes
(ii) Battle sign –
Bruise behind the ear [mastoid ecchymosis]
may indicate fracture of posterior cranial fossa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-31-320.jpg)











![5) Manner of production:
(i) Self inflicted – Very rare because painful.
May be seen in hysteria and mentally ill persons.
(ii) Accidental – (a) Very common
(b) Seen on prominences [forehead, nose, elbows, knees]
(iii) Homicidal - (a) On any part of the body
(b) Associated injuries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-46-320.jpg)
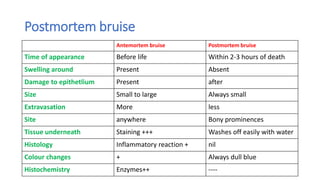
![6) Medicolegal value –
medicolegally less valuable than abrasions
because:
(i) Ectopic bruises - appear away from the site of injury.
(ii) Direction of force – not indicated
(iii) Shape and size - does not correspond to weapon [due to oozing]
(iv) Time of appearance –may be too long after infliction
(v) Visibility - in dark skinned persons
7) Patterned bruises – May indicate the surface features of offending weapon
8) Size – can indicate the degree of violence.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-47-320.jpg)





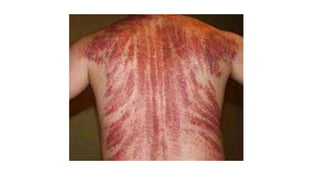
![• (4) Shape and size:
• (i) May not correspond - with the weapon
• (ii) Linear –long, thin objects eg crowbars, pipes.
• (iii) Irregular, ragged or Y-shaped –objects with flat surfaces
• (iv) if curved - convexity of curvature points towards the direction of force
• (v) Stellate [star shaped] – blunt round object
• (vi) Crescentic–blunt object with an edge, eg hammer head
• (vii) Semicircular –head against wall or other hard surface (convexity of head)
• (viii) Patterned lacerations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-53-320.jpg)


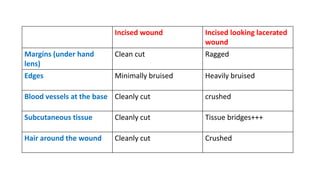
![(5) Gaping –
present due to pull of elastic and muscular tissues.
(6) Bruising: in skin or s/c around the wound
(7) Tissue bridges – at the base of wound
Signature of a BLUNT FORCE
deeper tissues [BV, connective tissue, elastic fibres, nerves etc]
are unevenly divided.
(8) Hair bulbs – crushed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-56-320.jpg)


![TYPES
(1) Tear- the most general
having sufficient amount of underlying fat and muscle (eg thigh).
(2) Split laceration
skin direclty overlying a bone,
with minimal amount of underlying fat and muscle.
(eg: scalp, shin of tibia)
mimics an incised wound [called incised looking lacerated wound].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-59-320.jpg)






![(4) Manner of production –
(i) Accidental - falls etc
(ii) Suicidal lacerations – are very rare, (painful and rarely effective)
May be seen in suicidal jumping from high buildings.
(iii) Homicidal –
(a) Lacerations on the vertex generally indicate homicide.
Bagh Nakh [tiger claws]
designed to lacerate skin and muscle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-67-320.jpg)







![4. Abrasions and contusions – only if it is perfectly sharp
5. Shape
(1) usually spindle shaped – retraction of edges
(2) Crescentic – if blade is curved or struck surface is convex
(3) Zigzag – if skin folds are loose
6. Gaping –
is greater if muscle fibres are cut transversely or obliquely
[due to retraction].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-75-320.jpg)

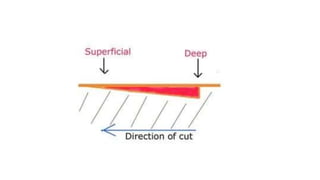










![• Penetrating wound
• enters into a body cavity without coming out.
• Should be described in a sequential order,
i.e. entrance wound,
depth and direction of track
specific location of termination
Ex - (i) Stab wound to the chest or abdomen [having no exit]
(ii) Gunshot wound to the head [having no exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-89-320.jpg)


![Characteristics
• 1. Length stab wound ‘l’ is normally less than width ‘w’ of weapon.
• 2. Width may not indicate the true thickness of blade, because of retraction of
wound edges,
• 3. Margins
• (1) If weapon has sharp edges Margins are clean cut [incised stab wound]
• (2) If weapon has rounded edges Margins are contused and lacerated
[lacerated stab wound].
• 4. Depth (1) Greatest dimension - Depth is the greatest dimension in stab
wounds.
• 5. Shape
• which runs across the lines of Langer wound causes gaping;
• a parallel /an oblique cut - a crescentic or semicircular wound](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalinjuries-230603133914-f79972c1/85/Mechanical-injuries-pptx-92-320.jpg)






