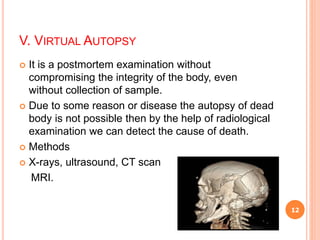
The document discusses different types of autopsies including medical, anatomical, psychological, virtual, and medico-legal autopsies. It describes the objectives and procedures for a medico-legal autopsy, which is performed to determine cause and manner of death and rule out foul play. The pre-autopsy formalities discussed include identification of the body, examination of police papers, and use of an autopsy register to document details of the examination.























![STORAGE OF DEAD BODIES
There are two types of storage..
Long term at -20 0C [for preservation]
Short term +4 0C[for autopsy purpose]
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autopsy-160221112209/85/Autopsy-26-320.jpg)













