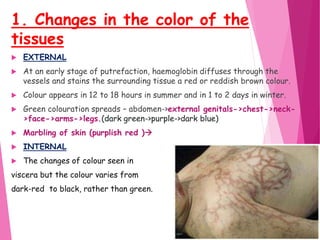
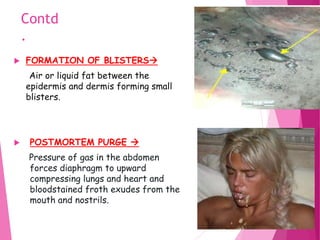
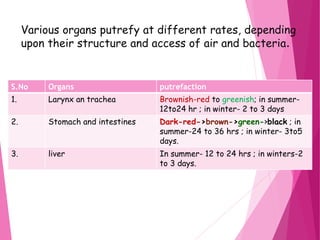
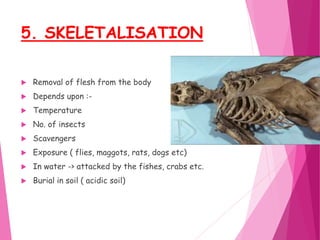
The document discusses the process of putrefaction following death. It begins with an introduction defining putrefaction as the final stage of decomposition caused by bacteria after death and disappearance of rigor mortis, typically occurring 4-10 days after death. It then describes the characteristics features of putrefaction including changes in tissue color, evolution of gases causing foul smell, and liquefaction of tissues. The document also discusses factors that can affect the putrefaction process both externally such as temperature, moisture, and air exposure, and internally such as age, sex, and cause of death. It provides details on how putrefaction occurs differently in various environments like water or burial in soil.