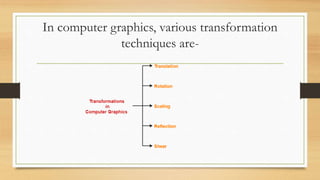
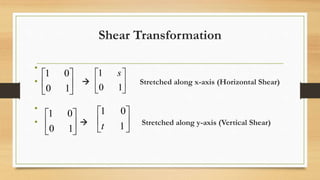
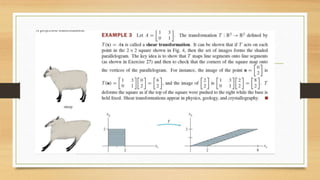
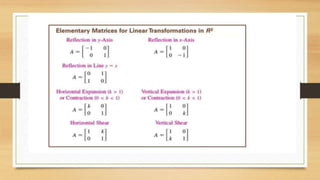
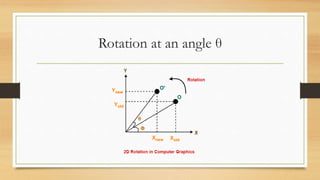
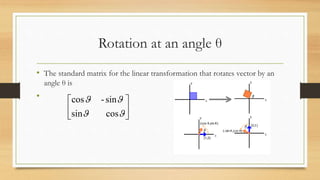
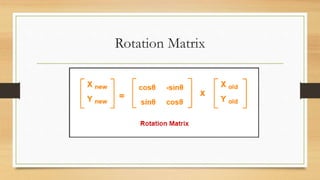
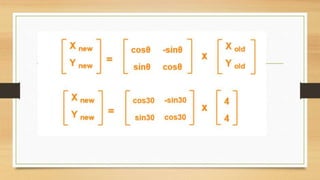
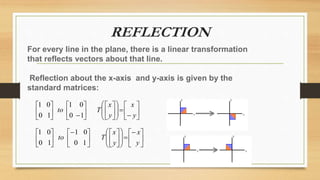
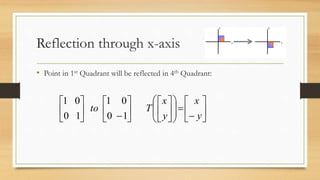
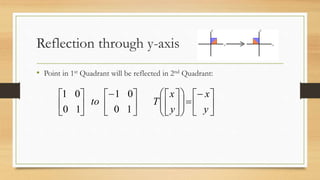
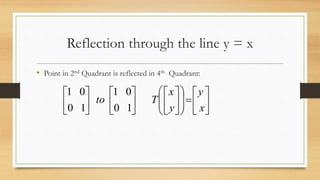
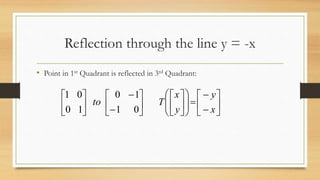
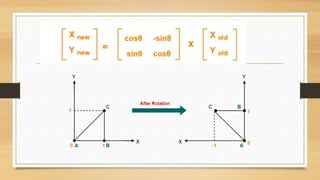
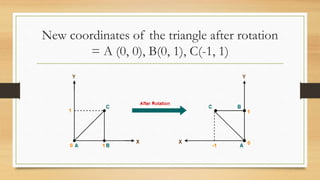
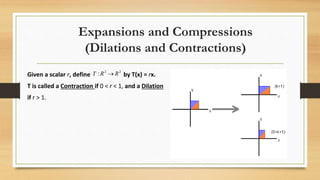
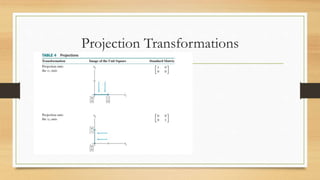
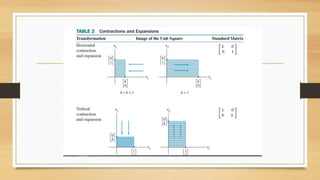
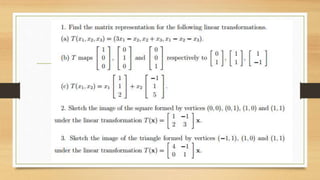
This document discusses various types of linear transformations, including rotations, reflections, shears, dilations, projections, and their representations as matrices. It provides examples of transforming lines and triangles under rotations of different angles. Linear transformations are important in computer graphics for modifying objects by changing their position, size, orientation or shape. Matrix representations allow linear transformations to be described geometrically.