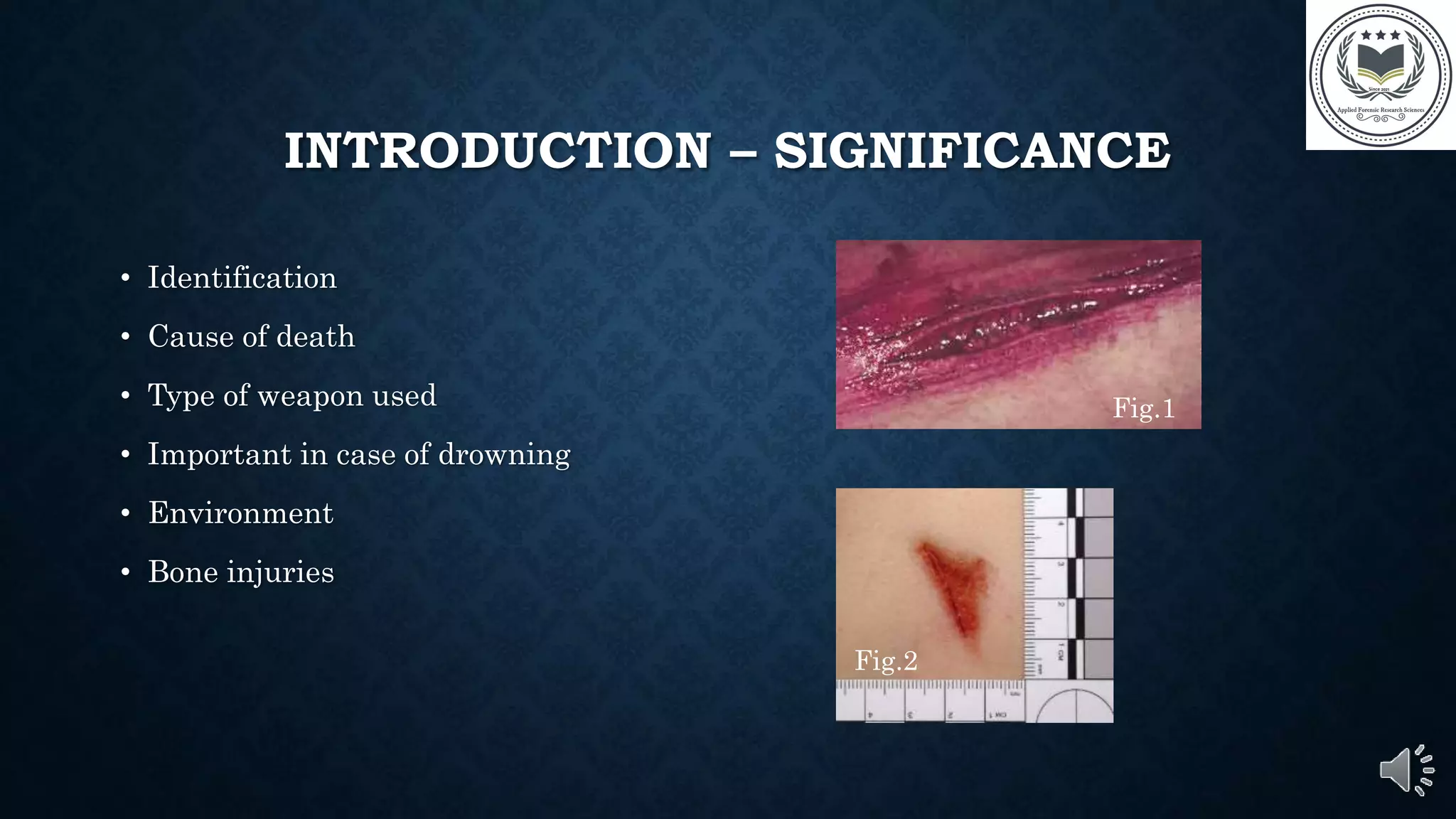
This document provides information about ante mortem and post mortem wounds. It begins with defining key terms like wounds, ante mortem, and post mortem. The document then discusses the significance of distinguishing between ante mortem and post mortem wounds for identification purposes, determining cause of death, and the type of weapon used. It outlines the key differences between ante mortem wounds, which occur before death and show bleeding and blood clotting, and post mortem wounds, which occur after death and show lividity and lack of clotting. References are provided for additional information.