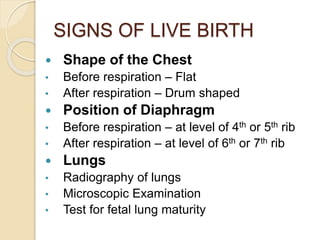
This document discusses infanticide and the signs of live birth in infants. It defines different types of infant deaths such as stillbirth, dead birth, and live birth. It outlines signs that indicate a live birth occurred, including lung examination and changes to the stomach and ears. The causes of infant death are categorized as natural, unnatural-accidental, unnatural-criminal acts of commission or omission. A case study example of a suspicious infant death investigated by autopsy is also provided.
























![References
https://www.slideshare.net [Infanticide
and Child Abuse]
https://www.slideshare.net [Infant Death
1]
https://studylib.net [Infanticide [PPT] ]
The Essentials of Forensic Medicine and
Toxicology by Dr. KS Narayan Reddy
Infanticide - Handbook of Forensic
Medicine and Toxicology
Textbook of Forensic Medicine &
Toxicology by Nageshkumar G Rao
Case Study -
file:///H:/Infanticide%20Case%20Study.p
df](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infanticide-190827141703/85/Infanticide-26-320.jpg)

